
Which of the following is a vic-dihalide?
A.Dichloromethane
B.1,2-dichloroethane
C.Ethylidene chloride
D.Allyl chloride
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Vicinal dihalides are those compounds that have halogens on the adjacent carbon. They are prepared by the reaction between a halogen and alkene.
Complete step by step answer:
In option A, the structure of dichloromethane is given below:
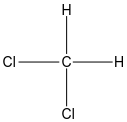
In the structure of dichloromethane, we can see both halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon hence it is not a vicinal halogen. It is the example of geminal dihalides.
In the case of option B, the structure of 1,2-dichloroethane is given below:
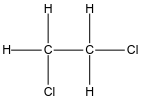
In the case of 1,2-dichloroethane as we see both halogens are attached to adjacent carbon hence we can say it is a vicinal dihalide.
In the case of option C, the structure of ethylidene chloride is given below:
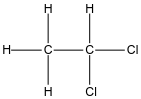
Again in this structure, the halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon so again we can say it is an example of geminal dihalides.
In case of option D, the structure of allyl chloride is given as:
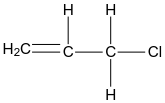
In this structure only one halogen group is present and dihalides mean there are two halogen atoms so we can say it is not a vicinal dihalide.
So the correct answer is option B .
Note:
Vicinal dihalides are identified by treating an ether or THF solution of the material with zinc dust. And due to the dissolution of some zinc and localized boiling of solvent one can observe warming and bubbling. Also, since vicinal means adjacent carbon and geminal means the same carbon so we can say vicinal dihalides and geminal dihalides are the brothers from different mothers.
Complete step by step answer:
In option A, the structure of dichloromethane is given below:

In the structure of dichloromethane, we can see both halogen atoms are bonded to the same carbon hence it is not a vicinal halogen. It is the example of geminal dihalides.
In the case of option B, the structure of 1,2-dichloroethane is given below:

In the case of 1,2-dichloroethane as we see both halogens are attached to adjacent carbon hence we can say it is a vicinal dihalide.
In the case of option C, the structure of ethylidene chloride is given below:

Again in this structure, the halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon so again we can say it is an example of geminal dihalides.
In case of option D, the structure of allyl chloride is given as:

In this structure only one halogen group is present and dihalides mean there are two halogen atoms so we can say it is not a vicinal dihalide.
So the correct answer is option B .
Note:
Vicinal dihalides are identified by treating an ether or THF solution of the material with zinc dust. And due to the dissolution of some zinc and localized boiling of solvent one can observe warming and bubbling. Also, since vicinal means adjacent carbon and geminal means the same carbon so we can say vicinal dihalides and geminal dihalides are the brothers from different mothers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




