
Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions?
A. ${C_3}{H_6}$
B. ${C_2}{H_6}$
C. $C{H_4}$
D. ${C_3}{H_8}$
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: The most important point to note down in such questions is that only unsaturated hydrocarbons (i.e. the hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atoms) undergo addition reactions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Addition reactions are characteristic of unsaturated organic compounds—i.e., alkenes, which include a carbon-to-carbon double bond, and alkynes, which possess a carbon-to-carbon triple bond and as well as aldehydes and ketones, which have a carbon-to-oxygen double bond. Addition reactions can also be defined as a process in which the double or triple bonds are fully or partially broken so that they can accommodate additional extra atoms or groups of atoms in the molecule. Addition reactions on alkenes and alkynes are sometimes also referred to as saturation reactions because the reaction causes the carbon atoms to turn saturated with the maximum number of attached groups.
Now only alkanes and alkenes would undergo addition reactions due to presence of double and triple bonds. So the hydrocarbons ${C_2}{H_6}$ (ethane), $C{H_4}$ (methane) and ${C_3}{H_8}$ (propane) would not undergo addition reaction as they all come under the classification of alkanes (single bonds between the adjacent carbon atoms).
The structure of ${C_3}{H_6}$ (propene) is:
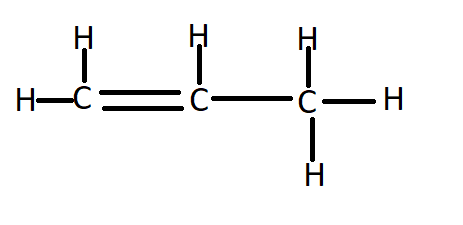
Since it has a double bond, therefore it will undergo an addition reaction.
Thus, option A is the correct answer.
Note: Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons that include only single bonds linking between the carbon atoms. As a consequence, every carbon atom is bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as feasible. Hydrocarbons can also develop straight chains, branched chains, or rings.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Addition reactions are characteristic of unsaturated organic compounds—i.e., alkenes, which include a carbon-to-carbon double bond, and alkynes, which possess a carbon-to-carbon triple bond and as well as aldehydes and ketones, which have a carbon-to-oxygen double bond. Addition reactions can also be defined as a process in which the double or triple bonds are fully or partially broken so that they can accommodate additional extra atoms or groups of atoms in the molecule. Addition reactions on alkenes and alkynes are sometimes also referred to as saturation reactions because the reaction causes the carbon atoms to turn saturated with the maximum number of attached groups.
Now only alkanes and alkenes would undergo addition reactions due to presence of double and triple bonds. So the hydrocarbons ${C_2}{H_6}$ (ethane), $C{H_4}$ (methane) and ${C_3}{H_8}$ (propane) would not undergo addition reaction as they all come under the classification of alkanes (single bonds between the adjacent carbon atoms).
The structure of ${C_3}{H_6}$ (propene) is:

Since it has a double bond, therefore it will undergo an addition reaction.
Thus, option A is the correct answer.
Note: Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons that include only single bonds linking between the carbon atoms. As a consequence, every carbon atom is bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as feasible. Hydrocarbons can also develop straight chains, branched chains, or rings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




