
Which of the following is a cross-linked polymer?
A: Teflon
B: Orlon
C: Nylon
D: Bakelite
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Cross-link refers to a bond which links one polymer chain to another polymer chain. We can say that cross-linked polymers are those polymers that are obtained when a cross-link bond is formed between the monomeric units. The cross-linked polymer leads to the formation of long chains which can be either branched or linear, that can create covalent bonds between the polymeric molecules. As cross-linked polymers create covalent bonds (much stronger than intermolecular forces which attract other polymeric chains), the resultant is a stronger and much more stable material.
Complete step by step answer:
Teflon (Option A), also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a thermoplastic polymer which becomes soft on heating and hard on cooling. It is basically non-reactive, and comprises carbon–fluorine bonds. It is made from tetrafluoroethylene via free-radical polymerization as shown below:

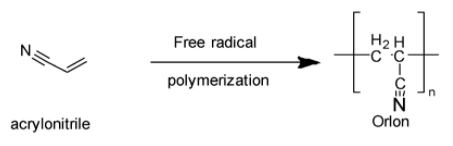
Orlon (Option B), generally known as Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), is also a thermoplastic polymer but it decomposes before melting. It is made from acrylonitrile via free-radical polymerization as shown below:
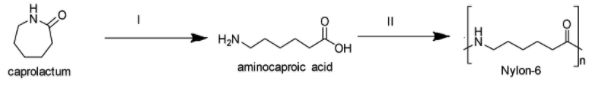
Nylon (Option C), generally known as polyamide, is also a synthetic thermoplastic material that can be processed into films, fibers or shapes. It is a condensation polymer or copolymer consisting of amide linkages formed by the reaction of difunctional monomers consisting of equal parts of carboxylic acid and amines. Nylon 6, Nylon 66, Nylon 510 are few types of Nylon. Synthesis of Nylon 6 is shown below in which ring opening of caprolactam takes place in the first stage (I) followed by condensation polymerization (II).
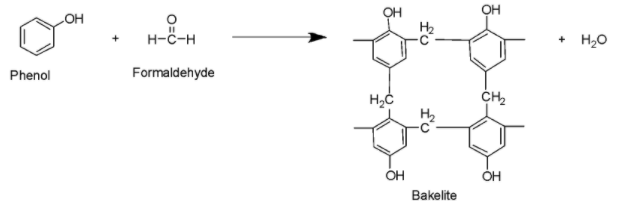
Bakelite (Option D) is a thermosetting plastic possessing a permanent shape as well as size which cannot be altered on exposure to heat and pressure without decomposing it. Thermosetting Plastics are prepared via low molecular mass semi-fluid substances. On heating in a mould, these plastics get highly cross-linked leading to the formation of hard infusible and insoluble products. Moreover, thermosetting plastics can tolerate very high temperatures. The polymers link together during the curing process to form a permanent chemical bond. These types of polymers are poor conductors of heat or electricity and hence can be effectively used in electric switches, sockets, frying pan handles, etc. Bakelite is a condensation polymer made from formaldehyde and phenol as shown below:
Thus, the correct answer is option D i.e. Bakelite is a cross-linked polymer.
Note: Cross-linked polymers are polymers in which long polymer chains are cross-linked together to create a three dimensional network. Cross-linked polymers are utilised in making a large number of materials as they are mechanically strong and even resistant to heat, wear or attack by solvents. Examples of these polymers include bakelite, melamine and formaldehyde resin.
Complete step by step answer:
Teflon (Option A), also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a thermoplastic polymer which becomes soft on heating and hard on cooling. It is basically non-reactive, and comprises carbon–fluorine bonds. It is made from tetrafluoroethylene via free-radical polymerization as shown below:

Orlon (Option B), generally known as Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), is also a thermoplastic polymer but it decomposes before melting. It is made from acrylonitrile via free-radical polymerization as shown below:

Nylon (Option C), generally known as polyamide, is also a synthetic thermoplastic material that can be processed into films, fibers or shapes. It is a condensation polymer or copolymer consisting of amide linkages formed by the reaction of difunctional monomers consisting of equal parts of carboxylic acid and amines. Nylon 6, Nylon 66, Nylon 510 are few types of Nylon. Synthesis of Nylon 6 is shown below in which ring opening of caprolactam takes place in the first stage (I) followed by condensation polymerization (II).

Bakelite (Option D) is a thermosetting plastic possessing a permanent shape as well as size which cannot be altered on exposure to heat and pressure without decomposing it. Thermosetting Plastics are prepared via low molecular mass semi-fluid substances. On heating in a mould, these plastics get highly cross-linked leading to the formation of hard infusible and insoluble products. Moreover, thermosetting plastics can tolerate very high temperatures. The polymers link together during the curing process to form a permanent chemical bond. These types of polymers are poor conductors of heat or electricity and hence can be effectively used in electric switches, sockets, frying pan handles, etc. Bakelite is a condensation polymer made from formaldehyde and phenol as shown below:

Thus, the correct answer is option D i.e. Bakelite is a cross-linked polymer.
Note: Cross-linked polymers are polymers in which long polymer chains are cross-linked together to create a three dimensional network. Cross-linked polymers are utilised in making a large number of materials as they are mechanically strong and even resistant to heat, wear or attack by solvents. Examples of these polymers include bakelite, melamine and formaldehyde resin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




