
Which of the following is an example of azo dye?
A.Orange-1
B.Malachite green
C.Indigo
D.Martius yellow
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: The characteristic feature of an azo dye is the presence of ―N=N―this bond in the structure of the compound. There are different types of dyes, but not all are azo dyes, some are organic dyes while some are just coloured compounds that impart colour on using.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Azo dye is a large class of synthetic organic dyes that contain nitrogen in the form of the azo group ―N=N― as part of their molecular structures. More than half of the commercial dyes belong to this class. In general, azo dye compounds come in yellow, orange, red, brown, and blue colour. The colour differences in the azo dye are caused by different substituents that are attached on the aromatic rings which lead to differences in the extent of conjugation of the \[\pi \] system. The more extensive the conjugated \[\pi \] system of a molecule, the longer the wavelength of visible light it will absorb.
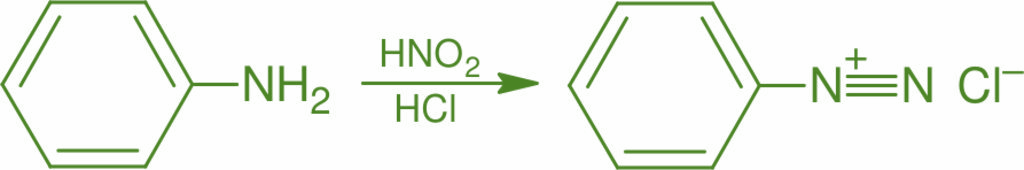
The synthesis of an azo dye requires two organic compounds - a diazonium salt and a coupling component. The chemical equation involved the synthesis of azo dyes is shown below.
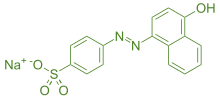
Orange-1 is an azo dye having red colour. It is a food dye because it is soluble in water. It is prepared by the azo coupling reaction of 2,4-diaminotoluene and phenyldiazonium.
Malachite green has intense green colour prepared by the condensation of dimethylaniline and benzaldehyde. It is chosen as model dye for azo. So, it is not an azo dye. Indigo is a natural dye which is extracted from the plants and has a distinctive blue colour. It is not an azo dye, rather it is an organic dye. Martius yellow is a yellow coloured organic compound which has poor light-fastness.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Our eye perceives colour when a dye absorbs some wavelength and reflects others. For example, if a dye compound absorbs in the green visible region, the combination of the remaining wavelengths which gets reflected makes the compound appear red in colour
Complete step-by-step answer:
Azo dye is a large class of synthetic organic dyes that contain nitrogen in the form of the azo group ―N=N― as part of their molecular structures. More than half of the commercial dyes belong to this class. In general, azo dye compounds come in yellow, orange, red, brown, and blue colour. The colour differences in the azo dye are caused by different substituents that are attached on the aromatic rings which lead to differences in the extent of conjugation of the \[\pi \] system. The more extensive the conjugated \[\pi \] system of a molecule, the longer the wavelength of visible light it will absorb.
The synthesis of an azo dye requires two organic compounds - a diazonium salt and a coupling component. The chemical equation involved the synthesis of azo dyes is shown below.

Orange-1 is an azo dye having red colour. It is a food dye because it is soluble in water. It is prepared by the azo coupling reaction of 2,4-diaminotoluene and phenyldiazonium.

Malachite green has intense green colour prepared by the condensation of dimethylaniline and benzaldehyde. It is chosen as model dye for azo. So, it is not an azo dye. Indigo is a natural dye which is extracted from the plants and has a distinctive blue colour. It is not an azo dye, rather it is an organic dye. Martius yellow is a yellow coloured organic compound which has poor light-fastness.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: Our eye perceives colour when a dye absorbs some wavelength and reflects others. For example, if a dye compound absorbs in the green visible region, the combination of the remaining wavelengths which gets reflected makes the compound appear red in colour
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




