
Which of the following represents the C-4 epimer of L-glucose?
A.
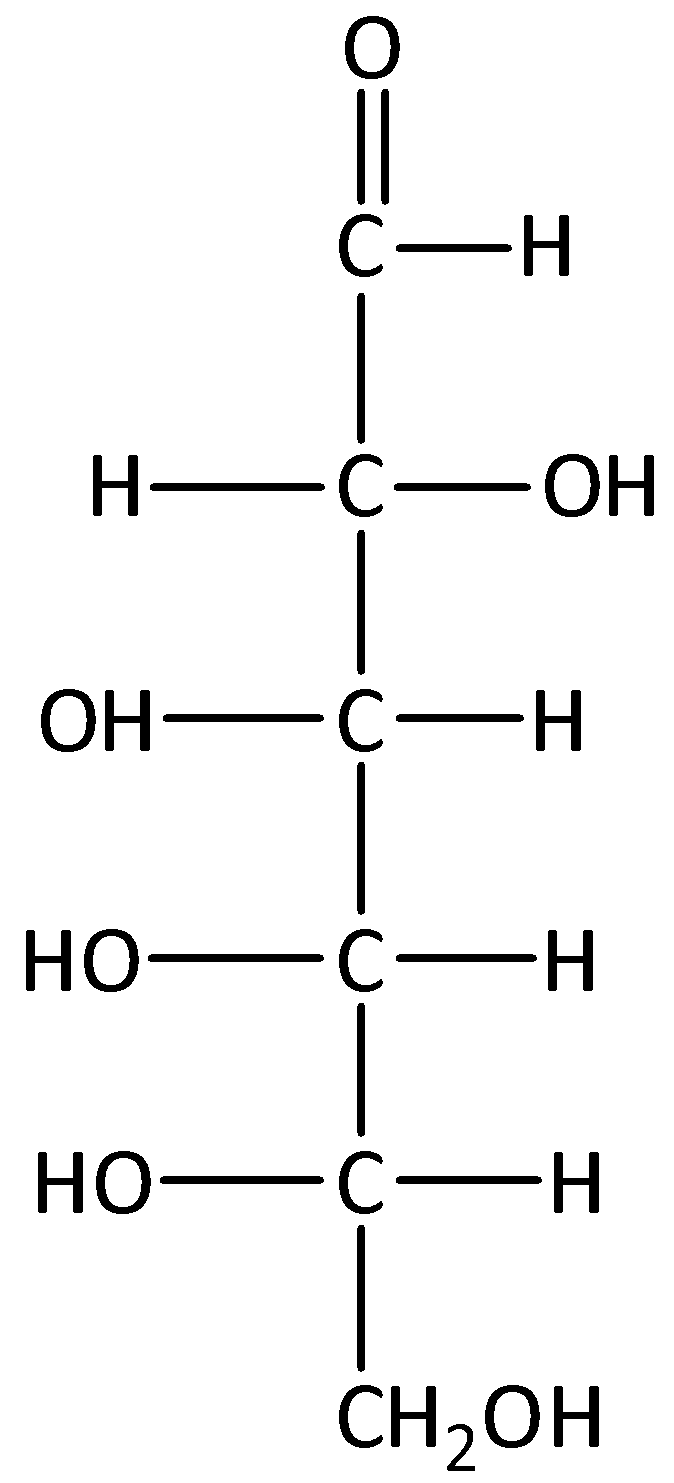
B.
