
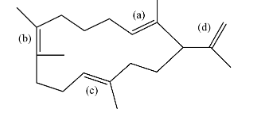
Which ($\pi -bond$) will reduce first when above compound undergoes catalytic hydrogenation?

Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint:As we know that catalytic hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen to a compound with a double or triple bond.In this reaction, the double bond gets reduced easily. Since unstable $\pi -bond$will try to react and reduce itself first, therefore we need to see for most unstable double bonds in the given compounds.
Complete step-by-step answer:It is very well known that alkene hydrogenation is the syn-addition of hydrogen to an alkene which is also referred as saturating the bond. The alkene reacts with ${{H}_{2}}$ gas in the presence of a metal catalyst such as platinum or palladium in carbon beads which allows the reaction to occur quickly. The energy released during this process is called the heat of hydrogenation which indicates the relative stability of the double bond in a molecule.
- Since double bonds break in the reaction, the energy released in hydrogenation is directly proportional to the energy in the double bond of the molecule. The more stable the double bond, the stronger it is and more difficulty will be faced in breaking this bond whereas the weak unstable bonds will be reactive and ready to reduce itself.
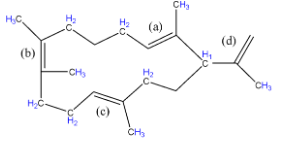
-Stability can be checked by various factors and here we will use hyperconjugation. More the number of $\alpha -H$ (hydrogen atoms attached to the first carbon near double bond) around the C=C, more will be the stability of double bond. So let us check the number of $\alpha -H$around each double bond.
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (a) C=C: 2+3+1 = 6
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (b) C=C: 3+3+2+2 = 10
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (c) C=C: 2+2+3 = 7
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (d) C=C: 1+3 =4
From the above data we can see that the minimum number of $\alpha -H$is present around (d) C=C, therefore it will be the most unstable double bond and tend to react rapidly.
Hence the correct option is (d).
Note:-We can learn some rules to directly see which double bond should react first among many. These rules are as follows:-
-Those alkenes will get reduced first which are less substituted or less sterically hindered.
-Reduces isolated or non-conjugated alkene first.
-Added hydrogen atom will choose the stereo opposite to the steric groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:It is very well known that alkene hydrogenation is the syn-addition of hydrogen to an alkene which is also referred as saturating the bond. The alkene reacts with ${{H}_{2}}$ gas in the presence of a metal catalyst such as platinum or palladium in carbon beads which allows the reaction to occur quickly. The energy released during this process is called the heat of hydrogenation which indicates the relative stability of the double bond in a molecule.
- Since double bonds break in the reaction, the energy released in hydrogenation is directly proportional to the energy in the double bond of the molecule. The more stable the double bond, the stronger it is and more difficulty will be faced in breaking this bond whereas the weak unstable bonds will be reactive and ready to reduce itself.

-Stability can be checked by various factors and here we will use hyperconjugation. More the number of $\alpha -H$ (hydrogen atoms attached to the first carbon near double bond) around the C=C, more will be the stability of double bond. So let us check the number of $\alpha -H$around each double bond.
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (a) C=C: 2+3+1 = 6
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (b) C=C: 3+3+2+2 = 10
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (c) C=C: 2+2+3 = 7
-Number of $\alpha -H$around (d) C=C: 1+3 =4
From the above data we can see that the minimum number of $\alpha -H$is present around (d) C=C, therefore it will be the most unstable double bond and tend to react rapidly.
Hence the correct option is (d).
Note:-We can learn some rules to directly see which double bond should react first among many. These rules are as follows:-
-Those alkenes will get reduced first which are less substituted or less sterically hindered.
-Reduces isolated or non-conjugated alkene first.
-Added hydrogen atom will choose the stereo opposite to the steric groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




