
Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
(A)

(B)
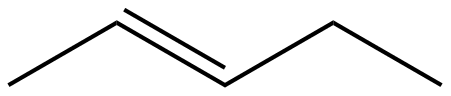
(C)
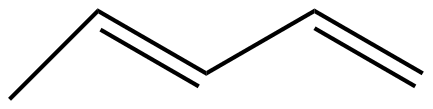
(D)
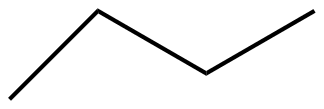




Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The boiling point of organic compounds can give important information about their physical and structural characteristics. The boiling point helps identify and characterize a compound. A liquid boils when its vapor pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. Vapour is determined from the kinetic energy of a molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
The effect of the boiling point on alkanes, alkenes, and dienes as the number of carbons increased, change in the relative strength of hydrogen bonding, Vanderwal depression forces, and decreases with increasing branching in carbon chains.
The given molecules IUPAC names for option A, B,C, and D are n-pentane, pent-2-ene, 2,4-pentadiene, and n-butane respectively.
The following factors affect the boiling point,
1. strength of intermolecular forces
2. length of carbon-carbon chain
3. branching decreases the boiling point
From the above factors, consider the second factor that as the number of carbon chains increases or the length of the carbon-carbon chain increases, the boiling point also increases. While considering given molecules n-pentane has more boiling point than n-butane in the case of alkanes.
In the case of alkenes, the intermolecular gets stronger with an increase in the size of the molecules.
Alkenes are lower boiling points than alkanes because intermolecular forces get stronger with increased size in alkenes.
By following the factors affecting the boiling point, the decreasing order of given molecules as follows,
N-pentane > n-butane > pent-2-ene > pent-2,4-diene.
Hence, n-pentane has a more boiling point than other compounds.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The boiling point in the carbon chain also alters with the given functional group, boiling point increases with molecular weight and the symmetry of the carbon chain impacts the boiling point of the resulting molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
The effect of the boiling point on alkanes, alkenes, and dienes as the number of carbons increased, change in the relative strength of hydrogen bonding, Vanderwal depression forces, and decreases with increasing branching in carbon chains.
The given molecules IUPAC names for option A, B,C, and D are n-pentane, pent-2-ene, 2,4-pentadiene, and n-butane respectively.
The following factors affect the boiling point,
1. strength of intermolecular forces
2. length of carbon-carbon chain
3. branching decreases the boiling point
From the above factors, consider the second factor that as the number of carbon chains increases or the length of the carbon-carbon chain increases, the boiling point also increases. While considering given molecules n-pentane has more boiling point than n-butane in the case of alkanes.
In the case of alkenes, the intermolecular gets stronger with an increase in the size of the molecules.
Alkenes are lower boiling points than alkanes because intermolecular forces get stronger with increased size in alkenes.
By following the factors affecting the boiling point, the decreasing order of given molecules as follows,
N-pentane > n-butane > pent-2-ene > pent-2,4-diene.
Hence, n-pentane has a more boiling point than other compounds.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The boiling point in the carbon chain also alters with the given functional group, boiling point increases with molecular weight and the symmetry of the carbon chain impacts the boiling point of the resulting molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




