
Which of the following is a mode of asexual reproduction?
A. Fission
B. Budding
C. Spore formation
D. All of the above
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: There are different modes of reproductions namely sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes from two different individuals, whereas, asexual reproduction involves a single parent to give rise to a new offspring.
Complete answer: Asexual reproduction is observed in both multicellular and unicellular organisms. Asexual reproduction involves a single parent without the fertilization or formation of gametes. The offspring produced are genetically as well as physically identical to each other and hence are termed as clones.
There are different modes of asexual reproduction are as follows:
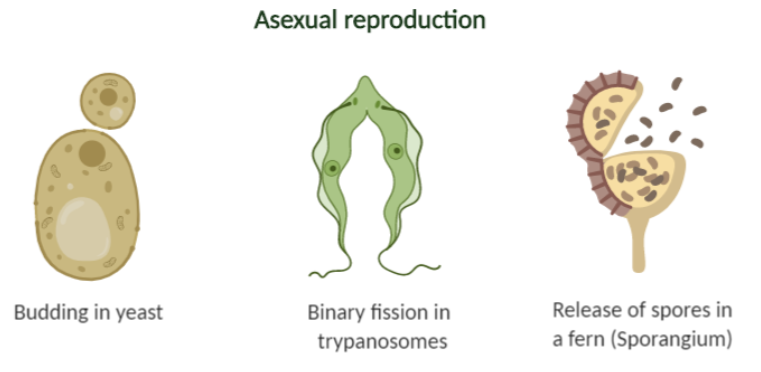
1. Fission is the division of the parent cell into two or more cells. Binary fission and multiple fission are the two types of fission. Binary fission is exhibited by organisms such as the bacteria, Amoeba, Euglena,, etc., whereas, multiple fission is exhibited by organisms such as algae and sporozoans.
2. Budding is the process of development of buds on the organism’s body. The bud arising from the parent organism matures into a new organism of the same kind and detaches itself from the parent organism’s body. Hydra is one such example of an organism that exhibits budding as a mode of reproduction.
3. Spore formation is another mode of asexual reproduction, wherein organisms like fungi, fern, etc. produce spores in a sporangium, which is a sac-like structure. The sporangium under favorable conditions, burst to release the spores. These spores mature and germinate to form new offspring.
Thus, budding (e.g. Hydra), binary fission (e.g. Amoeba, bacteria), vegetative propagation (e.g. Onion), fragmentation (e.g. Planaria<./i>), and spore formation (e.g. ferns).
Therefore, the correct answer is option D-All of the above.
Note: Other modes of asexual reproduction include vegetative propagation and fragmentation. Fragmentation involves the multicellular organism to break down into segments, wherein each segment germinates to form a new organism. And vegetative propagation occurs in the leaves, stems, and roots of a plant. Specific vegetative parts undergo regeneration and fragmentation in this type of asexual reproduction.
Complete answer: Asexual reproduction is observed in both multicellular and unicellular organisms. Asexual reproduction involves a single parent without the fertilization or formation of gametes. The offspring produced are genetically as well as physically identical to each other and hence are termed as clones.
There are different modes of asexual reproduction are as follows:

1. Fission is the division of the parent cell into two or more cells. Binary fission and multiple fission are the two types of fission. Binary fission is exhibited by organisms such as the bacteria, Amoeba, Euglena,, etc., whereas, multiple fission is exhibited by organisms such as algae and sporozoans.
2. Budding is the process of development of buds on the organism’s body. The bud arising from the parent organism matures into a new organism of the same kind and detaches itself from the parent organism’s body. Hydra is one such example of an organism that exhibits budding as a mode of reproduction.
3. Spore formation is another mode of asexual reproduction, wherein organisms like fungi, fern, etc. produce spores in a sporangium, which is a sac-like structure. The sporangium under favorable conditions, burst to release the spores. These spores mature and germinate to form new offspring.
Thus, budding (e.g. Hydra), binary fission (e.g. Amoeba, bacteria), vegetative propagation (e.g. Onion), fragmentation (e.g. Planaria<./i>), and spore formation (e.g. ferns).
Therefore, the correct answer is option D-All of the above.
Note: Other modes of asexual reproduction include vegetative propagation and fragmentation. Fragmentation involves the multicellular organism to break down into segments, wherein each segment germinates to form a new organism. And vegetative propagation occurs in the leaves, stems, and roots of a plant. Specific vegetative parts undergo regeneration and fragmentation in this type of asexual reproduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




