
Which of the following is used in the isomerization of alkanes:
A.\[Cu/{300^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}\]
B.$LiAl{H_4}$
C.${\text{Anhy}}{\text{. }}AlC{l_3}/HCl$
D.\[{V_2}{O_5}/{500^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}}\]
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question you should recall the concept of isomerism or isomerization of alkanes. Isomers refer to compounds with similar chemical formulas but a different arrangement of constituent atoms. It is formed in the presence of a Lewis acid.
Complete step by step solution:
Process of conversion of one isomer into another is called isomerisation, in this process \[AlC{l_3} + HCl\] is used as a catalyst under high temperature and pressure.
In isomerisation n-alkanes on heating in the presence of anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] and \[HCl\;\] gas isomerise to branched-chain alkanes. The mechanism of the above reaction has been represented below using an alkane. For simplicity let us take a molecule of butane:
Initiation: The Lewis acid, \[AlC{l_3}\] helps in stabilizing the chloride ion from \[HCl\] when hydrogen ion is used to protonate the butene. This results in the formation of a secondary carbocation which undergoes methyl shift to form a primary carbocation.
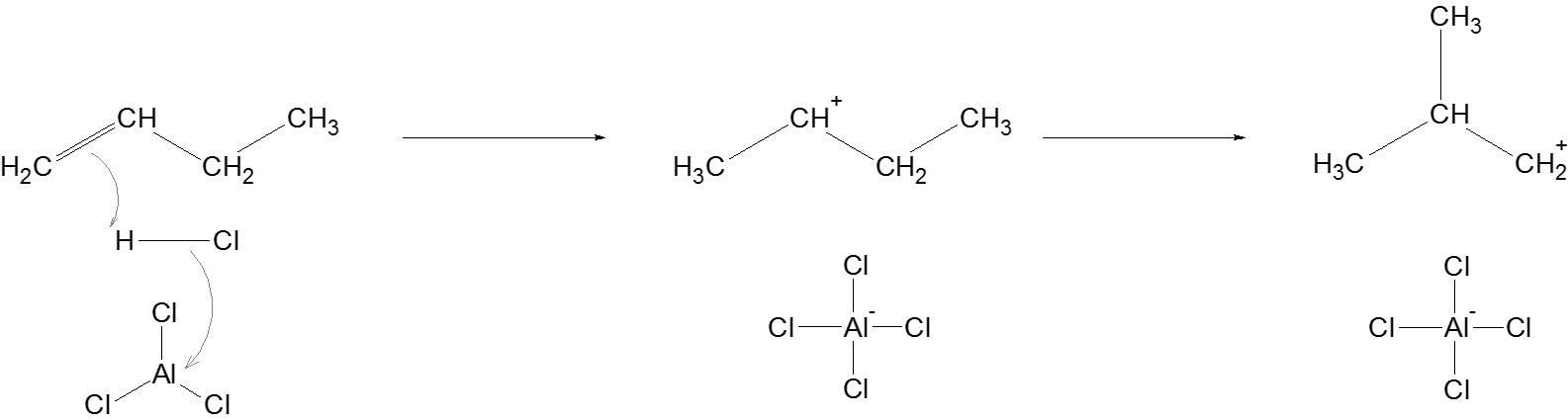
Propagation: Another alkane attacks the newly formed carbocation, and supplies a hydride ion to the carbocation to complete this reaction involving the carbocation. The same process is followed to generate another carbocation which regenerates a carbocation at the beginning of this step.
