
Which one of the following is a lyophilic colloidal solution
A. Smoke
B. Gold sol
C. Starch aqueous solution
D. Cloud
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we should be having a basic idea about the lyophilic colloidal solutions. The characteristics of the options that are provided, should also be known.
Complete answer:
Lyophilic colloids are ‘liquid loving’ colloids. When these colloids are mixed with the suitable liquid, a high force of attraction exists between colloidal particles and liquid. This results in the formation of a very stable solution causing a lyophilic solution.
Starch is an example of lyophilic colloid solution.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
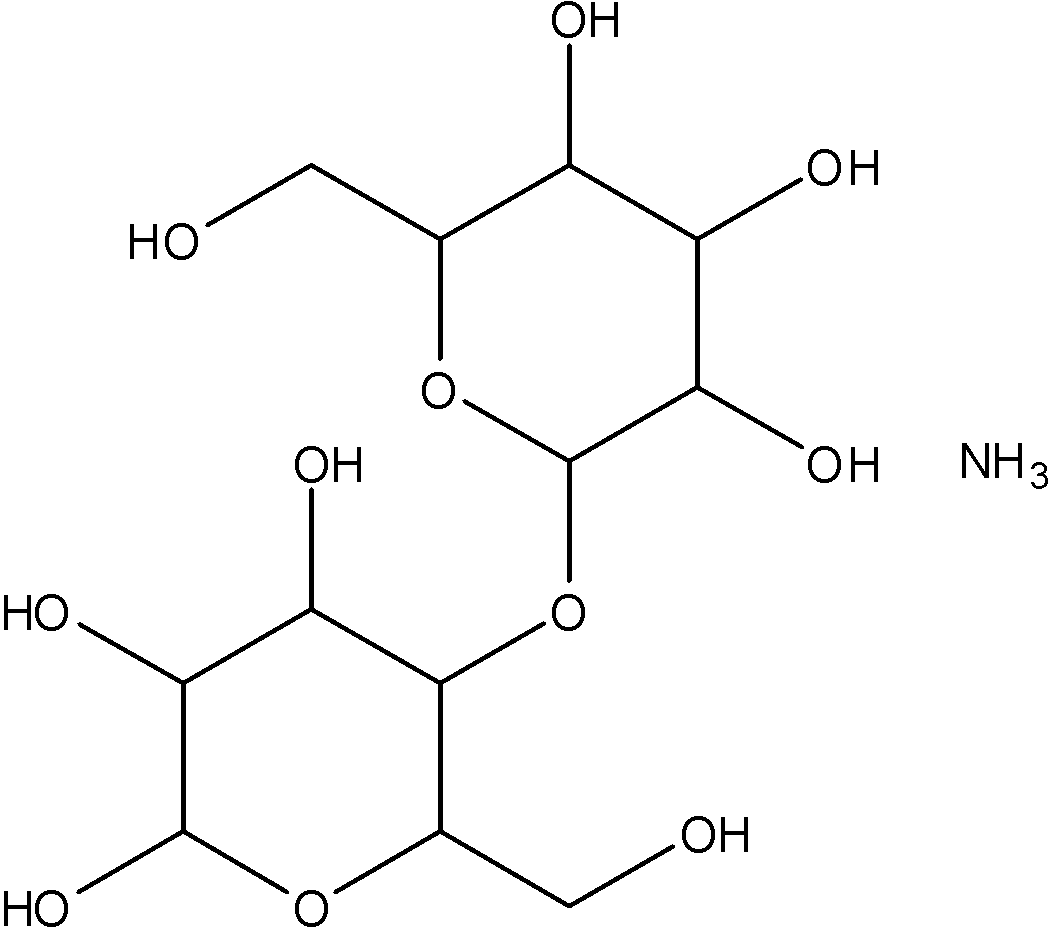
Starch becomes soluble in water when heated. The granules swell and burst and the semi crystalline structure is lost and smaller amylose molecules start leaching out of the granule forming a network that holds water and increases the mixture's viscosity. This process is called starch gelatinization.
Pure starch is a white tasteless and odourless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules which are the linear and helical amylose and the branch amylopectin.
Due to the fact that starch is a polysaccharide, a long chain compound consisting of glucose monomers it has poor solubility in most solvents. Some starches are water soluble because of the hydroxyl groups involved in the polysaccharide chain, some like the branched form amylopectin are more insoluble.
Note: Lyophilic sols are defined as liquid loving solutions. Smoke is a gas and even if it is mixed with water, it forms a suspension, so this cannot be the answer. In a gold sol, gold is insoluble in water and hence, it cannot form a colloidal liquid. Clouds are clumps of water vapour that are bound together due to hydrogen bonding, they cannot be sols as they themselves are water.
Complete answer:
Lyophilic colloids are ‘liquid loving’ colloids. When these colloids are mixed with the suitable liquid, a high force of attraction exists between colloidal particles and liquid. This results in the formation of a very stable solution causing a lyophilic solution.
Starch is an example of lyophilic colloid solution.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.

Starch becomes soluble in water when heated. The granules swell and burst and the semi crystalline structure is lost and smaller amylose molecules start leaching out of the granule forming a network that holds water and increases the mixture's viscosity. This process is called starch gelatinization.
Pure starch is a white tasteless and odourless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules which are the linear and helical amylose and the branch amylopectin.
Due to the fact that starch is a polysaccharide, a long chain compound consisting of glucose monomers it has poor solubility in most solvents. Some starches are water soluble because of the hydroxyl groups involved in the polysaccharide chain, some like the branched form amylopectin are more insoluble.
Note: Lyophilic sols are defined as liquid loving solutions. Smoke is a gas and even if it is mixed with water, it forms a suspension, so this cannot be the answer. In a gold sol, gold is insoluble in water and hence, it cannot form a colloidal liquid. Clouds are clumps of water vapour that are bound together due to hydrogen bonding, they cannot be sols as they themselves are water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




