
Which of the following will give Walden inversion?
A.

B.
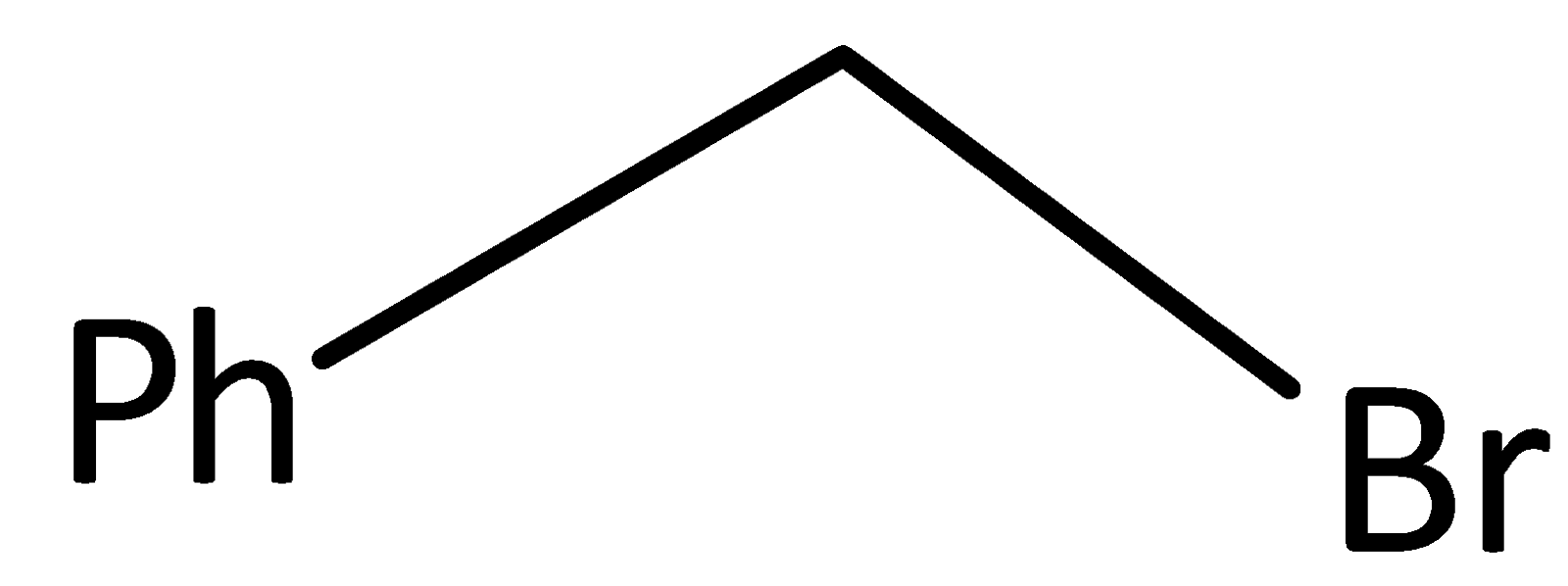
C.
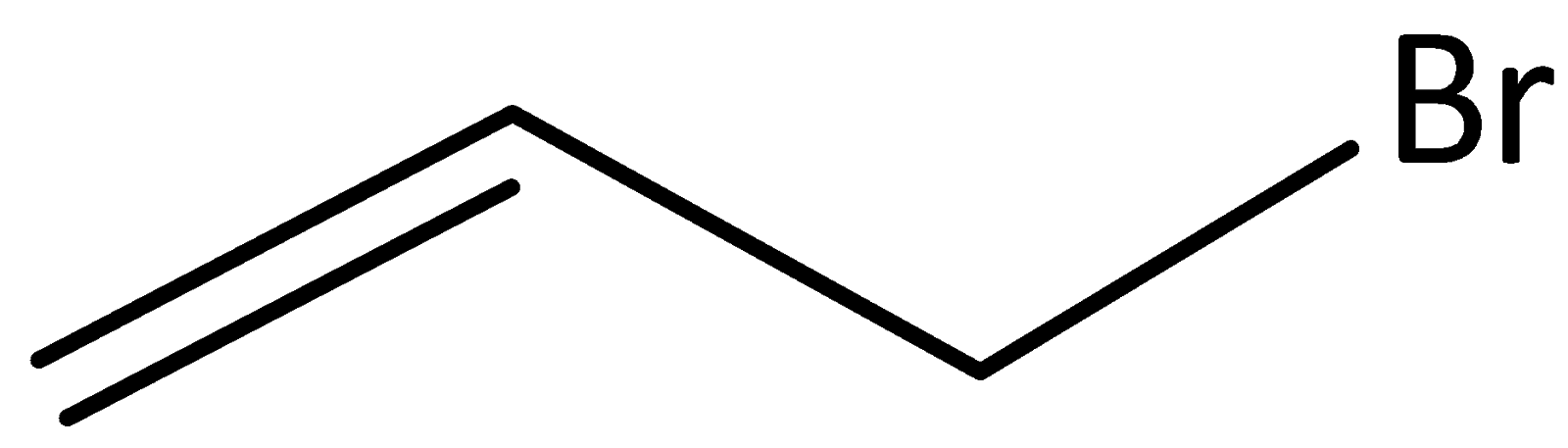
D. All



Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: We know that the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a chemical reaction is called Walden inversion. A molecule will form two enantiomers around a chiral center; the Walden inversion converts the configuration of the molecule from one enantiomeric form to the opposite.
Complete step by step answer: Walden inversion:
Inversion of the configuration of one optically active compound into another may or may not lead to a change in the direction of optical rotation and that may be of either of two general types. In $S{N_2}$ reaction, Walden inversion occurs at a tetrahedral carbon atom.
From the above given option, option A is optically active because it has chiral carbon, and will have Walden inversion.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: We see what is chirality and enantiomer.
- Chirality:
A molecule or ion is called chiral only when there is no superimposable mirror image and there is no plane of symmetry in the molecule. This property is known as chirality.
- Conditions for optical activity:
The molecule should posse's asymmetric central atom (chiral atom).
There should be no plane of symmetry or axis.
The molecule should have a non-superimposable mirror image.
- Enantiomers:
The compounds which are mirror images but are not identical; to each other are called enantiomers.
Note: We must remember that if the molecular composition is preserved during the reaction then it is referred to as retention of configuration. Inversion means the mechanism in which the structure of the molecules is changed during the reaction. The result is thus of the opposite enantiomeric form relative to the reactant.
Complete step by step answer: Walden inversion:
Inversion of the configuration of one optically active compound into another may or may not lead to a change in the direction of optical rotation and that may be of either of two general types. In $S{N_2}$ reaction, Walden inversion occurs at a tetrahedral carbon atom.
From the above given option, option A is optically active because it has chiral carbon, and will have Walden inversion.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information: We see what is chirality and enantiomer.
- Chirality:
A molecule or ion is called chiral only when there is no superimposable mirror image and there is no plane of symmetry in the molecule. This property is known as chirality.
- Conditions for optical activity:
The molecule should posse's asymmetric central atom (chiral atom).
There should be no plane of symmetry or axis.
The molecule should have a non-superimposable mirror image.
- Enantiomers:
The compounds which are mirror images but are not identical; to each other are called enantiomers.
Note: We must remember that if the molecular composition is preserved during the reaction then it is referred to as retention of configuration. Inversion means the mechanism in which the structure of the molecules is changed during the reaction. The result is thus of the opposite enantiomeric form relative to the reactant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




