
Which of the following is not a straight chain hydrocarbon?
(A).
(B).
(C).
(D).




Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint: Read the IUPAC Nomenclature rules for assigning names to the compounds. Have a look at each compound and try to select the longest carbon chain to determine its parent name in order to get the answer.
Complete answer:
- Straight chain compounds are one of the types of isomers of organic compounds in which there is no substituent attached on the parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Let’s have a look at the given compounds in the question.
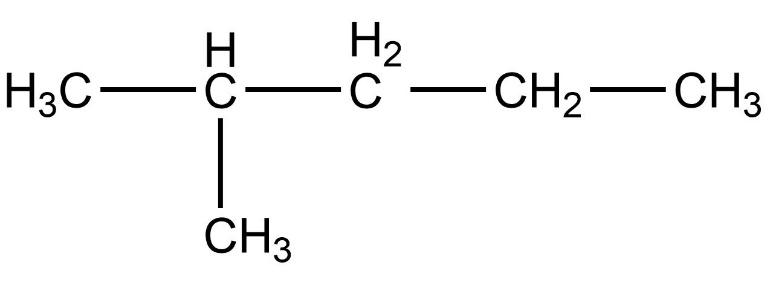
- First compound is,
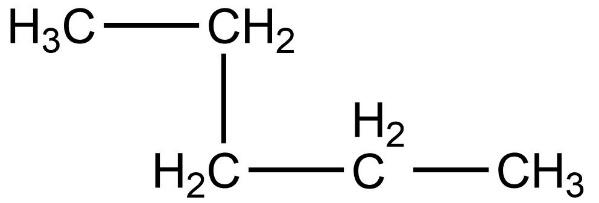
- Now, we need to count the total number of carbon atoms present in this compound. The total number of carbon atoms present in this compound is five. Also, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain present in the compound is pentane only. There are no substituents attached on the chain. Therefore, this is a straight chain compound.
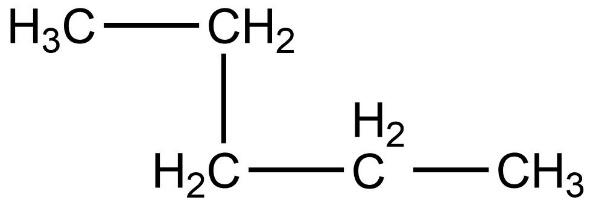
- Second compound is,
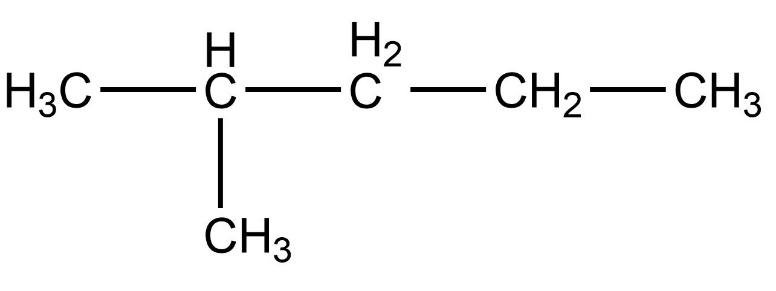
- In this compound, the total number of carbon atoms is six and but, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain is pentane. There is one methyl substituent attached to the second carbon atom in the chain. Therefore, this compound is not a straight chain compound. This compound is a branched chain compound, iso-hexane.
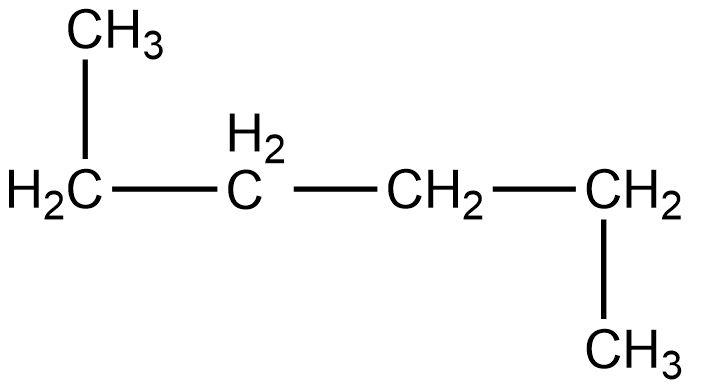
- Third compound is,
- In this compound, the total number of carbon atoms is six and also, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain is hexane. There are no substituents attached on the chain. Therefore, this compound is a straight chain compound, n-hexane.
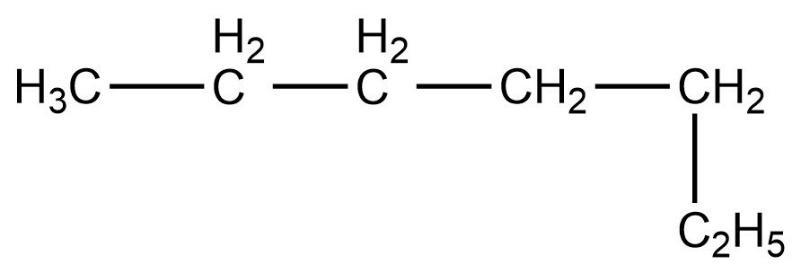
- Fourth compound is,
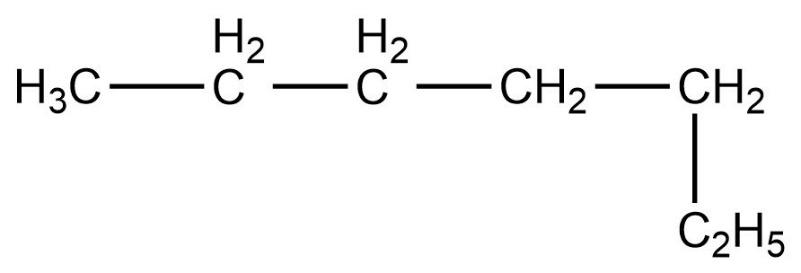
- In this compound, the total number of carbon atoms is six and also, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain is hexane. There are no substituents attached on the chain. Therefore, this compound is a straight chain compound, n-hexane.
- Therefore, compound (B) iso-hexane is not a straight chain compound.
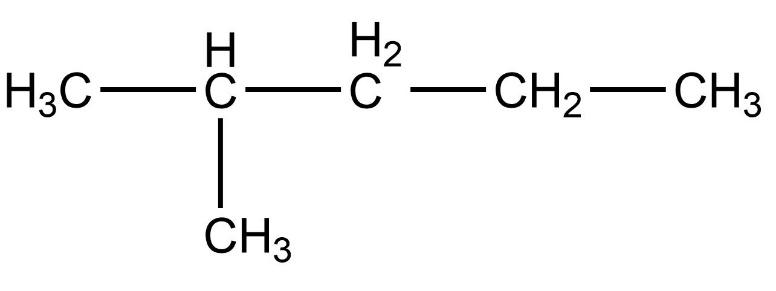
Therefore, the correct option is option (B).
Note:
