
Which of the following is absent in an animal cell?
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus
(c) Cell membrane
(d) Cell wall
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: This is tough and it provides rigidity, flexibility, structural support, and also protection to the plant cell. It is also present in bacteria and fungi but the composition is different.
Complete answer:
The cell wall is present in plant cells. They are very tough, flexible, and rigid layers that surround the cell. This rigidity allows plants to stand upright without the need for bones and grow as tall as possible. Animal cells don’t have cell walls because they do not need them. The cytoplasm is a thick solution mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. It is enclosed by the cell membrane. It acts as a buffer and protects the genetic material and also the cell organelles from damage.
The nucleus may be a membrane-bound organelle that contains genetic material (DNA) of eukaryotic organisms. It is the largest organelle. inside the cell taking over a few tenths of the entire cell volume.
The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane.
It is consists of a thin layer of amphipathic .
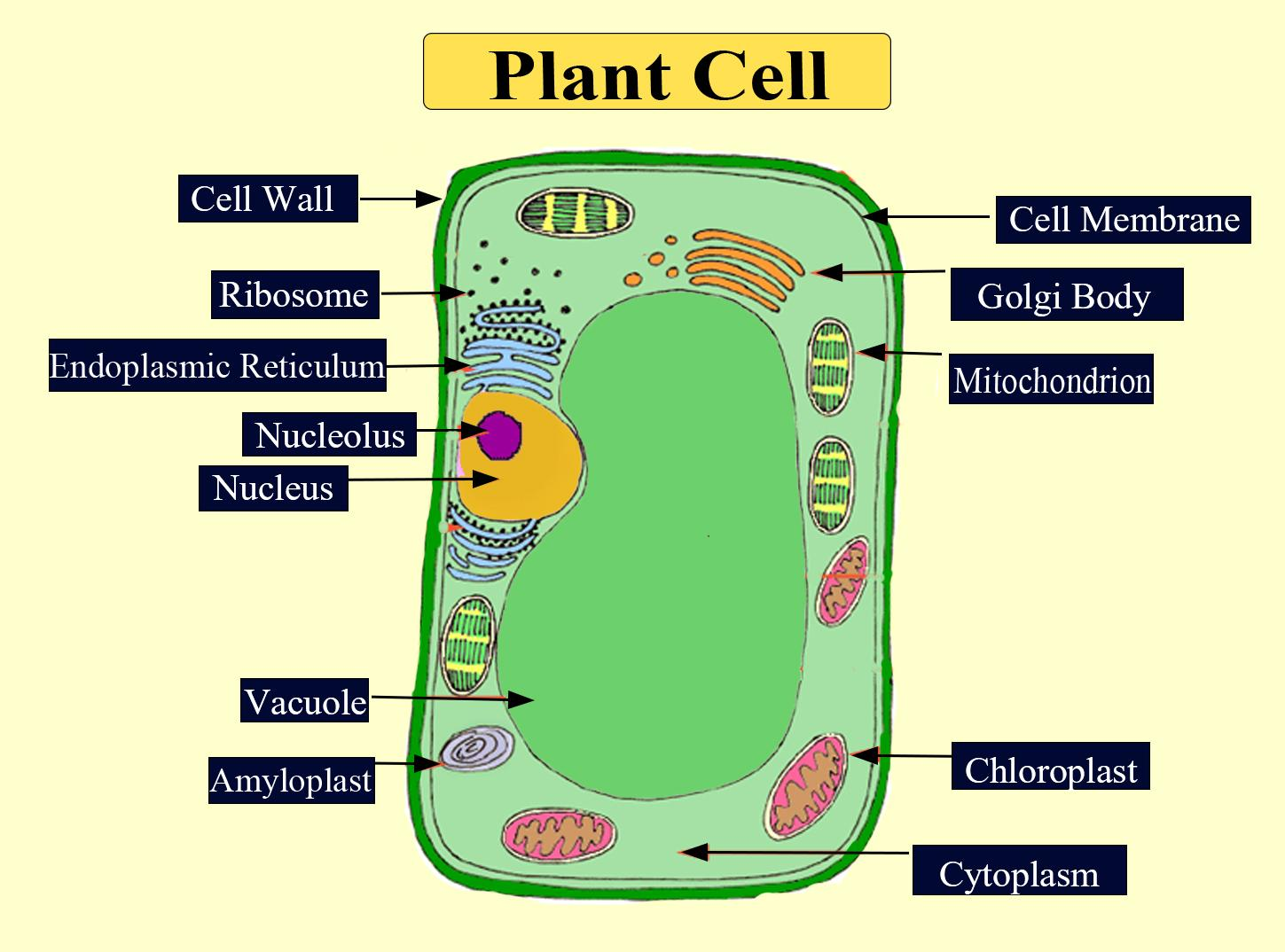
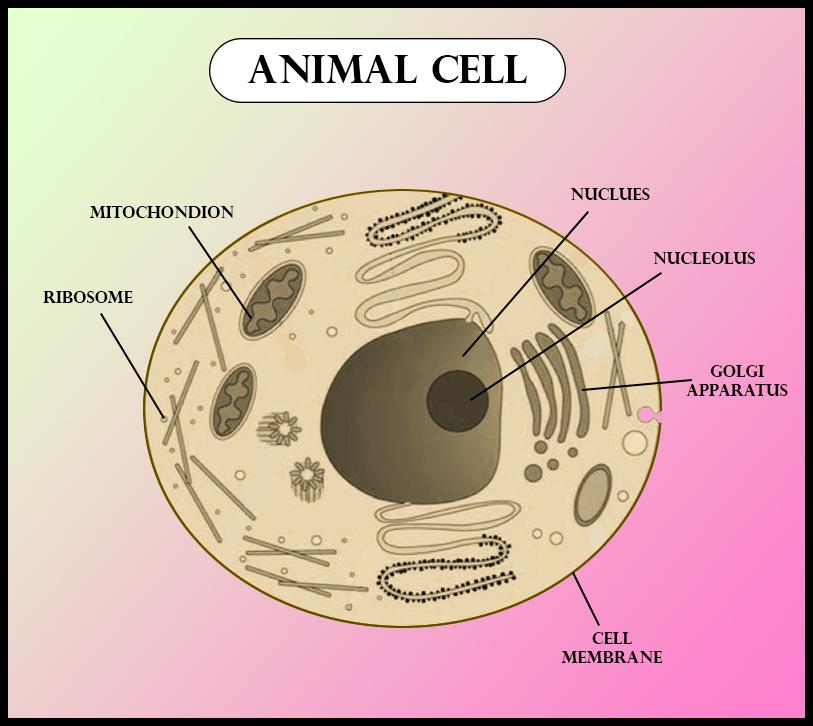
Additional Information:
-Cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm with glycolysis.
-The nucleus controls all the activities that are performed by a cell, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein synthesis, and also reproduction (cell division)
-The cell membranes consist of a lipid bilayer, including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures.
So, the correct answer is the’ cell wall’.
Note:
-Nucleus was discovered by Mr. Brown(Robert Brown) in 1831. With the help of grafting experiments on Acetabularia, Hammerling in 1953 proved that the nucleus is a storehouse of hereditary information.
