
Which one of the following can be considered as an example of a secondary consumer?
(a) A fish that feeds on algae
(b) A hawk that feeds on a mouse that feeds on an insect
(c) A plant that is parasitic to another plant
(d) A lion that eats a gazelle that feeds on grass
(e) A beetle that feeds on nectar
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Organisms have a place in the environment or community that they live in depending upon their feeding relationship with other organisms. Based on the source of nutrition, the position or place occupied by an organism is known as their trophic level.
Complete Answer:
The organism that produces its own food through the process of photosynthesis is known as producers such as plants. The organisms that feed on these producers are known as primary consumers such as herbivores. Organisms that feed on herbivores are known as secondary consumers such as carnivores.
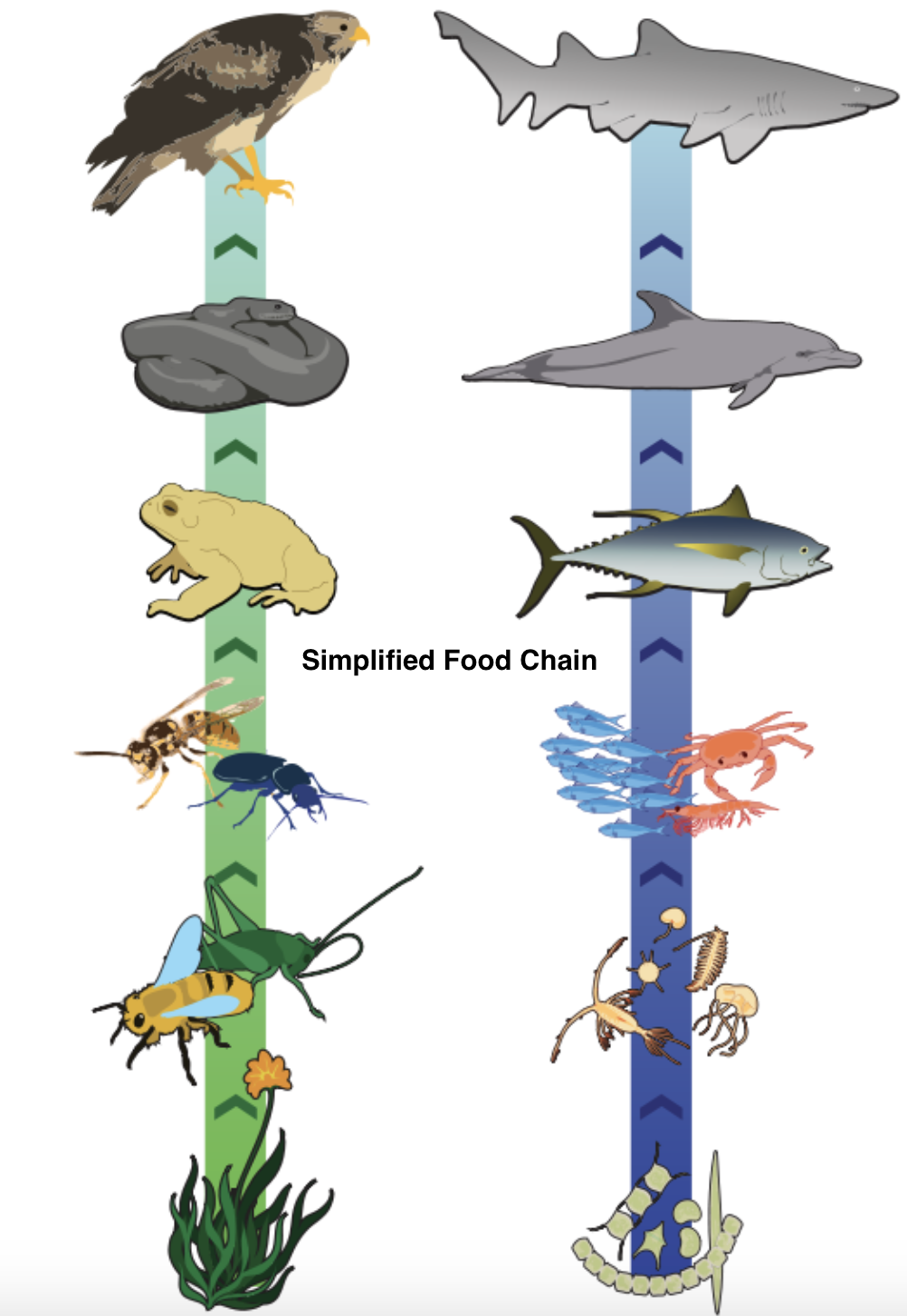
The producers are placed in the first trophic level, primary consumers in the second trophic level, and secondary consumers in the third trophic level. The grass is the producer and gazelle feeds on it thus it is the primary consumer. A lion feeds on this primary consumer hence it is an example of a secondary consumer.
Additional information: In a terrestrial ecosystem, energy flow occurs among organisms in a food chain known as the grazing food chain (GFC). An example of a grazing food chain consists of Grass (Producer), goat (Primary Consumer), and man (Secondary consumer).
A detritus food chain (DFC) consists of decomposers and saprophytes and begins with dead organic matter. Decomposers derive their energy from dead and decaying matter by releasing enzymes that cause their breakdown into simple, inorganic materials which are then absorbed by these organisms.
In an ecosystem detritus, food chains overlap with the grazing food chain as decomposers feed on any trophic level organisms if it is dead and decaying.
Since in an ecosystem there are many food chains running parallely and overlapping over each other, such a relationship is known as the food web.
So, the correct option is ‘(d) A lion that eats a gazelle that feeds on grass’.
Note: There is a unidirectional flow of energy from one trophic level to the next trophic level until all energy is lost to the surroundings. Only $10\%$ of the energy of an organism in a trophic level is passed on to the next trophic level. Sun is the source for all ecosystems except deep-sea hydrothermal ecosystems.
Complete Answer:
The organism that produces its own food through the process of photosynthesis is known as producers such as plants. The organisms that feed on these producers are known as primary consumers such as herbivores. Organisms that feed on herbivores are known as secondary consumers such as carnivores.

The producers are placed in the first trophic level, primary consumers in the second trophic level, and secondary consumers in the third trophic level. The grass is the producer and gazelle feeds on it thus it is the primary consumer. A lion feeds on this primary consumer hence it is an example of a secondary consumer.
Additional information: In a terrestrial ecosystem, energy flow occurs among organisms in a food chain known as the grazing food chain (GFC). An example of a grazing food chain consists of Grass (Producer), goat (Primary Consumer), and man (Secondary consumer).
A detritus food chain (DFC) consists of decomposers and saprophytes and begins with dead organic matter. Decomposers derive their energy from dead and decaying matter by releasing enzymes that cause their breakdown into simple, inorganic materials which are then absorbed by these organisms.
In an ecosystem detritus, food chains overlap with the grazing food chain as decomposers feed on any trophic level organisms if it is dead and decaying.
Since in an ecosystem there are many food chains running parallely and overlapping over each other, such a relationship is known as the food web.
So, the correct option is ‘(d) A lion that eats a gazelle that feeds on grass’.
Note: There is a unidirectional flow of energy from one trophic level to the next trophic level until all energy is lost to the surroundings. Only $10\%$ of the energy of an organism in a trophic level is passed on to the next trophic level. Sun is the source for all ecosystems except deep-sea hydrothermal ecosystems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




