
Which of the following nitroso compounds are in a dynamic equilibrium with their tautomers?
(A)
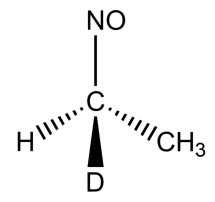
(B)
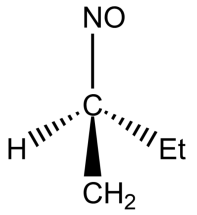
(C)
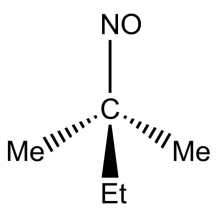
(D)
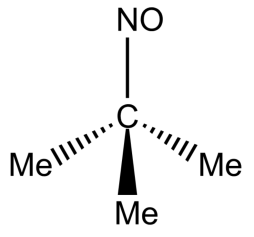




Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: The isomers of compounds which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons are known as tautomers. When a reaction between such compounds occurs, there is only a transfer of protons.
Complete Step by step answer:
-The phenomenon where a single chemical compound tends to exist in two or more interconvertible structures that are different in terms of the relative position of one atomic nucleus which is generally the hydrogen is known as tautomerism.
-Tautomerism is also known as desmotropism.
- For a compound to exhibit tautomerism, it must have the following structural requirements-
(i) the compound must have at least one alpha hydrogen
(ii) the compound must contain polar molecules and weakly acidic functional groups.
(iii) generally, tautomerism occurs in planar or non-planar molecules.
-Let us now see tautomerism in nitroso compounds.
The shifting of hydrogen produces two forms of tautomers of nitroso compounds, which are ketoxime and aldoxime.
$C{{H}_{3}}-N=O(Ketoxime)\leftrightarrow C{{H}_{2}}=N-OH(Aldoxime)$
-Let us now match with the options and find out which one does exhibit all the structural requirements to be in dynamic equilibrium with their tautomers-
-In option A, the compound has alpha hydrogen, thus it can exhibit tautomerism.
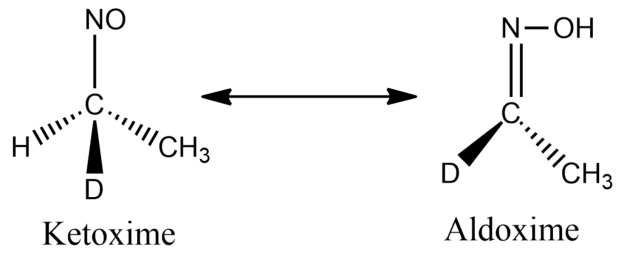
-In option B, the compound has alpha hydrogen, thus it can exhibit tautomerism.
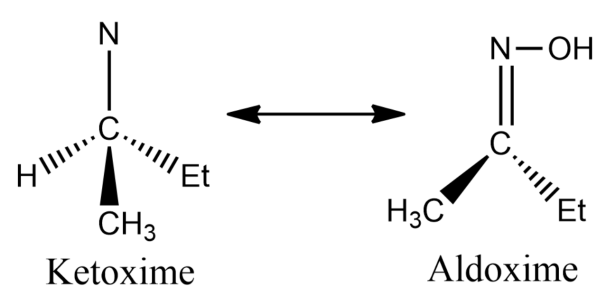
-In option C, the compound does not have alpha hydrogen, hence it will not exhibit tautomerism.
-In option D, the compound does not have alpha hydrogen, hence it will not exhibit tautomerism.
Therefore, the correct answers are options A and B.
Note: Tautomerism happens in the presence of a catalyst which can be either acid-catalyst or base catalyst. In presence of acid-catalyst, the protonation occurs and cation will be delocalized followed by deprotonation occurring in the adjacent position of the cation. In the presence of base-catalyst, the deprotonation occurs in the first step. In this case, anion delocalization occurs instead of cation delocalization and finally, protonation occurs to the different position of the anion.
Complete Step by step answer:
-The phenomenon where a single chemical compound tends to exist in two or more interconvertible structures that are different in terms of the relative position of one atomic nucleus which is generally the hydrogen is known as tautomerism.
-Tautomerism is also known as desmotropism.
- For a compound to exhibit tautomerism, it must have the following structural requirements-
(i) the compound must have at least one alpha hydrogen
(ii) the compound must contain polar molecules and weakly acidic functional groups.
(iii) generally, tautomerism occurs in planar or non-planar molecules.
-Let us now see tautomerism in nitroso compounds.
The shifting of hydrogen produces two forms of tautomers of nitroso compounds, which are ketoxime and aldoxime.
$C{{H}_{3}}-N=O(Ketoxime)\leftrightarrow C{{H}_{2}}=N-OH(Aldoxime)$
-Let us now match with the options and find out which one does exhibit all the structural requirements to be in dynamic equilibrium with their tautomers-
-In option A, the compound has alpha hydrogen, thus it can exhibit tautomerism.

-In option B, the compound has alpha hydrogen, thus it can exhibit tautomerism.

-In option C, the compound does not have alpha hydrogen, hence it will not exhibit tautomerism.
-In option D, the compound does not have alpha hydrogen, hence it will not exhibit tautomerism.
Therefore, the correct answers are options A and B.
Note: Tautomerism happens in the presence of a catalyst which can be either acid-catalyst or base catalyst. In presence of acid-catalyst, the protonation occurs and cation will be delocalized followed by deprotonation occurring in the adjacent position of the cation. In the presence of base-catalyst, the deprotonation occurs in the first step. In this case, anion delocalization occurs instead of cation delocalization and finally, protonation occurs to the different position of the anion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




