
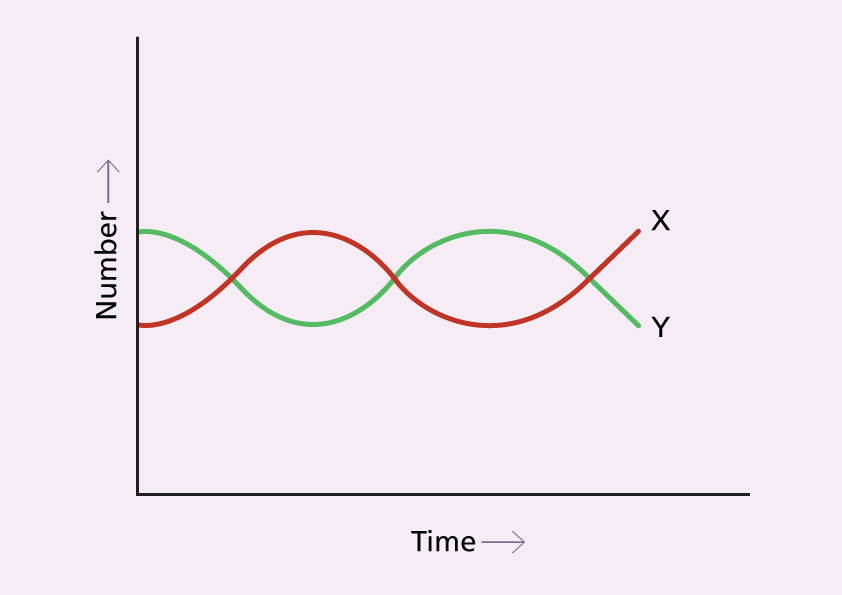
Which of the interaction shows in this graph between two organisms X and Y
(a) Mutualism
(b) Commensalism
(c) Parasitism
(d) Predation

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: The interspecific interaction where only one species is benefitted and another species is harmed. It helps in maintaining species diversity and also acts as a biological agent.
Complete answer:
Interaction of populations of two different species is called inter-specific Interaction. Predation is a type of interspecific Interaction. They act as a biological control agent, maintain species diversity, predators are prudent pertaining to prey.
In the graph, X and Y are predators and prey respectively. This representation is given by the lotka-Volterra equation that describes the Interaction specific Interaction i.e, predation
Additional information:
- Interspecific Interaction is grouped into six types namely Mutualism, competition, predation, commensalism, and amensalism.
- In predation, predators besides acting as conduits for energy transfers across their trophic levels, keep the prey population under control.
- Biological methods are adopted in pest control methods in agriculture are based on the ability of predators to regulate prey population
- They maintain species diversity by reducing the intensity of competition between the prey population.
- If the predator is too efficient and over exploits its prey, extinction of the prey population and gradually the extinction of the predator population due to lack of food is observed.
- Preys, to protect themselves from predators, evolved several defenses such as preys fool, preys defend by becoming distasteful to predators to lessen the impact of predators.
So, the correct answer is 'predation'
Note: In Mutualism both the organisms get benefitted, in competition, either of the species won't get benefitted, in predation and parasitism any one of the species is benefitted, in commensalism, one species is benefitted and another is neither benefited or harmed, in amensalism one species is harmed and another is neither benefited or harmed.
Complete answer:
Interaction of populations of two different species is called inter-specific Interaction. Predation is a type of interspecific Interaction. They act as a biological control agent, maintain species diversity, predators are prudent pertaining to prey.
In the graph, X and Y are predators and prey respectively. This representation is given by the lotka-Volterra equation that describes the Interaction specific Interaction i.e, predation
Additional information:
- Interspecific Interaction is grouped into six types namely Mutualism, competition, predation, commensalism, and amensalism.
- In predation, predators besides acting as conduits for energy transfers across their trophic levels, keep the prey population under control.
- Biological methods are adopted in pest control methods in agriculture are based on the ability of predators to regulate prey population
- They maintain species diversity by reducing the intensity of competition between the prey population.
- If the predator is too efficient and over exploits its prey, extinction of the prey population and gradually the extinction of the predator population due to lack of food is observed.
- Preys, to protect themselves from predators, evolved several defenses such as preys fool, preys defend by becoming distasteful to predators to lessen the impact of predators.
So, the correct answer is 'predation'
Note: In Mutualism both the organisms get benefitted, in competition, either of the species won't get benefitted, in predation and parasitism any one of the species is benefitted, in commensalism, one species is benefitted and another is neither benefited or harmed, in amensalism one species is harmed and another is neither benefited or harmed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