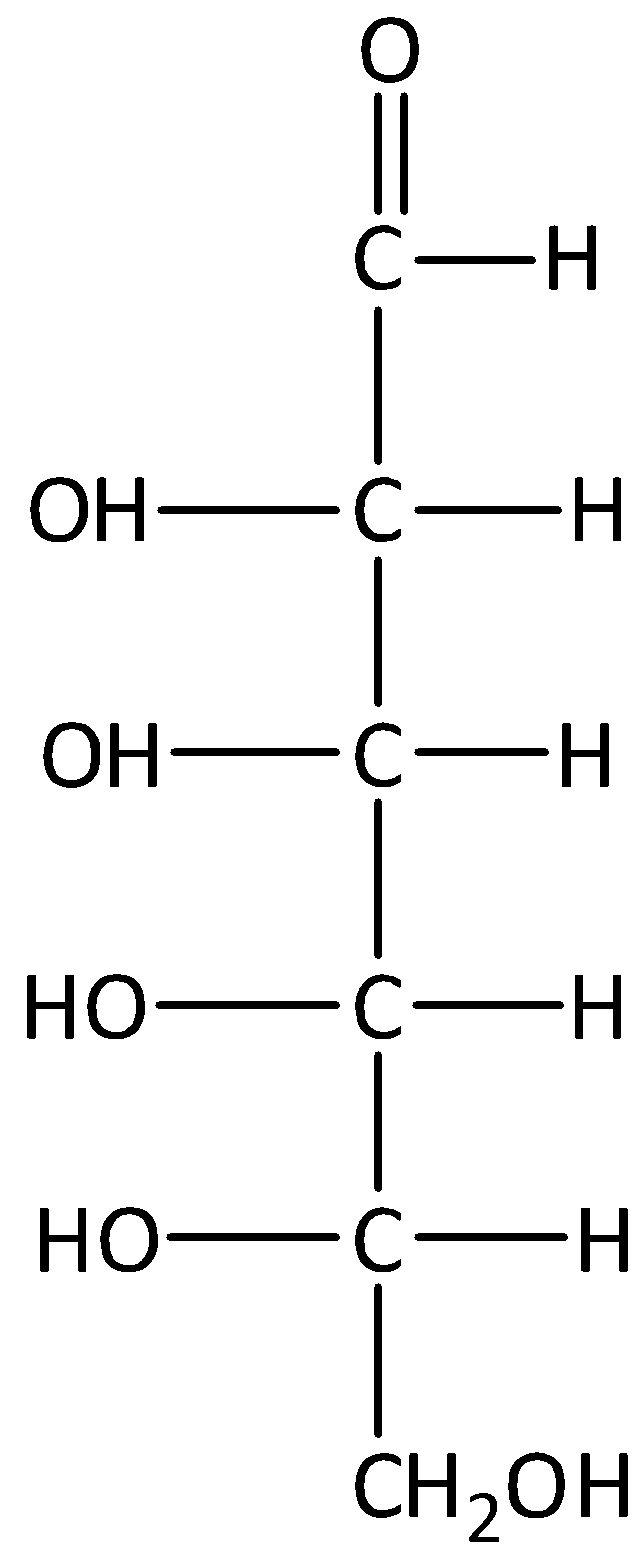
C.
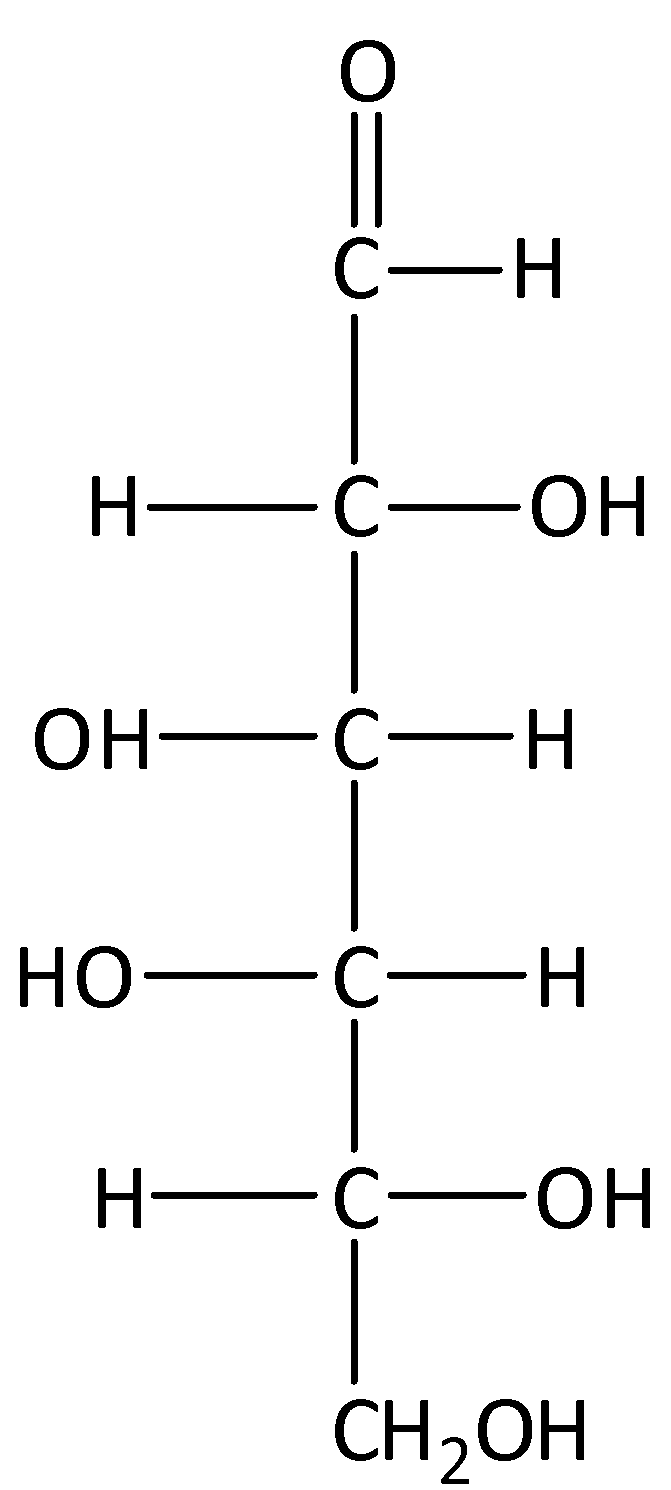
D.
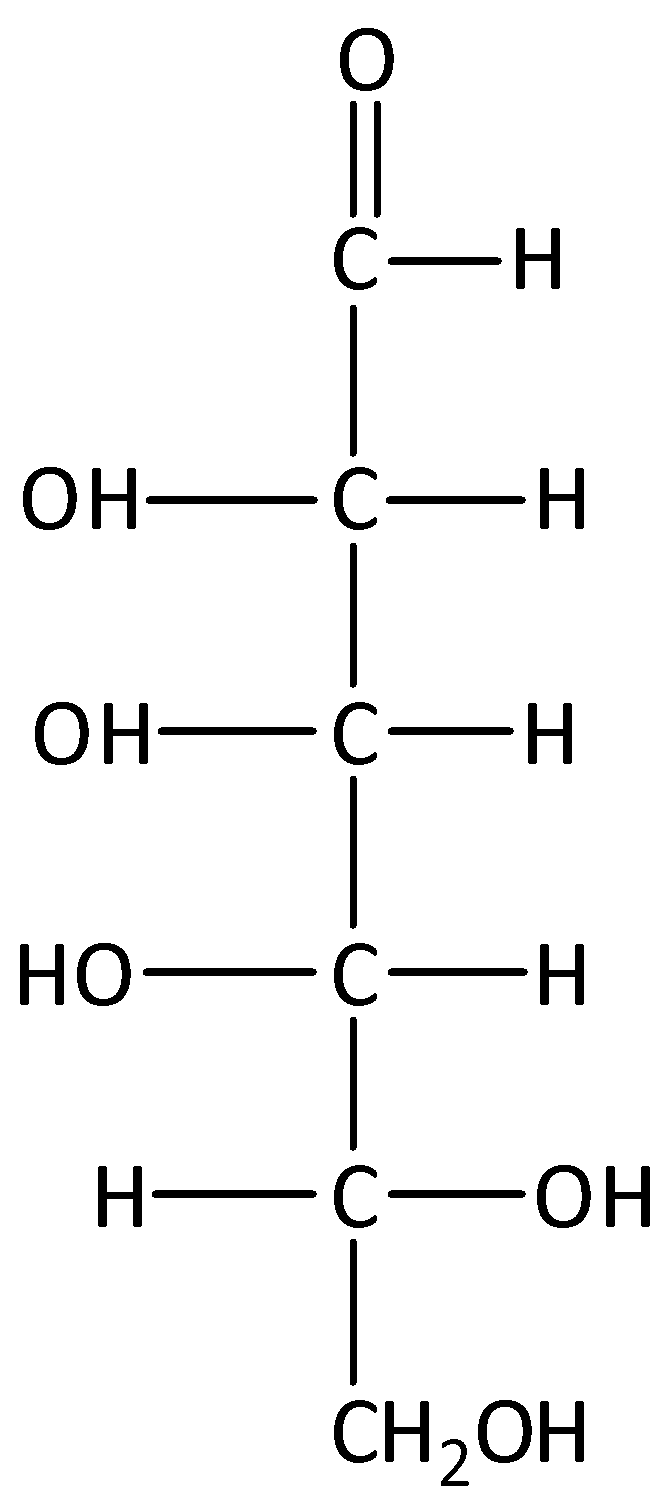




Answer
585k+ views
Hint:We have to know that in stereochemistry, an epimer is one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers