
Which plot is the adsorption isobar for chemisorption where $x$ is the amount of gas adsorbed on mass $m$ (at constant pressure) at temperature T?
A. 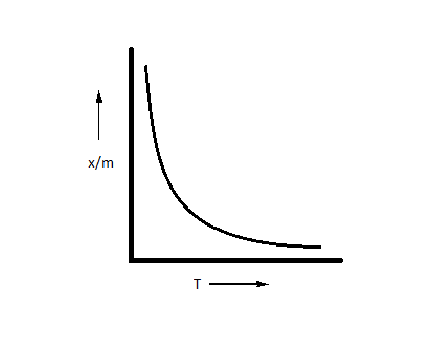
B.
C.
D.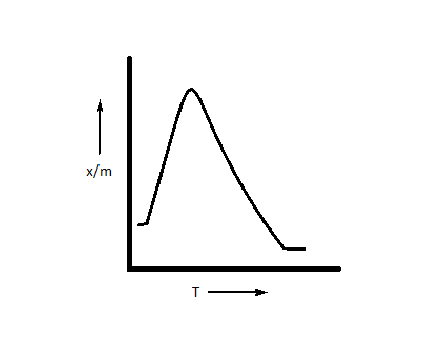
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The adsorption involving a chemical reaction between the surface and the adsorbate is called chemisorption. It can also be regarded as a chemical reaction occurring between the adsorbate and the adsorbent.
Complete step by step answer:
During chemisorption, new bonds (ionic or covalent) are generated at the adsorbent surface. It includes processes like corrosion and reactions using heterogeneous catalysts. It requires activation energy in order to occur. It is an irreversible process and can be regarded as a chemical reaction occurring between the adsorbate and the adsorbent. As chemisorption requires activation energy so like any other chemical reaction, we can say that by increasing the temperature, chemisorption increases, i.e. $\dfrac{x}{m}$ increases.
Adsorption is also a spontaneous reaction, i.e. it occurs at room temperature. So, we can say that the bond formation energy between the adsorbate and adsorbent is low. This also means that adsorption is an exothermic reaction. As we know that according to Le-Chartelier’s principle, as the temperature of an exothermic reaction is increased, the reaction proceeds backwards, i.e. in this case, adsorption decreases. So with increase in temperature, $\dfrac{x}{m}$ also decreases.
So, combining the two factors, we can conclude that if we increase the temperature, in the case of chemisorption:
$\dfrac{x}{m}$ increases as heat is absorbed by the particles in the system to achieve required activation energy and thus, higher rates of adsorption.
$\dfrac{x}{m}$ decreases after a certain point when all the particles already possess the required amount of activation energy, as adsorption being an exothermic process decreases with increase in temperature.
The correct option is option D, i.e. $\dfrac{x}{m}$ first increases and then decreases.
Note:
In the case of physisorption, the bonds formed are due to Vander Waal force of attraction. The reaction is reversible and not dependent on activation energy and thus, only decreases with the increase in temperature. In the case of chemisorption, the factors of both activation energy and exothermic process are taken into account.
Complete step by step answer:
During chemisorption, new bonds (ionic or covalent) are generated at the adsorbent surface. It includes processes like corrosion and reactions using heterogeneous catalysts. It requires activation energy in order to occur. It is an irreversible process and can be regarded as a chemical reaction occurring between the adsorbate and the adsorbent. As chemisorption requires activation energy so like any other chemical reaction, we can say that by increasing the temperature, chemisorption increases, i.e. $\dfrac{x}{m}$ increases.
Adsorption is also a spontaneous reaction, i.e. it occurs at room temperature. So, we can say that the bond formation energy between the adsorbate and adsorbent is low. This also means that adsorption is an exothermic reaction. As we know that according to Le-Chartelier’s principle, as the temperature of an exothermic reaction is increased, the reaction proceeds backwards, i.e. in this case, adsorption decreases. So with increase in temperature, $\dfrac{x}{m}$ also decreases.
So, combining the two factors, we can conclude that if we increase the temperature, in the case of chemisorption:
$\dfrac{x}{m}$ increases as heat is absorbed by the particles in the system to achieve required activation energy and thus, higher rates of adsorption.
$\dfrac{x}{m}$ decreases after a certain point when all the particles already possess the required amount of activation energy, as adsorption being an exothermic process decreases with increase in temperature.
The correct option is option D, i.e. $\dfrac{x}{m}$ first increases and then decreases.
Note:
In the case of physisorption, the bonds formed are due to Vander Waal force of attraction. The reaction is reversible and not dependent on activation energy and thus, only decreases with the increase in temperature. In the case of chemisorption, the factors of both activation energy and exothermic process are taken into account.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




