
Which one of the following halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism?
(A) Tertiary butyl chloride
(B) Isopropyl chloride
(C) Benzyl Chloride
(D) Chlorobenzene
(E) Allyl chloride
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: For determining which of this halogen compound is difficult to be hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism we need to find out in which of them halogen atom is firmly attached and cannot be replaced by nucleophile $O{{H}^ {-}} $ easily.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been provided with halogen compounds Tertiary butyl chloride, Isopropyl chloride, Benzyl Chloride, Chlorobenzene and Allyl chloride.
We need to find out which of the halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
So, for that:
First, we have tertiary butyl chloride:
So, tertiary butyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Next, we have, isopropyl chloride:
Isopropyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Next, is benzyl chloride:
Benzyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Next, we have, chlorobenzene:
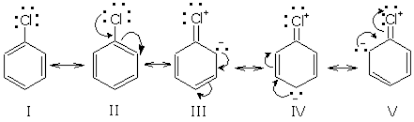
Chlorobenzene is quite stable due to the delocalization of electrons by resonance. Also, (C-Cl) bonds possess a double bond character due to which it is very difficult to hydrolyze by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Last one is Allyl chloride:
Allyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism. So, we can say that chlorobenzene is very difficult to hydrolyze by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Therefore, we can conclude that option (D) is correct.
Note: The stability of resonance increases with the number of covalent bonds. Number of atoms with an octet of electrons. A negative charge if any on a more electronegative atom, a positive charge if any on the more electropositive atom, increases the stability of the atom.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been provided with halogen compounds Tertiary butyl chloride, Isopropyl chloride, Benzyl Chloride, Chlorobenzene and Allyl chloride.
We need to find out which of the halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
So, for that:
First, we have tertiary butyl chloride:
So, tertiary butyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Next, we have, isopropyl chloride:
Isopropyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Next, is benzyl chloride:
Benzyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Next, we have, chlorobenzene:

Chlorobenzene is quite stable due to the delocalization of electrons by resonance. Also, (C-Cl) bonds possess a double bond character due to which it is very difficult to hydrolyze by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Last one is Allyl chloride:
Allyl chloride is unstable and can easily be hydrolyzed or hydrated by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism. So, we can say that chlorobenzene is very difficult to hydrolyze by ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Therefore, we can conclude that option (D) is correct.
Note: The stability of resonance increases with the number of covalent bonds. Number of atoms with an octet of electrons. A negative charge if any on a more electronegative atom, a positive charge if any on the more electropositive atom, increases the stability of the atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




