
Who invented the voltaic cell?
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint: Recall that a voltaic cell carries out an electrochemical reaction and converts chemical energy into electrical energy. A series of redox reactions and subsequent ion diffusion across the half-cells ensures the production of electrical energy as well as the renewal of the same to carry out the process again. A device close to this description was first developed by this Italian physicist, and it was called as the voltaic pile, and it was built based on Luigi Galvani’s discovery of how a circuit of two metals in contact with a frog’s leg (acting as an electrolyte) made the frog’s muscles contract.
Complete answer:
A voltaic cell, or a galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell which generates electric current from spontaneous redox reactions. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy. In redox reactions, energy is released if the reaction occurs spontaneously. A voltaic cell consists of two half-cells connected by a porous disk. The zinc$\;(Zn)$ half-cell consists of a zinc electrode immersed in a solution of zinc sulphate $(ZnSO_4)$ and the copper$\;(Cu)$ half-cell consists of a copper electrode immersed in a solution of copper sulphate $(CuSO_4)$.
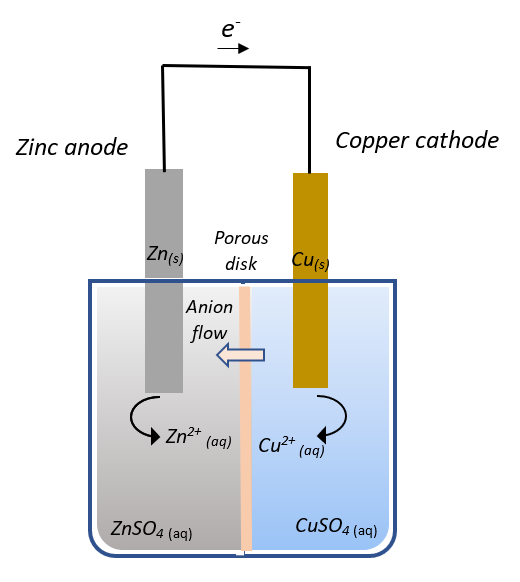
Now, when the zinc and copper electrodes are connected by an external electrical conductor, zinc from the zinc electrode dissolves into the solution as $Zn^{2+}$ ions releasing electrons that enter the external conductor, i.e.,
$Zn_{(s)} \rightarrow Zn^{2+} _{(aq)} + 2e^{-}$ [Oxidation]
To compensate for the increased zinc ion concentration, the zinc ions leave the zinc half-cell through the porous disc and sulphate anions enter the zinc half-cell.
In the copper half-cell, the copper ions plate on to the copper electrode by taking up the electrons that leave the external conductor, i.e.,
$ Cu^{2+} _{(aq)} + 2e^{-} \rightarrow Cu_{(s)}$ [Reduction]
The electrochemical processes in the cell occurs because reactants of high free energy (metallic zinc and aqueous copper ions) are converted into low energy products (metallic copper and aqueous zinc ions), and the porous disk allows the ions to pass from one solution to the other which balances the charges of the solutions and allows the reaction to continue.
Such a cell based on this principle was first devised by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta.
Note:
The standard electrode potential of copper’s half-reaction is $E^{\circ} = +0.34\;V$ and that of zinc’s half-reaction is $E^{\circ} = -0.76\;V$. Since the standard potential for zinc is more negative than that of copper, zinc metal is more reducing than copper. This is why zinc metal loses electrons to copper ions and develops a positive electrical charge.
Thus, for the overall reaction, the standard potential will be: $+0.34 – (-0.76) = 1.10\;V$
Note that the current produced by galvanic or voltaic cells is by nature, direct current. Also, a set of galvanic or voltaic cells connected together form a single source of voltage called a battery. A typical 12V lead-acid battery has six voltaic cells connected in series with the anodes composed of lead and cathodes composed of lead dioxide, both immersed in sulphuric acid.
Complete answer:
A voltaic cell, or a galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell which generates electric current from spontaneous redox reactions. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy. In redox reactions, energy is released if the reaction occurs spontaneously. A voltaic cell consists of two half-cells connected by a porous disk. The zinc$\;(Zn)$ half-cell consists of a zinc electrode immersed in a solution of zinc sulphate $(ZnSO_4)$ and the copper$\;(Cu)$ half-cell consists of a copper electrode immersed in a solution of copper sulphate $(CuSO_4)$.

Now, when the zinc and copper electrodes are connected by an external electrical conductor, zinc from the zinc electrode dissolves into the solution as $Zn^{2+}$ ions releasing electrons that enter the external conductor, i.e.,
$Zn_{(s)} \rightarrow Zn^{2+} _{(aq)} + 2e^{-}$ [Oxidation]
To compensate for the increased zinc ion concentration, the zinc ions leave the zinc half-cell through the porous disc and sulphate anions enter the zinc half-cell.
In the copper half-cell, the copper ions plate on to the copper electrode by taking up the electrons that leave the external conductor, i.e.,
$ Cu^{2+} _{(aq)} + 2e^{-} \rightarrow Cu_{(s)}$ [Reduction]
The electrochemical processes in the cell occurs because reactants of high free energy (metallic zinc and aqueous copper ions) are converted into low energy products (metallic copper and aqueous zinc ions), and the porous disk allows the ions to pass from one solution to the other which balances the charges of the solutions and allows the reaction to continue.
Such a cell based on this principle was first devised by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta.
Note:
The standard electrode potential of copper’s half-reaction is $E^{\circ} = +0.34\;V$ and that of zinc’s half-reaction is $E^{\circ} = -0.76\;V$. Since the standard potential for zinc is more negative than that of copper, zinc metal is more reducing than copper. This is why zinc metal loses electrons to copper ions and develops a positive electrical charge.
Thus, for the overall reaction, the standard potential will be: $+0.34 – (-0.76) = 1.10\;V$
Note that the current produced by galvanic or voltaic cells is by nature, direct current. Also, a set of galvanic or voltaic cells connected together form a single source of voltage called a battery. A typical 12V lead-acid battery has six voltaic cells connected in series with the anodes composed of lead and cathodes composed of lead dioxide, both immersed in sulphuric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