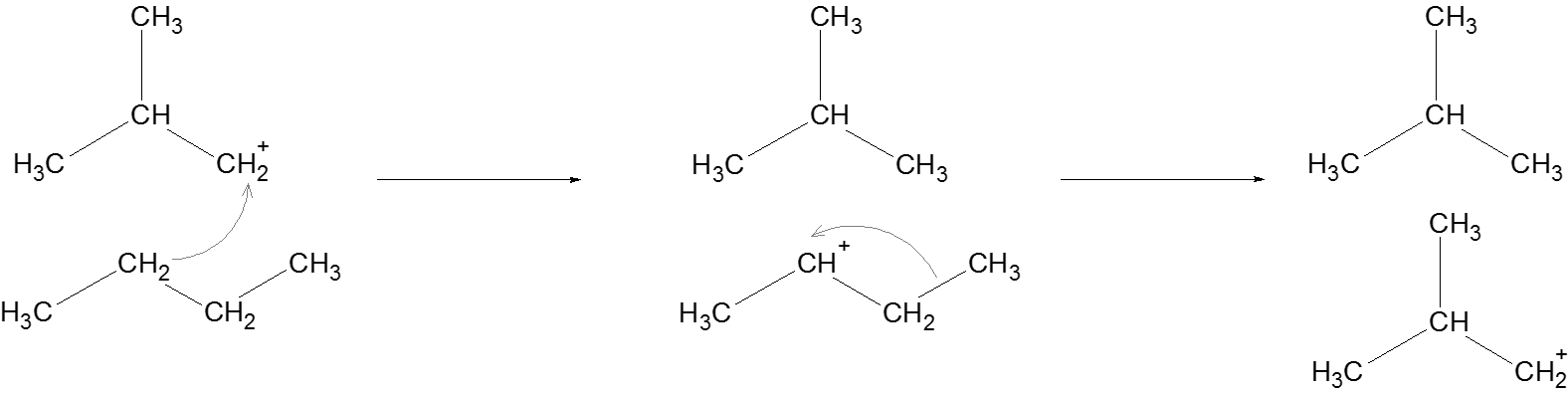
Termination
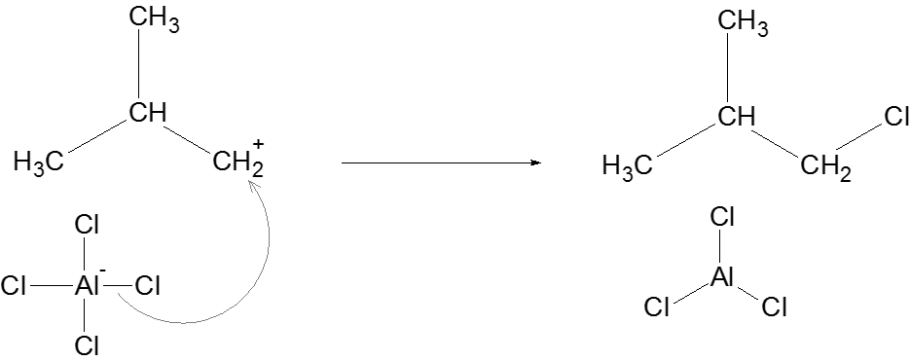
Thus, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note:
You should know about the isomerisation of an alkene. Terminal alkenes isomerize to internal alkenes in the presence of metal catalysts. An important process which involves this mechanism is Shell higher olefin process to convert alpha-olefins to internal olefins, which are subjected to olefin metathesis.
Complete step by step solution:
Process of conversion of one isomer into another is called isomerisation, in this process \[AlC{l_3} + HCl\] is used as a catalyst under high temperature and pressure.
In isomerisation n-alkanes on heating in the presence of anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] and \[HCl\;\] gas isomerise to branched-chain alkanes. The mechanism of the above reaction has been represented below using an alkane. For simplicity let us take a molecule of butane:
Initiation: The Lewis acid, \[AlC{l_3}\] helps in stabilizing the chloride ion from \[HCl\] when hydrogen ion is used to protonate the butene. This results in the formation of a secondary carbocation which undergoes methyl shift to form a primary carbocation.

Propagation: Another alkane attacks the newly formed carbocation, and supplies a hydride ion to the carbocation to complete this reaction involving the carbocation. The same process is followed to generate another carbocation which regenerates a carbocation at the beginning of this step.

Termination
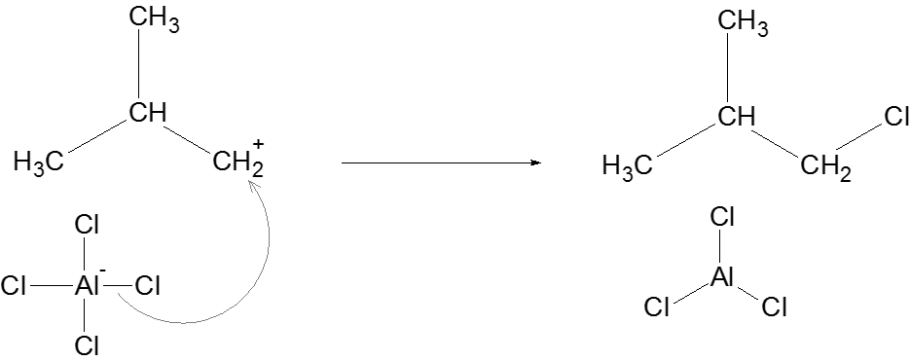
Thus, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note:
You should know about the isomerisation of an alkene. Terminal alkenes isomerize to internal alkenes in the presence of metal catalysts. An important process which involves this mechanism is Shell higher olefin process to convert alpha-olefins to internal olefins, which are subjected to olefin metathesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