-The cell wall is protective and it protects the cell membrane, a semipermeable membrane, next to the outermost layer of a plant cell. Its major function is to give the cell strength and structure and to filter molecules that pass in and out of the cell.
Complete answer:
The cell wall is present in plant cells. They are very tough, flexible, and rigid layers that surround the cell. This rigidity allows plants to stand upright without the need for bones and grow as tall as possible. Animal cells don’t have cell walls because they do not need them. The cytoplasm is a thick solution mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. It is enclosed by the cell membrane. It acts as a buffer and protects the genetic material and also the cell organelles from damage.
The nucleus may be a membrane-bound organelle that contains genetic material (DNA) of eukaryotic organisms. It is the largest organelle. inside the cell taking over a few tenths of the entire cell volume.
The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane.
It is consists of a thin layer of amphipathic .


Additional Information:
-Cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm with glycolysis.
-The nucleus controls all the activities that are performed by a cell, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, protein synthesis, and also reproduction (cell division)
-The cell membranes consist of a lipid bilayer, including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures.
So, the correct answer is the’ cell wall’.
Note:
-Nucleus was discovered by Mr. Brown(Robert Brown) in 1831. With the help of grafting experiments on Acetabularia, Hammerling in 1953 proved that the nucleus is a storehouse of hereditary information.
-The cell wall is protective and it protects the cell membrane, a semipermeable membrane, next to the outermost layer of a plant cell. Its major function is to give the cell strength and structure and to filter molecules that pass in and out of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




