
Which one of these is not true for benzene?
A.) It forms only one type of monosubstituted product.
B.) There are three carbon - carbon single bonds and three carbon-carbon double bonds.
C.) Heat of hydrogenation of benzene is less than its theoretical value.
D.) The bond angle between carbon – carbon double bond is \[120^\circ \]
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, we should know that all carbon – carbon bonds in benzene are partially double bonded to each other due to resonance and there is no carbon – carbon single bond.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that benzene has six carbons and six hydrogens with chemical formula ${C_6}{H_6}$ and also we know that its structure is:
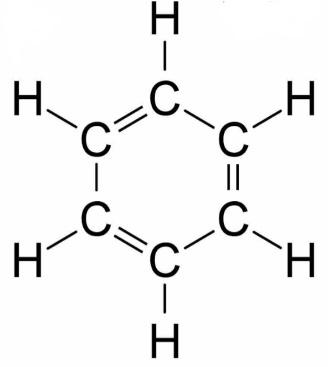
For option A.)
In this option, by monosubstituted products we mean that one hydrogen is replaced by another atom or molecule. Benzene can form only one type of monosubstituted means that it cannot form different atoms just by replacing the position of attached atom like in ortho, para or meta position which occurs when two atoms are attached to it. Hence it forms only one type of monosubstituted product.
For option B.)
In benzene, we have all bonds as partially double bonds this is because the pi bonds in the benzene ring delocalised around the ring. This delocalisation provides partial double bond character to all the carbons. Hence, all carbons will have partial double bond character.
The delocalised structure of benzene can be given as:
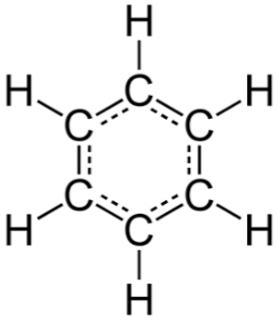
For option C.)
In this option, heat of hydrogenation can be understood as the measure of stability of carbon – carbon double bonds. When stability is high, then the heat of hydrogenation is low. In benzene, as we know there is resonance and delocalisation which makes it more stable. Due to this delocalisation, its heat of hydrogenation is lower than its theoretical value.
For option D.)
In benzene, each carbon atom has \[s{p^2}\]hybridisation and it is because each carbon is attached with carbon and hydrogen have 1 pi bonds and one pi bond. Due to this, it has a steric number (bone pairs plus lone pairs) is three(one of pi bond and two from two sigma bonds). For steric number three, the hybridisation is \[s{p^2}\]. As we know now that benzene is \[s{p^2}\] thus it has bond angle $120^\circ $.
Hence, option B.) is the correct option..
Note:
For the structure of benzene sometimes we get confused that it has three double bonds and three single bonds but we should always remember that benzene keeps on delocalisation which makes all carbon - carbon bonds as partially pi bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that benzene has six carbons and six hydrogens with chemical formula ${C_6}{H_6}$ and also we know that its structure is:

For option A.)
In this option, by monosubstituted products we mean that one hydrogen is replaced by another atom or molecule. Benzene can form only one type of monosubstituted means that it cannot form different atoms just by replacing the position of attached atom like in ortho, para or meta position which occurs when two atoms are attached to it. Hence it forms only one type of monosubstituted product.
For option B.)
In benzene, we have all bonds as partially double bonds this is because the pi bonds in the benzene ring delocalised around the ring. This delocalisation provides partial double bond character to all the carbons. Hence, all carbons will have partial double bond character.
The delocalised structure of benzene can be given as:

For option C.)
In this option, heat of hydrogenation can be understood as the measure of stability of carbon – carbon double bonds. When stability is high, then the heat of hydrogenation is low. In benzene, as we know there is resonance and delocalisation which makes it more stable. Due to this delocalisation, its heat of hydrogenation is lower than its theoretical value.
For option D.)
In benzene, each carbon atom has \[s{p^2}\]hybridisation and it is because each carbon is attached with carbon and hydrogen have 1 pi bonds and one pi bond. Due to this, it has a steric number (bone pairs plus lone pairs) is three(one of pi bond and two from two sigma bonds). For steric number three, the hybridisation is \[s{p^2}\]. As we know now that benzene is \[s{p^2}\] thus it has bond angle $120^\circ $.
Hence, option B.) is the correct option..
Note:
For the structure of benzene sometimes we get confused that it has three double bonds and three single bonds but we should always remember that benzene keeps on delocalisation which makes all carbon - carbon bonds as partially pi bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




