
Which of the following is used as Hinsberg’s reagent?
(A) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}S{{O}_{2}}Cl$
(B) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}S{{O}_{3}}H$
(C) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}NHC{{H}_{3}}$
(D) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COC{{H}_{3}}$
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Knowing the scientific name of Hinsberg’s reagent will help. It is an aromatic compound with a sulfonyl group.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hinsberg’s reagent is used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Its chemical formula is benzene sulphonyl chloride (${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}S{{O}_{2}}Cl$). Its structure is as below:
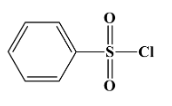
The correct answer for the above question is option (A)${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}S{{O}_{2}}Cl$.
Additional information:
Let’s know more about the reactions using Hinsberg’s reagent that distinguish the amines of different degrees.
- When a primary amine says ethyl amine reacts with this reagent, we get $N-methylbenzenesulfonamide$. This product is soluble in alkali due to the highly acidic hydrogen atom which is shown in red here:
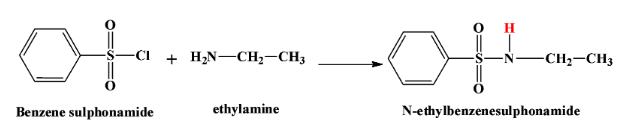
- When a secondary amine reacts with this reagent, there is no hydrogen atom left in the product which is $N,N-diethyl benzene sulphonamide$. Therefore the product is not soluble in alkali. The reaction is as below:
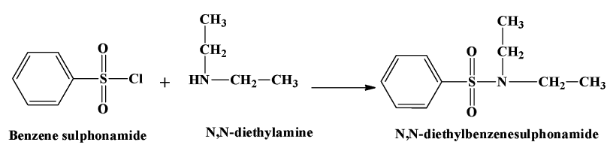
- Tertiary amines do not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride.
In this way we can separate or distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Note: In case of primary amines, when it is said that a product will dissolve in any solution, it just means that a reaction will take place and no precipitate will be left behind. If this is an acid-base reaction, as is the above case, we can get back the reactants if we want to. In this way we can separate our required compound from a mixture.
In case of secondary amines, the alkali cannot react with the product formed. This means there will be no reaction taking place when the alkali is added.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hinsberg’s reagent is used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Its chemical formula is benzene sulphonyl chloride (${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}S{{O}_{2}}Cl$). Its structure is as below:

The correct answer for the above question is option (A)${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}S{{O}_{2}}Cl$.
Additional information:
Let’s know more about the reactions using Hinsberg’s reagent that distinguish the amines of different degrees.
- When a primary amine says ethyl amine reacts with this reagent, we get $N-methylbenzenesulfonamide$. This product is soluble in alkali due to the highly acidic hydrogen atom which is shown in red here:

- When a secondary amine reacts with this reagent, there is no hydrogen atom left in the product which is $N,N-diethyl benzene sulphonamide$. Therefore the product is not soluble in alkali. The reaction is as below:

- Tertiary amines do not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride.
In this way we can separate or distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Note: In case of primary amines, when it is said that a product will dissolve in any solution, it just means that a reaction will take place and no precipitate will be left behind. If this is an acid-base reaction, as is the above case, we can get back the reactants if we want to. In this way we can separate our required compound from a mixture.
In case of secondary amines, the alkali cannot react with the product formed. This means there will be no reaction taking place when the alkali is added.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




