
Which of the following have sunken stomata?
(a)Nerium
(b)Mangifera
(c)Hydrilla
(d)Zea may
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Sunken stomata are stomata present in small pits in a leaf which helps reduce the rate of water loss due to transpiration.
Complete answer:
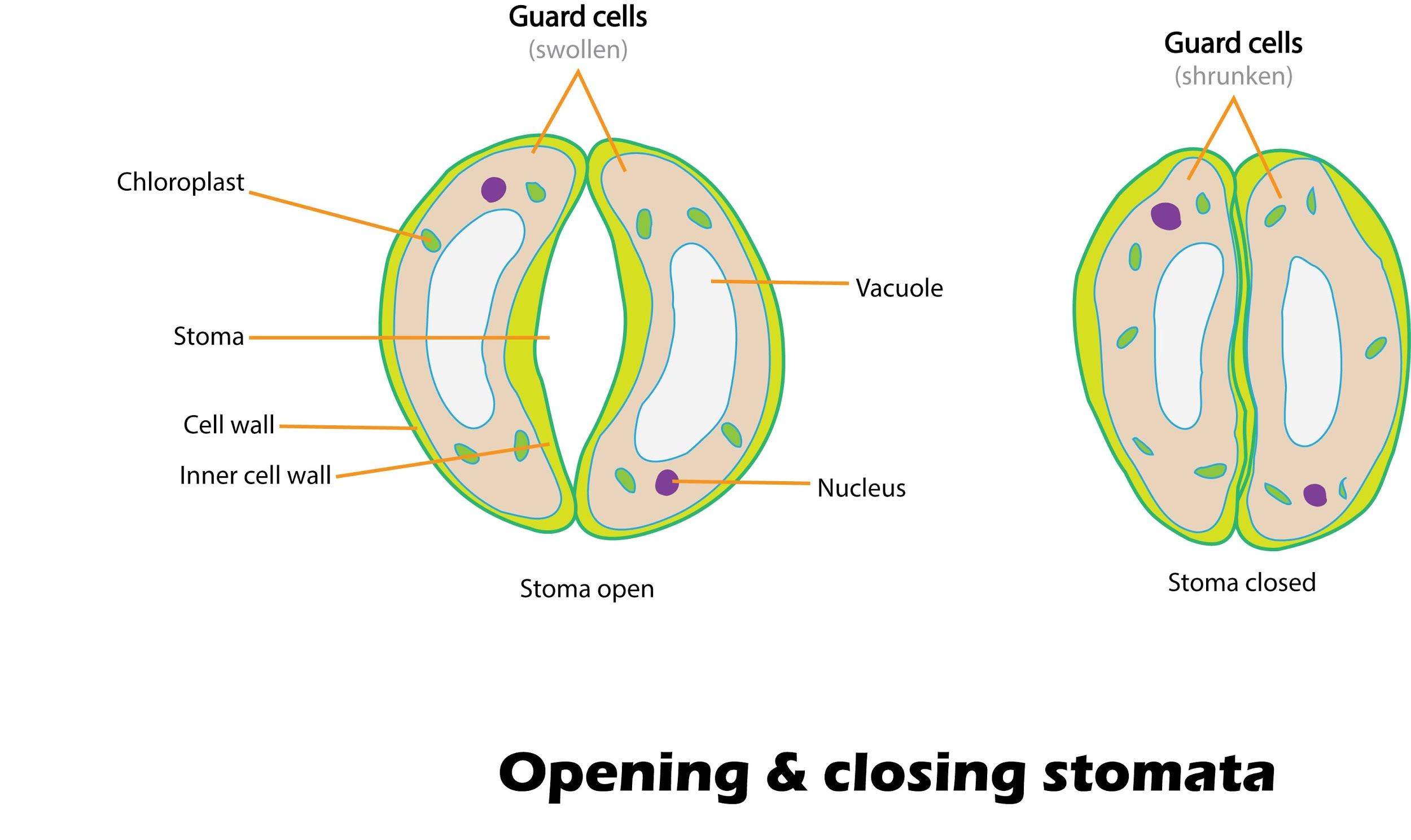
Sunken stomata are present in plants that are usually in areas of water scarcity i.e., arid areas or deserts where to prevent water loss due to transpiration. Plants generally have stomata on the surface of leaves, but sunken stomata are embedded in the left surface, also plants with sunken stomata have a fewer number of stomata on their leaves compared to regular plants. These sunken stomata are also surrounded by hair-like structures called trichomes to further prevent water loss. Plants with sunken stomata are usually xerophytes. This thus enables the plant to accomplish optimum gas exchange with minimal water loss since stomata can remain open longer and the $CO_2$ in the leaf or leave like structure can be maintained at required concentrations for these plants to be able to carry out photosynthesis throughout the day time.
So, the correct answer is ‘Nerium.’
Note:
- Leaves have different types of adaptations to tackle water loss due to transpiration:
-Leave are reduced to spines: Here spines reduce surface area thus drastically reducing the rate of transpiration.
-Reduction in the number of stomata: stomatal opening for gaseous exchange causes loss of water in arid conditions. Reduction in the number of stomata can help tackle this but almost maintain the gaseous exchange.
-Waxy cuticle on the leaves: Waxy cuticle physically stops water loss due to evaporation.
-Leaf rolling: this traps mist air which increases relative humidity and decreases exposed surface thus reducing the rate of transpiration.
Complete answer:
Sunken stomata are present in plants that are usually in areas of water scarcity i.e., arid areas or deserts where to prevent water loss due to transpiration. Plants generally have stomata on the surface of leaves, but sunken stomata are embedded in the left surface, also plants with sunken stomata have a fewer number of stomata on their leaves compared to regular plants. These sunken stomata are also surrounded by hair-like structures called trichomes to further prevent water loss. Plants with sunken stomata are usually xerophytes. This thus enables the plant to accomplish optimum gas exchange with minimal water loss since stomata can remain open longer and the $CO_2$ in the leaf or leave like structure can be maintained at required concentrations for these plants to be able to carry out photosynthesis throughout the day time.

So, the correct answer is ‘Nerium.’
Note:
- Leaves have different types of adaptations to tackle water loss due to transpiration:
-Leave are reduced to spines: Here spines reduce surface area thus drastically reducing the rate of transpiration.
-Reduction in the number of stomata: stomatal opening for gaseous exchange causes loss of water in arid conditions. Reduction in the number of stomata can help tackle this but almost maintain the gaseous exchange.
-Waxy cuticle on the leaves: Waxy cuticle physically stops water loss due to evaporation.
-Leaf rolling: this traps mist air which increases relative humidity and decreases exposed surface thus reducing the rate of transpiration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




