
Which one of the following traits studied by Mendel in garden pea was a recessive character?
(a)Axial flower position
(b)Green cotyledon colour
(c)Green pod colour
(d)Yellow seed colour
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Traits are defined as a specific characteristic of an organism that can be determined using genes. They constitute the physical characteristics of an individual and allow substantial variations.
Complete answer:
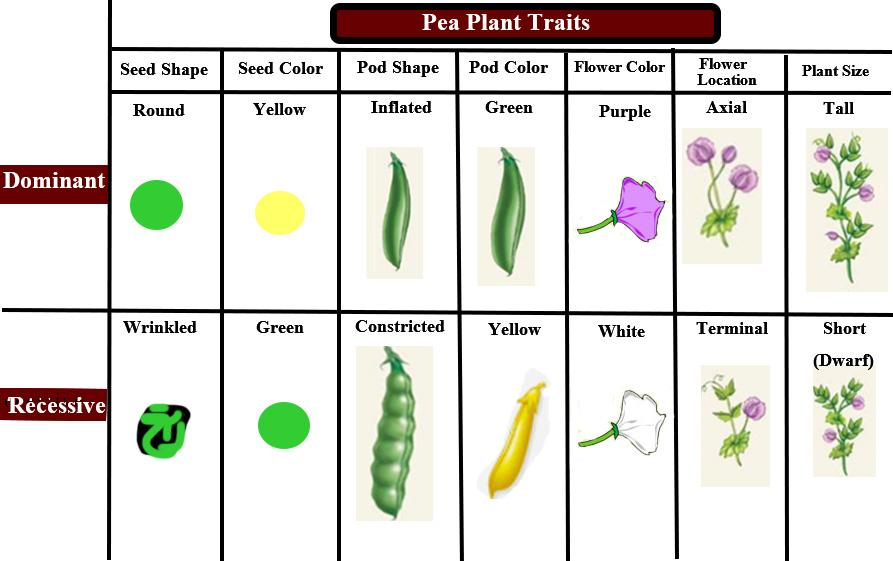
Green cotyledon colour was one of the recessive traits studied by Mendel in garden pea. Recessive traits are unexpressed traits and create no effect on the phenotype of heterozygous individuals. These traits reappear in the progeny of the hybrid offspring. This is because the recessive trait reappeared in the second filial generation which remained separate. It happened because of the copies of their offspring transmitted by each parent when they came together. The pea plant shows true-breeding offspring which consist of the same characteristics. The formation of ripened seed was wrinkled during recessive expression and the colour of seed albumin was green during recessive expression. The genes are expressed in the pairs and are inherited as distinct units from each of the parents. The segregation of parental genes was tracked by Mendel and their appearance in the offspring as recessive traits.
Additional Information: Pea plant exhibits a variety of contrasting traits and shapes of pea flower which is protected from foreign pollen. They reproduce by self-pollination and produce a flower with fertilizers and egg in the same flower and grows quickly without the requirement of much space. The colour of the flower was white and the formation of ripe pods was constricted during the recessive expression. The length of the stem and the colour of unripe and pods was yellow with the position of the flower at the terminal during a recessive expression. The exact position of the flower and the round seed shape were the dominant characters which include the green pod colour.
So, the correct answer is ' Green cotyledon colour'.
Note: Gregor Mendel became the 'father of genetics', who was a monk who discovered the basic principles of heredity through his experiments on the garden pea. He researched the transmission of hereditary traits in plant hybrids in 1854.
Complete answer:
Green cotyledon colour was one of the recessive traits studied by Mendel in garden pea. Recessive traits are unexpressed traits and create no effect on the phenotype of heterozygous individuals. These traits reappear in the progeny of the hybrid offspring. This is because the recessive trait reappeared in the second filial generation which remained separate. It happened because of the copies of their offspring transmitted by each parent when they came together. The pea plant shows true-breeding offspring which consist of the same characteristics. The formation of ripened seed was wrinkled during recessive expression and the colour of seed albumin was green during recessive expression. The genes are expressed in the pairs and are inherited as distinct units from each of the parents. The segregation of parental genes was tracked by Mendel and their appearance in the offspring as recessive traits.
Additional Information: Pea plant exhibits a variety of contrasting traits and shapes of pea flower which is protected from foreign pollen. They reproduce by self-pollination and produce a flower with fertilizers and egg in the same flower and grows quickly without the requirement of much space. The colour of the flower was white and the formation of ripe pods was constricted during the recessive expression. The length of the stem and the colour of unripe and pods was yellow with the position of the flower at the terminal during a recessive expression. The exact position of the flower and the round seed shape were the dominant characters which include the green pod colour.
So, the correct answer is ' Green cotyledon colour'.

Note: Gregor Mendel became the 'father of genetics', who was a monk who discovered the basic principles of heredity through his experiments on the garden pea. He researched the transmission of hereditary traits in plant hybrids in 1854.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




