
Which would undergo ${S_N}1$ reactions faster in the following pair?


Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: ${S_N}1$ reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction which involves a nucleophile replacing a leaving group. The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant.
Step by step answer: ${S_N}1$ reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. Its name refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism where “ ${S_N}$ ” stands for “nucleophilic substitution” and the “1” refers to the rate-determining step in unimolecular. The rate equation is often shown as having first-order dependence on electrophile and zero order dependence on nucleophile. They are nucleophilic substitutions involving a nucleophile replacing a leaving group. In this reaction, the rate of this reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant.
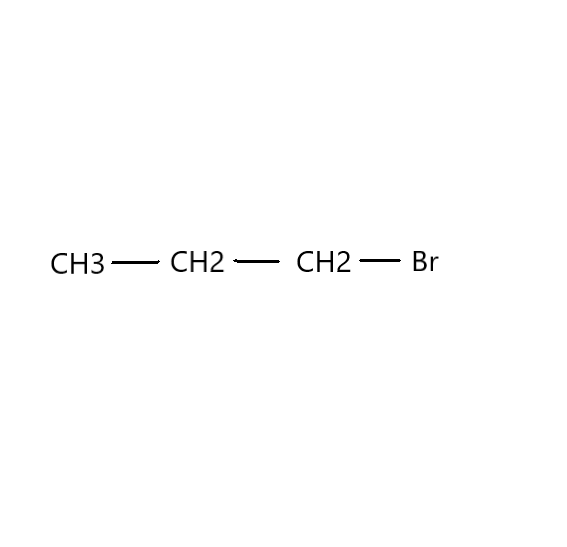
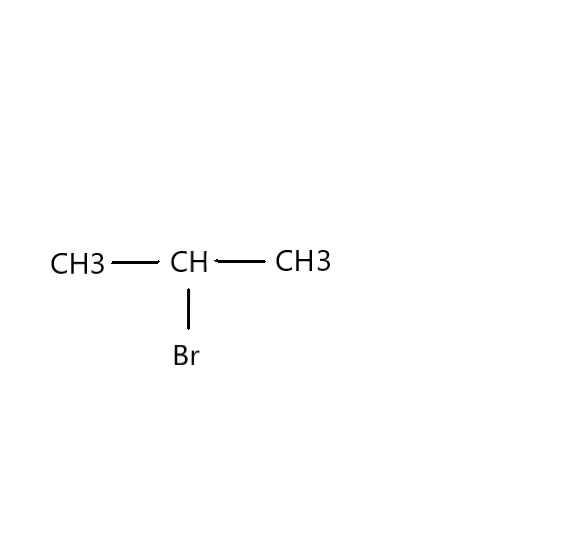
Now, we need to find in which compound nucleophilic substitution will take place faster. Since the first step of ${S_N}1$ reaction is the loss of a leaving group to give a carbocation, the rate of the reaction will be proportional to the stability of the carbocation. Carbocation stability increases with increasing substitution of the carbon (tertiary>secondary>primary) as well as resonance. Therefore, in this reaction, $C{H_3}CH(Br)C{H_3}$ is faster than $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}(Br)$ .
Additional Information: The IUPAC name of $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}(Br)$ is 1-Bromopropane. It is an organobromine compound which is a colourless liquid that is used as a solvent. It has a characteristic hydrocarbon odour. Its industrial applications have increased in the 21st century. It finds use in liquid or gaseous solvent. It is a solvent for adhesives in aerosol glues that glue foam cushions together.
The IUPAC name for $C{H_3}CH(Br)C{H_3}$ is 2-Bromopropane. It is also known as isopropyl bromide and 2-propyl bromide. It is the halogenated hydrocarbon which is a colourless liquid. It is used for introducing the isopropyl functional group in organic synthesis. It is prepared by heating isopropanol with hydrobromic acid.
Note: ${S_N}1$ reaction mechanism follows a step by step process wherein first, the carbocation is formed from the removal of the leaving group. Secondly, the carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile. And finally the deprotonation of the protonated nucleophile takes place to give the required product.
Step by step answer: ${S_N}1$ reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. Its name refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism where “ ${S_N}$ ” stands for “nucleophilic substitution” and the “1” refers to the rate-determining step in unimolecular. The rate equation is often shown as having first-order dependence on electrophile and zero order dependence on nucleophile. They are nucleophilic substitutions involving a nucleophile replacing a leaving group. In this reaction, the rate of this reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant.
Now, we need to find in which compound nucleophilic substitution will take place faster. Since the first step of ${S_N}1$ reaction is the loss of a leaving group to give a carbocation, the rate of the reaction will be proportional to the stability of the carbocation. Carbocation stability increases with increasing substitution of the carbon (tertiary>secondary>primary) as well as resonance. Therefore, in this reaction, $C{H_3}CH(Br)C{H_3}$ is faster than $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}(Br)$ .
Additional Information: The IUPAC name of $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}(Br)$ is 1-Bromopropane. It is an organobromine compound which is a colourless liquid that is used as a solvent. It has a characteristic hydrocarbon odour. Its industrial applications have increased in the 21st century. It finds use in liquid or gaseous solvent. It is a solvent for adhesives in aerosol glues that glue foam cushions together.
The IUPAC name for $C{H_3}CH(Br)C{H_3}$ is 2-Bromopropane. It is also known as isopropyl bromide and 2-propyl bromide. It is the halogenated hydrocarbon which is a colourless liquid. It is used for introducing the isopropyl functional group in organic synthesis. It is prepared by heating isopropanol with hydrobromic acid.
Note: ${S_N}1$ reaction mechanism follows a step by step process wherein first, the carbocation is formed from the removal of the leaving group. Secondly, the carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile. And finally the deprotonation of the protonated nucleophile takes place to give the required product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




