
which one of the following is a restriction site for restriction enzyme Bam HI
A) 5'-GAATTC-3'3'-CTTAAG-5'
B) 5'-GGATCC-3'5'-CCATGG-3'
C) 5'-GGATCC-3'3'-CCTAGG-5'
D) 5'-GAATTC-3'5'-GTTAAC-3'
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: BamHI is derived from bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain H. Here at a target site cleavage occurs at the short sequence of DNA that is up to 6 base pairs and is a type II restriction endonuclease.
Complete step by step answer:
The restriction enzyme is BamHI. A restriction enzyme is a protein that recognizes a short nucleotide sequence that cuts the DNA at a specific site. The specific site is also known as a restriction site or target sequence.
- BamHI recognizes sequence 5'-G/GATCC-3' and cleaves between the two G's( shown by ' /' in sequence) just after the 5'guanine on each strand.
- This cleave will result in a 4 base pair with a long sticky end.
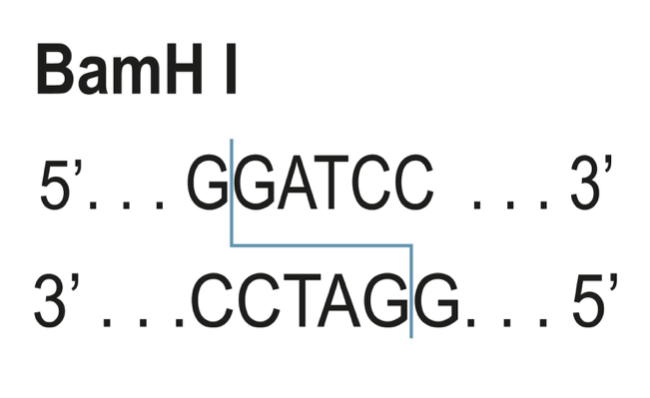
So, the correct answer is, "5'-GGATCC-3'3'-CCTAGG-5'".
Additional information: BamHI belongs to type II enzymes. Class II enzymes are an important class of restriction enzymes. Type II enzymes and their modification i.e methyl transferase work as a separate protein. Water restriction of DNA and modification of DNA will be carried out by separate enzymes, which make it easy to cleave DNA molecules in the absence of modification.
- The enzymes that belong to this class are site-specific. They usually hydrolyzed phosphodiester bonds in both the strands of DNA which lie near to the recognition sequence.
- Type II enzymes have many practical benefits in molecular biology for cloning, generation of libraries, for DNA sequencing, for detection and overproduction of enzymes, hormones, etc.
- Restriction recognition sites can be unambiguous or ambiguous. Unambiguous means the enzyme BamHI is the only enzyme that recognizes sequence GGATCC and no other enzyme will recognize.
- The site of recognition of one enzyme may have the site of restriction for another enzyme.
Note:
- The restriction enzymes make cuts, one through each of the sugar-phosphate backbones on each strand of DNA without harming the nitrogenous base.
- The nomenclature of every enzyme is done on the basis of bacteria that they were isolated.
Complete step by step answer:
The restriction enzyme is BamHI. A restriction enzyme is a protein that recognizes a short nucleotide sequence that cuts the DNA at a specific site. The specific site is also known as a restriction site or target sequence.
- BamHI recognizes sequence 5'-G/GATCC-3' and cleaves between the two G's( shown by ' /' in sequence) just after the 5'guanine on each strand.
- This cleave will result in a 4 base pair with a long sticky end.

So, the correct answer is, "5'-GGATCC-3'3'-CCTAGG-5'".
Additional information: BamHI belongs to type II enzymes. Class II enzymes are an important class of restriction enzymes. Type II enzymes and their modification i.e methyl transferase work as a separate protein. Water restriction of DNA and modification of DNA will be carried out by separate enzymes, which make it easy to cleave DNA molecules in the absence of modification.
- The enzymes that belong to this class are site-specific. They usually hydrolyzed phosphodiester bonds in both the strands of DNA which lie near to the recognition sequence.
- Type II enzymes have many practical benefits in molecular biology for cloning, generation of libraries, for DNA sequencing, for detection and overproduction of enzymes, hormones, etc.
- Restriction recognition sites can be unambiguous or ambiguous. Unambiguous means the enzyme BamHI is the only enzyme that recognizes sequence GGATCC and no other enzyme will recognize.
- The site of recognition of one enzyme may have the site of restriction for another enzyme.
Note:
- The restriction enzymes make cuts, one through each of the sugar-phosphate backbones on each strand of DNA without harming the nitrogenous base.
- The nomenclature of every enzyme is done on the basis of bacteria that they were isolated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




