
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name?
A.3-Ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane
B.4,4-dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
C.5-Ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane
D.4,4-bis(methyl)-3-ethylheptane
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint:We know that all alkanes do not contain straight-chain. Some alkanes are known as branched alkanes. We have to know that branched alkanes vary from straight-chain alkanes in the chains of carbon atoms that replaces a few hydrogen atoms present along the chain. Substituent is the term given to groups (or) atoms, which replaces hydrogen in an alkane.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to know that naming a straight chain alkane is much easier than naming a branched alkane. We will discuss some of the steps to derive the IUPAC names of substituted alkanes.
1.The first step is to count the longest chain of carbons. The longest chain has to be continuous.
2.In the second step, we have to count the number of carbons present in the chain beginning with the side which is close to the branch. We call the longest chain present in branched alkane as the parent chain.
3.In the third step, we have to count the number of carbons present in each branch. The carbons present in branches are called alkyl groups and they contain one carbon less than the alkane group. For example, if there is one carbon present, we call the group a methyl group, if it’s two carbons, then it is ethyl and so on.
4.We have to attach the number of carbon from each substituent branch to the front of the alkyl group name. For example, if a group containing two carbons is bonded to a third carbon present in the chain, then we call the group as 3-ethyl.
5.In the fifth step, we have to check for repeated alkyl groups. If we notice multiple groups present with the same number of carbons branched off the parent chain, we should not repeat the name. In such instances, we have to use prefixes such as di-, tri-, and tetra-.
6.In the sixth step, we have to place the names of the substituent groups before the name of the parent chain in alphabetical order. We need not alphabetize the prefixes such as di-, tri-, and tetra-.
Now let us identify the correct IUPAC name.
When we write the names of substituents, we need to write them in alphabetical order. So, e of ethyl comes before m of dimethyl. The number 3 is given to the ethyl group and is written first. So the correct IUPAC name is 3-Ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane.
The structure of 3-Ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane is,
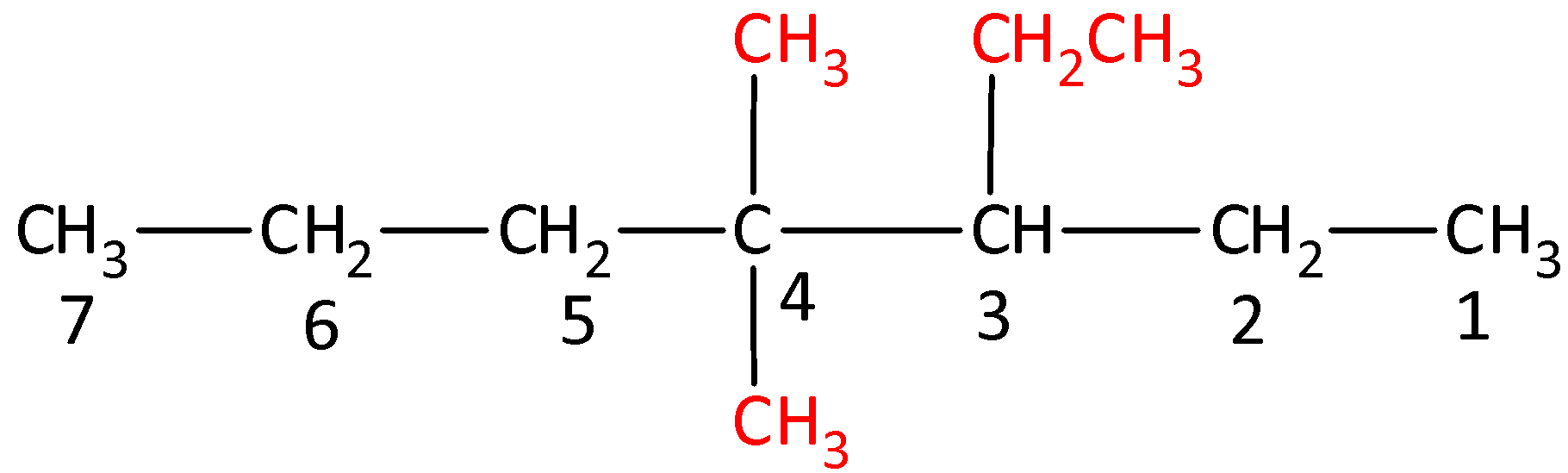
Options (B), (C) and (D) are incorrect as the naming is not done as per the IUPAC nomenclature of substituted alkanes.
Therefore, the option (A) is correct.
Note:
We shall discuss the rules for naming alkanes.
We know that saturated hydrocarbons are called alkanes. Each atom in an alkane shows the presence of four single bonds in a tetrahedral arrangement with $s{p^3}$ hybridization. The name of alkane ends with “-ane”.
Rules for naming compound:
1.The carbon atoms in the longest chain have to be counted.
2.The substituents have to be identified and counted.
3.The backbone carbon atoms have to be numbered by assigning the lowest number from the starting end.
For example: Write the IUPAC name for the given compound. The given compound is,

The parent chain of the compound is pentane. One methyl group is present in the carbon third position. So, the systematic name of the given compound is 3-methylpentane.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to know that naming a straight chain alkane is much easier than naming a branched alkane. We will discuss some of the steps to derive the IUPAC names of substituted alkanes.
1.The first step is to count the longest chain of carbons. The longest chain has to be continuous.
2.In the second step, we have to count the number of carbons present in the chain beginning with the side which is close to the branch. We call the longest chain present in branched alkane as the parent chain.
3.In the third step, we have to count the number of carbons present in each branch. The carbons present in branches are called alkyl groups and they contain one carbon less than the alkane group. For example, if there is one carbon present, we call the group a methyl group, if it’s two carbons, then it is ethyl and so on.
4.We have to attach the number of carbon from each substituent branch to the front of the alkyl group name. For example, if a group containing two carbons is bonded to a third carbon present in the chain, then we call the group as 3-ethyl.
5.In the fifth step, we have to check for repeated alkyl groups. If we notice multiple groups present with the same number of carbons branched off the parent chain, we should not repeat the name. In such instances, we have to use prefixes such as di-, tri-, and tetra-.
6.In the sixth step, we have to place the names of the substituent groups before the name of the parent chain in alphabetical order. We need not alphabetize the prefixes such as di-, tri-, and tetra-.
Now let us identify the correct IUPAC name.
When we write the names of substituents, we need to write them in alphabetical order. So, e of ethyl comes before m of dimethyl. The number 3 is given to the ethyl group and is written first. So the correct IUPAC name is 3-Ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane.
The structure of 3-Ethyl-4,4-dimethylheptane is,

Options (B), (C) and (D) are incorrect as the naming is not done as per the IUPAC nomenclature of substituted alkanes.
Therefore, the option (A) is correct.
Note:
We shall discuss the rules for naming alkanes.
We know that saturated hydrocarbons are called alkanes. Each atom in an alkane shows the presence of four single bonds in a tetrahedral arrangement with $s{p^3}$ hybridization. The name of alkane ends with “-ane”.
Rules for naming compound:
1.The carbon atoms in the longest chain have to be counted.
2.The substituents have to be identified and counted.
3.The backbone carbon atoms have to be numbered by assigning the lowest number from the starting end.
For example: Write the IUPAC name for the given compound. The given compound is,

The parent chain of the compound is pentane. One methyl group is present in the carbon third position. So, the systematic name of the given compound is 3-methylpentane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