contain opposite configurations at only one stereogenic center out of at least two. When the molecule contains only one stereocenter, the epimers are enantiomers. When the molecule contains two or more stereocenters, the epimers are diastereomers.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that glucose has D-form and L-form. The structures of D-form and L-form of glucose are,
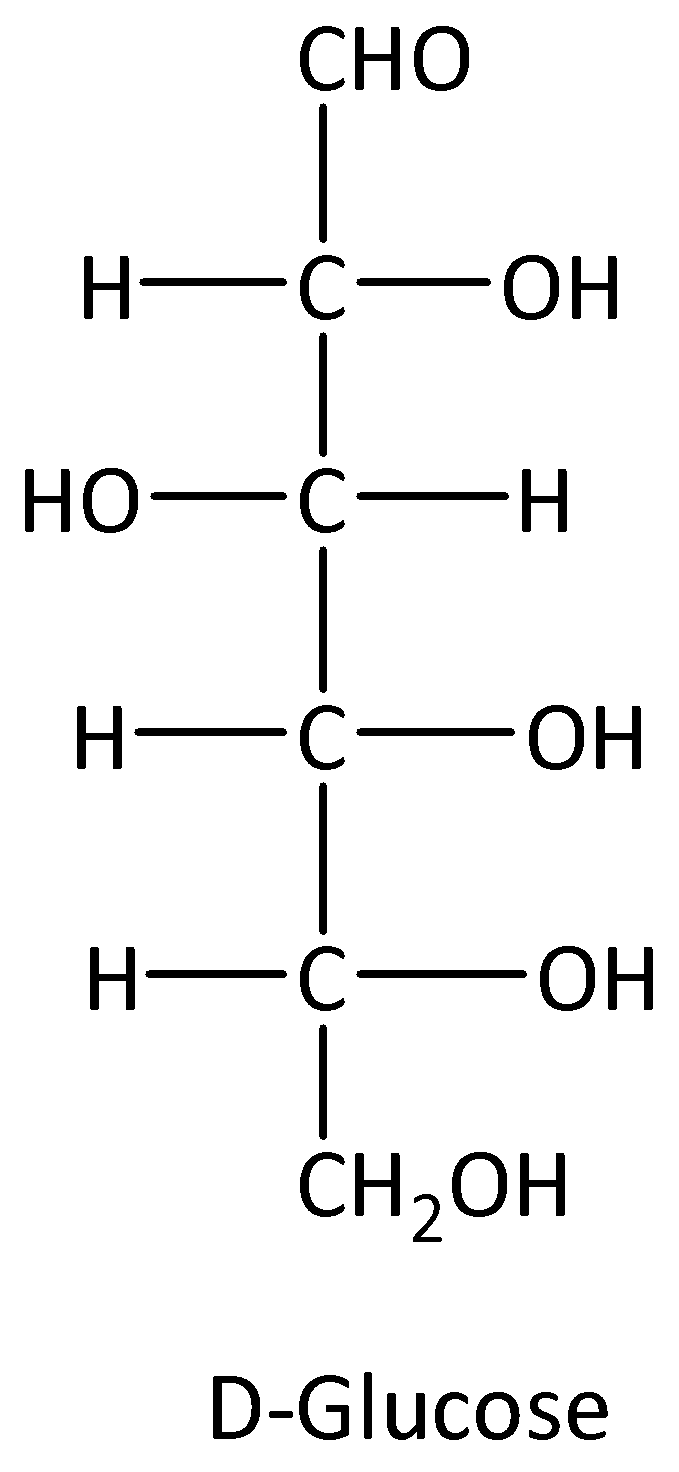
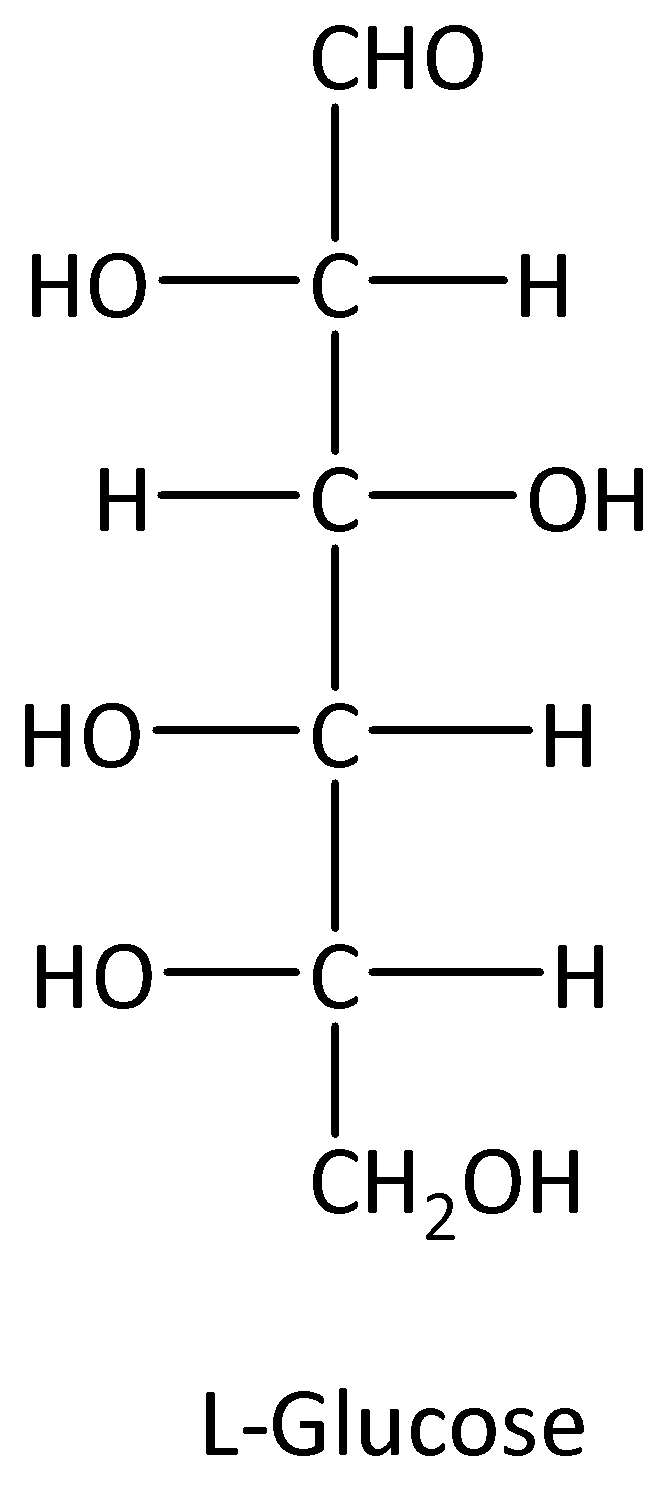
Glucose involves the formation of glycogen, starch, oligosaccharides, glucose, and polysaccharides. Because of the presence of carbon in glucose molecules it exhibits stereoisomerism, which is enantiomers and diastereomers.
