
Which of the following is the functional group of amide?
(A)
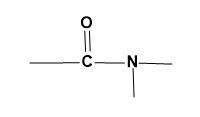
(B)
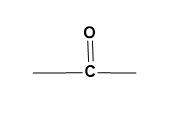
(C)
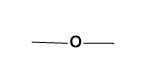
(D) None of the above



Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The functional groups mentioned above can be represented in different molecules which can be named with respect to the specific nomenclature.
The parent name is enough to describe the functional group and its constituent atoms, for example; presence of ‘N’ atom shows the functional group which is related to nitrogen i.e. ammonia, amine, amide, etc.
Complete answer:
Let us analyse each option one by one-
For (A)-
The given group can also be generally stated as, $-CO-NH$ . This functional group has a nitrogen atom as its basic constituent. The parent atom as nitrogen describes the functional group as amide.
Amide functional group is derived from ammine which is then attached to a carbonyl group which is obtained when ammine is reacted with carboxylic acids. But amide and amine groups can be differentiated even though the parent atom is same as;
1. Amide nitrogen is considerably less basic than amine nitrogen.
2. The N-H bond in amide is more acidic than the N-H bond in amine.
3. Amide has the restricted rotation against the C-N bond.
Thus, the given functional group is amide.
For (B)-
The given functional group is of ketone. The carbon atom attached to an oxygen atom through a double bond and has alkyl groups on other two bonds represents the functional of acetone.
For (C)-
The given functional group is the representation of ether. When an oxygen atom is directly bonded to alkyl groups on both sides and thus acts as a bridge, it represents the ether group.
Therefore, as stated above option (A) represents the amide functional group.
Note:
Sometimes the word ‘amide’ is also used to refer to the conjugate bases of amines as sodium amide ($NaN{{H}_{2}}$) . Only the pronunciation can differentiate it as a functional group or a base of amine.
The parent name is enough to describe the functional group and its constituent atoms, for example; presence of ‘N’ atom shows the functional group which is related to nitrogen i.e. ammonia, amine, amide, etc.
Complete answer:
Let us analyse each option one by one-
For (A)-
The given group can also be generally stated as, $-CO-NH$ . This functional group has a nitrogen atom as its basic constituent. The parent atom as nitrogen describes the functional group as amide.
Amide functional group is derived from ammine which is then attached to a carbonyl group which is obtained when ammine is reacted with carboxylic acids. But amide and amine groups can be differentiated even though the parent atom is same as;
1. Amide nitrogen is considerably less basic than amine nitrogen.
2. The N-H bond in amide is more acidic than the N-H bond in amine.
3. Amide has the restricted rotation against the C-N bond.
Thus, the given functional group is amide.
For (B)-
The given functional group is of ketone. The carbon atom attached to an oxygen atom through a double bond and has alkyl groups on other two bonds represents the functional of acetone.
For (C)-
The given functional group is the representation of ether. When an oxygen atom is directly bonded to alkyl groups on both sides and thus acts as a bridge, it represents the ether group.
Therefore, as stated above option (A) represents the amide functional group.
Note:
Sometimes the word ‘amide’ is also used to refer to the conjugate bases of amines as sodium amide ($NaN{{H}_{2}}$) . Only the pronunciation can differentiate it as a functional group or a base of amine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




