
Which one is the largest unicellular organism?
a. Planaria
b. Volvox
c. Blue green algae
d. Yeast
e. Acetabularia
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Out of planaria, Volvox, blue green algae, yeast and Acetabularia, Acetabularia is the largest among all of these and has complex form, which makes it a good model organism to study cell biology.
Complete answer:
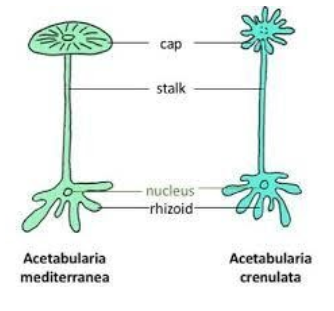
> Acetabularia: It is one of the genuses of organisms belonging to green algae that are found in subtropical waters. These are single celled organisms with large size and complex structure. This unicellular organism reaches the amazing size of 3–5 cm.
> Planaria:It is a multicellular organism which possesses a high regenerative capacity. To our surprise, these organisms can reproduce sexually as well as asexually.
> Volvox: it belongs to the group of algae that form the border between multicellular and colonial organisms. These organisms survive in colonies. Their colony consists of several photosynthetic volvox units(upto 1000-3000 units)which are grouped together in a hollow sphere.Thus,on a broad view these are considered to be multicellular.
> Blue green algae: The blue green algae or commonly called cyanobacteria are bacterias. They are aquatic and photosynthetic.These are generally unicellular but some of these exist in colonies.
> Yeast: Yeasts are eukaryotic fungi which are classified as members of the kingdom fungi. These are unicellular in nature. But their size varies greatly, depending on species and environment, these can go from measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size.
From above information we shall conclude that the largest unicellular living being is Acetabularia.
Additional information:
During the phase of sexual reproduction, its nucleus undergoes numerous mitotic divisions forming many daughter nuclei all in one nuclear membrane. These nuclei undergo meiosis and are transported to sporangia, from where they are released as gametes.
Note: Acetabularia has three basic parts: rhizoids, median stalk and its apex. Rhizoids are the short root-like appendages that contain the nucleus and anchor the cell to the substrate. The median stalk accounts for most of the length and its apex is the place where cap-like structure is formed.
Complete answer:
> Acetabularia: It is one of the genuses of organisms belonging to green algae that are found in subtropical waters. These are single celled organisms with large size and complex structure. This unicellular organism reaches the amazing size of 3–5 cm.

> Planaria:It is a multicellular organism which possesses a high regenerative capacity. To our surprise, these organisms can reproduce sexually as well as asexually.
> Volvox: it belongs to the group of algae that form the border between multicellular and colonial organisms. These organisms survive in colonies. Their colony consists of several photosynthetic volvox units(upto 1000-3000 units)which are grouped together in a hollow sphere.Thus,on a broad view these are considered to be multicellular.
> Blue green algae: The blue green algae or commonly called cyanobacteria are bacterias. They are aquatic and photosynthetic.These are generally unicellular but some of these exist in colonies.
> Yeast: Yeasts are eukaryotic fungi which are classified as members of the kingdom fungi. These are unicellular in nature. But their size varies greatly, depending on species and environment, these can go from measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size.
From above information we shall conclude that the largest unicellular living being is Acetabularia.
Additional information:
During the phase of sexual reproduction, its nucleus undergoes numerous mitotic divisions forming many daughter nuclei all in one nuclear membrane. These nuclei undergo meiosis and are transported to sporangia, from where they are released as gametes.
Note: Acetabularia has three basic parts: rhizoids, median stalk and its apex. Rhizoids are the short root-like appendages that contain the nucleus and anchor the cell to the substrate. The median stalk accounts for most of the length and its apex is the place where cap-like structure is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