Isomers that have various configurations of atoms about one of the several asymmetric carbon atoms present are called epimers. We can give structure of glucose and its C-4 epimer as,
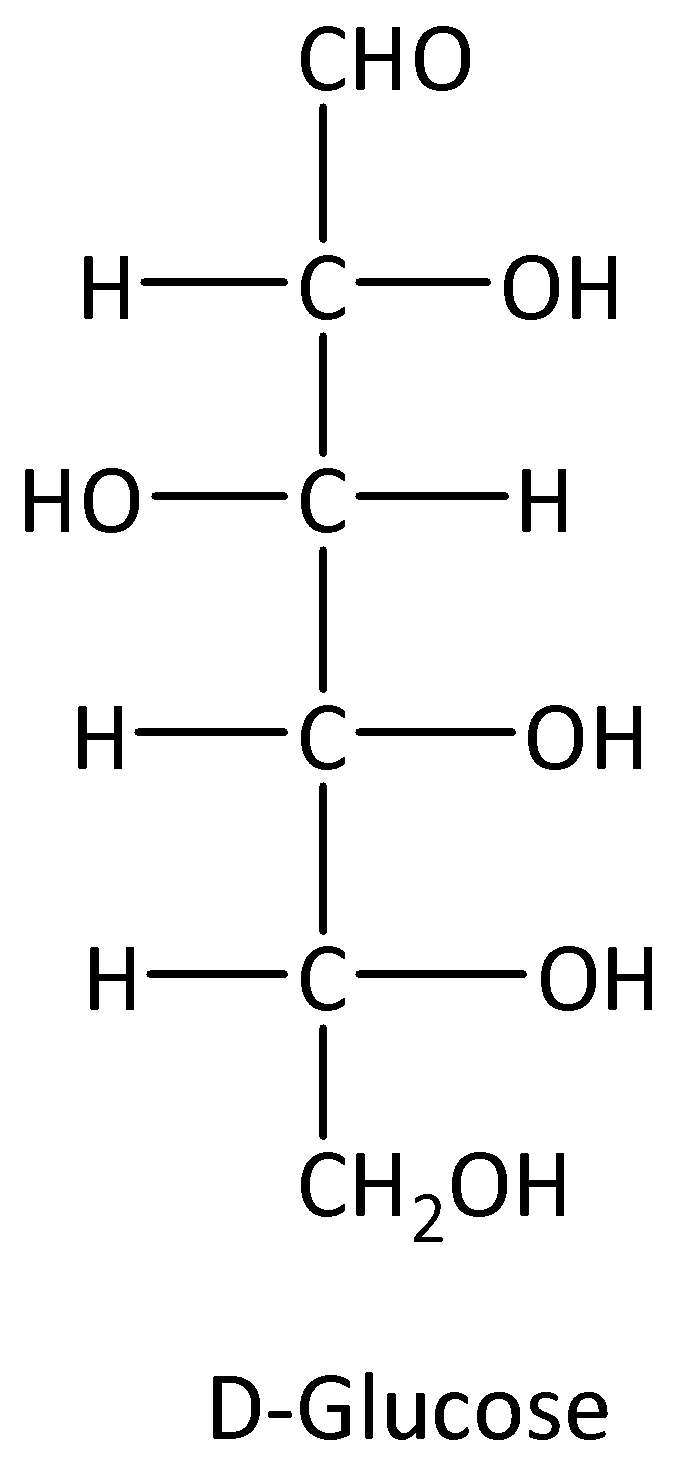
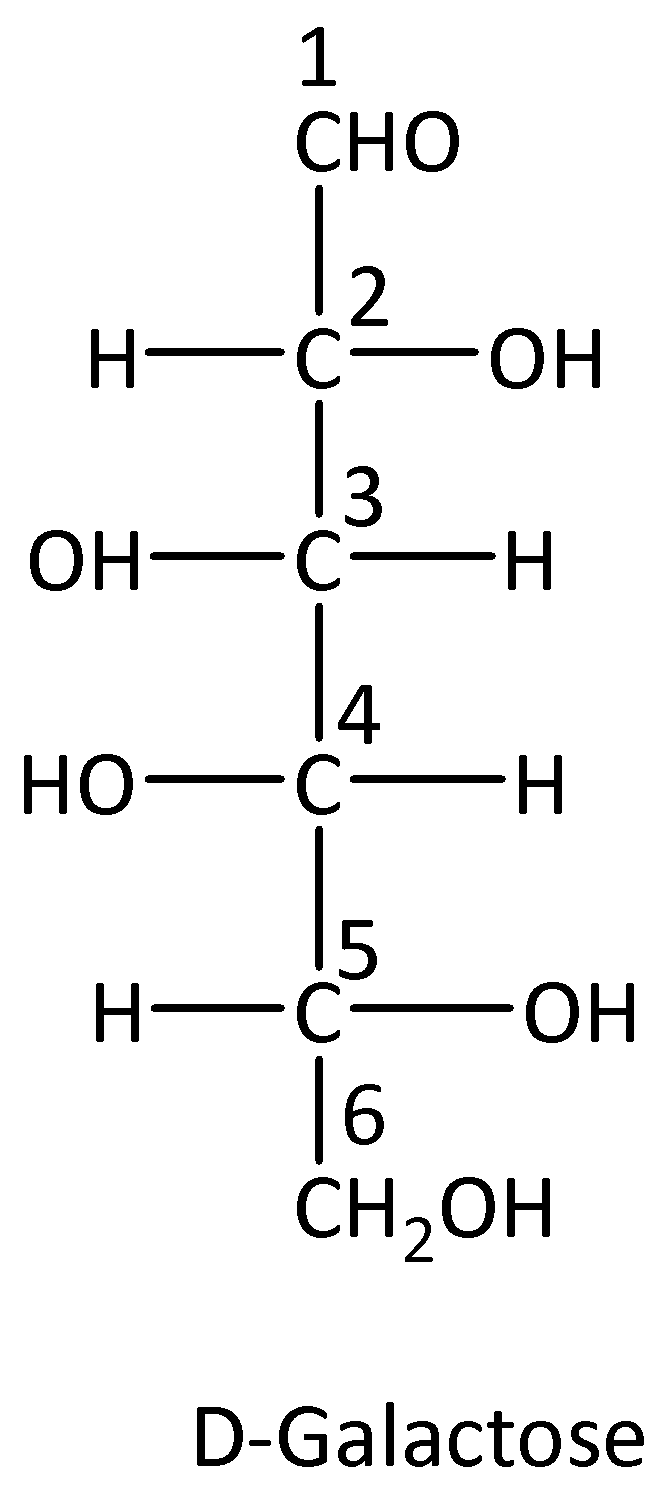
We have to know that D-Galactose is the epimer of Glucose at C-4 position. D-Mannose is the epimer of glucose at C-2 position.
D-Galactose is an epimer of glucose because the difference between the two sugars is the configuration at C-4 position.
Therefore, Option (C) is correct.
D-Mannose is an epimer of glucose because the difference between the two sugars is the configuration at C-2 position.
Note:
Epimerization is the interconversion of one epimer to the other epimer. In the process of epimerization we can convert an epimer into its chiral counterpart. It happens in condensed tannins depolymerisation reactions. Epimerization could be spontaneous or catalyzed by enzymes. Doxorubicin and epirubicin are two epimers which are used as drugs. An anomer is an epimer at the hemiacetal/hemiketal carbon in a cyclic saccharide and the atom is called the anomeric carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that glucose has D-form and L-form. The structures of D-form and L-form of glucose are,


Glucose involves the formation of glycogen, starch, oligosaccharides, glucose, and polysaccharides. Because of the presence of carbon in glucose molecules it exhibits stereoisomerism, which is enantiomers and diastereomers.
Isomers that have various configurations of atoms about one of the several asymmetric carbon atoms present are called epimers. We can give structure of glucose and its C-4 epimer as,


We have to know that D-Galactose is the epimer of Glucose at C-4 position. D-Mannose is the epimer of glucose at C-2 position.
D-Galactose is an epimer of glucose because the difference between the two sugars is the configuration at C-4 position.
Therefore, Option (C) is correct.
D-Mannose is an epimer of glucose because the difference between the two sugars is the configuration at C-2 position.
Note:
Epimerization is the interconversion of one epimer to the other epimer. In the process of epimerization we can convert an epimer into its chiral counterpart. It happens in condensed tannins depolymerisation reactions. Epimerization could be spontaneous or catalyzed by enzymes. Doxorubicin and epirubicin are two epimers which are used as drugs. An anomer is an epimer at the hemiacetal/hemiketal carbon in a cyclic saccharide and the atom is called the anomeric carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




