
Which of the following forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?
(a) The relative difference in the DNA occurrence in blood, skin, and saliva.
(b) The relative of DNA in the ridges and grooves of the fingerprints.
(c) Satellite DNA occurring as highly repeated short DNA segments.
(d) The relative proportions of purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
Answer
540.9k+ views
Hint: Its basis is a highly repetitive length of DNA that is repeated multiple number of times. It is a laboratory technique to establish a link between genome and suspect in a criminal investigation.
Complete answer:
DNA Fingerprinting or DNA Profiling is a technique that is used to determine an individual's biological characteristics that are unique to each and every person. This process involves satellite DNA or satDNA is a highly repetitive length of DNA that contains short nucleotide sequences repeated multiple numbers times. Because of the large number of repetitions, the composition of this section of DNA is different, and when centrifuged, forms a separate band.
DNA fingerprinting is the method in which a small sample is found in the investigating crime scene and to study it the forensic analyst amplifies it and makes copies of it to study properly. The copies made can then be used to study the DNA base sequence of criminals even after the destruction of the sample DNA. used to detect minisatellites present in DNA or genome to produce a pattern that is unique to every individual.
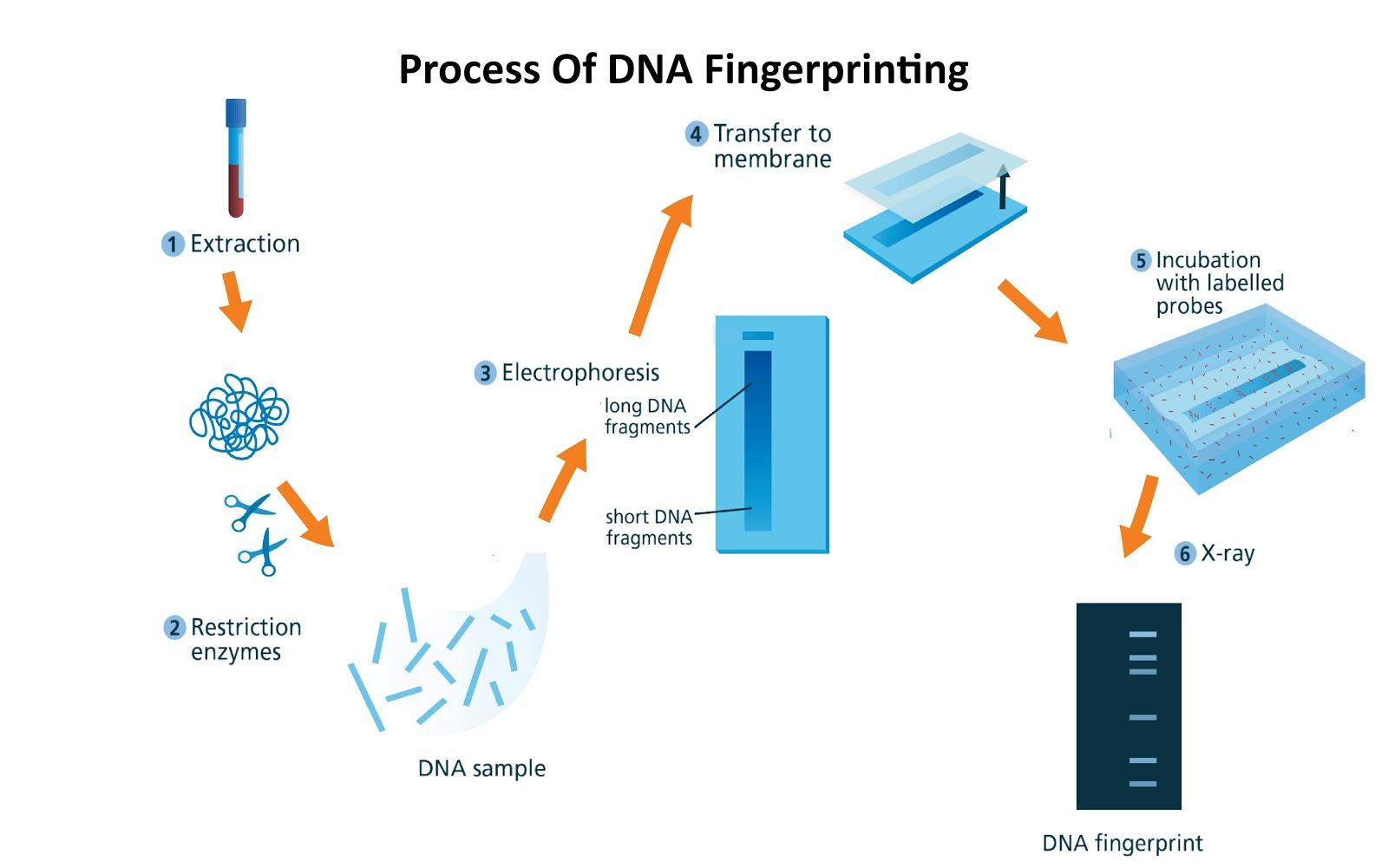
Following are the steps involved in the process of DNA Fingerprinting:
-Extraction
-Restriction enzymes
-Electrophoresis
-Transfer to membrane
-Incubation with labeled probes
-X-ray Analysis
Note:
DNA Fingerprinting has a wide range of applications including :
-It is used in forensics- DNA isolated from samples can be compared through the VNTR prototype which is used to solve murder cases.
-Paternity classification-Parent-Child VNTR prototype is used to solve disputed cases.
-Detection-It is also used for diagnosis of hydatidiform, and evaluation of tumor transmission after transplantation.
-Diagnosis of Inherited diseases- It detects both parental and newborn disorders like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, Huntington’s disease, etc.
Complete answer:
DNA Fingerprinting or DNA Profiling is a technique that is used to determine an individual's biological characteristics that are unique to each and every person. This process involves satellite DNA or satDNA is a highly repetitive length of DNA that contains short nucleotide sequences repeated multiple numbers times. Because of the large number of repetitions, the composition of this section of DNA is different, and when centrifuged, forms a separate band.
DNA fingerprinting is the method in which a small sample is found in the investigating crime scene and to study it the forensic analyst amplifies it and makes copies of it to study properly. The copies made can then be used to study the DNA base sequence of criminals even after the destruction of the sample DNA. used to detect minisatellites present in DNA or genome to produce a pattern that is unique to every individual.
Following are the steps involved in the process of DNA Fingerprinting:
-Extraction
-Restriction enzymes
-Electrophoresis
-Transfer to membrane
-Incubation with labeled probes
-X-ray Analysis

Note:
DNA Fingerprinting has a wide range of applications including :
-It is used in forensics- DNA isolated from samples can be compared through the VNTR prototype which is used to solve murder cases.
-Paternity classification-Parent-Child VNTR prototype is used to solve disputed cases.
-Detection-It is also used for diagnosis of hydatidiform, and evaluation of tumor transmission after transplantation.
-Diagnosis of Inherited diseases- It detects both parental and newborn disorders like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, Huntington’s disease, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




