
Which phase comes in between the ${ G }_{ 1 }$ and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ phases of the cell cycle?
(a)M phase
(b)${ G }_{ 0 }$ phase
(c)S phase
(d)Interphase
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint This is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA replication takes place. It is also called a synthesis phase. In this stage, the genetic material of a cell is doubled before it enters mitosis or meiosis, allowing there to be enough DNA to be split into daughter cells.
Complete answer:
New cells are formed from pre-existing cells. The cell cycle includes a sequence of events that helps in cell duplication where DNA synthesis takes place during one particular stage in the cell cycle. The interphase of the cell cycle comprises ${ G }_{ 1 }$, S, and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ phases. The S phase lies between the ${ G }_{ 1 }$ and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ stages. During interphase, the cell prepares for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication.
Additional information:
The four stages of the cell cycle are as follows:
${ G }_{ 1 }$ phase – It is the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication. The cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but DNA replication does not take place.
S phase – ( also known as synthesis phase) is the period during which DNA synthesis and DNA replication take place. The amount of DNA per cell doubles but there is no increase in chromosome number.
In animal cells during the S phase DNA replication begins in the nucleus and centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm.
${ G }_{ 2 }$ phase – During this stage which is generally between DNA synthesis and mitosis, the cell continues to grow and produces new proteins.
M phase(mitotic phase) – Cell growth and protein production stop at this stage in the cell cycle. This stage consists of nuclear division (karyokinesis) followed by cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis). Mitosis stage is shorter than interphase in terms of time taken, lasting perhaps only one to two hours.
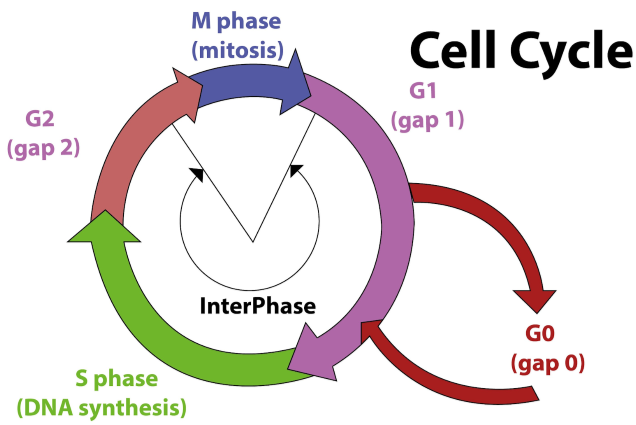
So, the correct answer is ‘ S phase’.
Note:
-During the ${ G }_{ 0 }$ phase, also known as the resting phase. Cells become inactive and do not divide. Examples of such cells are mature cardiac muscles and nerve cells.
-The interphase lasts for more than 95% of the duration of the cell cycle.
Complete answer:
New cells are formed from pre-existing cells. The cell cycle includes a sequence of events that helps in cell duplication where DNA synthesis takes place during one particular stage in the cell cycle. The interphase of the cell cycle comprises ${ G }_{ 1 }$, S, and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ phases. The S phase lies between the ${ G }_{ 1 }$ and ${ G }_{ 2 }$ stages. During interphase, the cell prepares for division by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication.
Additional information:
The four stages of the cell cycle are as follows:
${ G }_{ 1 }$ phase – It is the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication. The cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but DNA replication does not take place.
S phase – ( also known as synthesis phase) is the period during which DNA synthesis and DNA replication take place. The amount of DNA per cell doubles but there is no increase in chromosome number.
In animal cells during the S phase DNA replication begins in the nucleus and centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm.
${ G }_{ 2 }$ phase – During this stage which is generally between DNA synthesis and mitosis, the cell continues to grow and produces new proteins.
M phase(mitotic phase) – Cell growth and protein production stop at this stage in the cell cycle. This stage consists of nuclear division (karyokinesis) followed by cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis). Mitosis stage is shorter than interphase in terms of time taken, lasting perhaps only one to two hours.

So, the correct answer is ‘ S phase’.
Note:
-During the ${ G }_{ 0 }$ phase, also known as the resting phase. Cells become inactive and do not divide. Examples of such cells are mature cardiac muscles and nerve cells.
-The interphase lasts for more than 95% of the duration of the cell cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




