
Which of the following has a square planar structure?
[A] $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$
[B] $B{{F}_{4}}$
[C] $Xe{{F}_{4}}$
[D] $CC{{l}_{4}}$
Answer
587.7k+ views
HINT: To find the geometry of any complex, we need to determine the coordination number of the complex. If we know the coordination number, we can easily find out the hybridization and the geometry of the complex.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: Let us discuss each option to find out if they are in square planar geometry or not-
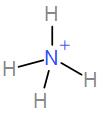
In the first option we have $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$
Number of valence electrons in nitrogen = 5.
From the hydrogen atoms we have a total contribution of 4.
Therefore, the total number of electrons is 9.
It has a positive overall charge so we will subtract 1 from 9. Therefore, the total number of electrons is 8.
Dividing it by 2 will give us the coordination number and which will give us the hybridisation and shape.
The coordination number is 4. Therefore, the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$ and shape is tetrahedral. Therefore, this is not the correct answer.
In the next option we have $B{{F}_{4}}$.
Valence electrons in boron are 3 and contribution for each fluorine atom is 1.
Therefore, the total number of electrons is 7.
Now as we can see it is not even so if we consider it as a cation or anion then the number of electrons will still be 6 or 8. Thus we will get a coordination number of either 3 or 4. So, this cannot be of square planar shape either.
Then we have $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
Number of valence electrons in xenon is 8 and contribution from each fluorine atom is 4 which will give us a total number of electrons of 12. Therefore, the coordination number will be 6. So, the shape is octahedral and the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ .
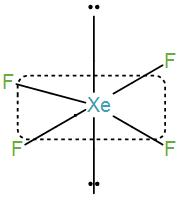
However, there are only four fluorine atoms so the remaining 4 electrons will exist as lone pairs and thus we will get a square planar structure here.
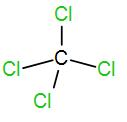
And lastly we have $CC{{l}_{4}}$.
Number of valence electron in carbon is 4 and each chlorine atom contributes 1 electron. So, the total electron will be 8 and thus coordination number is 4. Therefore, the shape is tetrahedral and the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
We can see from the above discussion that $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ has a square planar structure.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
NOTE: We have used VSEPR theory above to determine the shape and hybridisation of the given compounds. Although VSEPR is quite successful in determining the geometries of molecules, there are certain drawbacks to this theory. This theory fails to determine the shape of isoelectronic species. It also does not take the relative size of the constituents under consideration. It is unable to explain the atomic orbital overlaps.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: Let us discuss each option to find out if they are in square planar geometry or not-
In the first option we have $N{{H}_{4}}^{+}$
Number of valence electrons in nitrogen = 5.
From the hydrogen atoms we have a total contribution of 4.
Therefore, the total number of electrons is 9.
It has a positive overall charge so we will subtract 1 from 9. Therefore, the total number of electrons is 8.
Dividing it by 2 will give us the coordination number and which will give us the hybridisation and shape.
The coordination number is 4. Therefore, the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$ and shape is tetrahedral. Therefore, this is not the correct answer.

In the next option we have $B{{F}_{4}}$.
Valence electrons in boron are 3 and contribution for each fluorine atom is 1.
Therefore, the total number of electrons is 7.
Now as we can see it is not even so if we consider it as a cation or anion then the number of electrons will still be 6 or 8. Thus we will get a coordination number of either 3 or 4. So, this cannot be of square planar shape either.
Then we have $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
Number of valence electrons in xenon is 8 and contribution from each fluorine atom is 4 which will give us a total number of electrons of 12. Therefore, the coordination number will be 6. So, the shape is octahedral and the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ .

However, there are only four fluorine atoms so the remaining 4 electrons will exist as lone pairs and thus we will get a square planar structure here.
And lastly we have $CC{{l}_{4}}$.
Number of valence electron in carbon is 4 and each chlorine atom contributes 1 electron. So, the total electron will be 8 and thus coordination number is 4. Therefore, the shape is tetrahedral and the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$.

We can see from the above discussion that $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ has a square planar structure.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
NOTE: We have used VSEPR theory above to determine the shape and hybridisation of the given compounds. Although VSEPR is quite successful in determining the geometries of molecules, there are certain drawbacks to this theory. This theory fails to determine the shape of isoelectronic species. It also does not take the relative size of the constituents under consideration. It is unable to explain the atomic orbital overlaps.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