Don’t get confused that the term ‘straight’ indicates the number of carbon present in one line. That is a common mistake. Straight chain means number of carbon atoms forming a long continuous chain. It can be represented in many ways, zig-zag, or vertically, or horizontally, etc. Be thorough with this minor concept.
Complete answer:
- Straight chain compounds are one of the types of isomers of organic compounds in which there is no substituent attached on the parent hydrocarbon chain.
- Let’s have a look at the given compounds in the question.
- First compound is,

- Now, we need to count the total number of carbon atoms present in this compound. The total number of carbon atoms present in this compound is five. Also, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain present in the compound is pentane only. There are no substituents attached on the chain. Therefore, this is a straight chain compound.
- Second compound is,

- In this compound, the total number of carbon atoms is six and but, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain is pentane. There is one methyl substituent attached to the second carbon atom in the chain. Therefore, this compound is not a straight chain compound. This compound is a branched chain compound, iso-hexane.
- Third compound is,
- In this compound, the total number of carbon atoms is six and also, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain is hexane. There are no substituents attached on the chain. Therefore, this compound is a straight chain compound, n-hexane.
- Fourth compound is,

- In this compound, the total number of carbon atoms is six and also, the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain is hexane. There are no substituents attached on the chain. Therefore, this compound is a straight chain compound, n-hexane.
- Therefore, compound (B) iso-hexane is not a straight chain compound.

Therefore, the correct option is option (B).
Note:
Don’t get confused that the term ‘straight’ indicates the number of carbon present in one line. That is a common mistake. Straight chain means number of carbon atoms forming a long continuous chain. It can be represented in many ways, zig-zag, or vertically, or horizontally, etc. Be thorough with this minor concept.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




