
Why is $C{l_2}$ a covalent bond?
Answer
505.5k+ views
Hint: A covalent bond, also known as a molecular bond, is a bond formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons. Typically, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to fill their outermost shell completely, and thus, help them achieve their stable electronic configuration.
Complete answer:
The atomic number of chlorine is $17$ and it has $7$ valence electrons $(3{s^2}3{p^5})$. Chlorine needs one electron to attain a stable electronic configuration of argon, which has $8$ valence electrons $(3{s^2}3{p^6})$.
In the $C{l_2}$ molecule, each chlorine atom contributes one electron to form a common shared pair. By doing so, both of them complete their octets. In other words, they acquire the electronic configuration of argon.
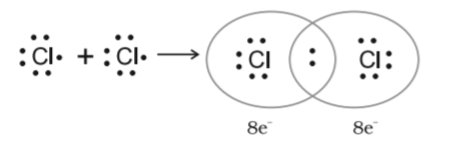
Both $Cl$ have $7$ electrons. Now, both $Cl$ have complete octet by sharing one electron from each other.
The number of electrons an atom shares with the other atoms to form a chemical bond is called its covalency. For Example, in the $C{l_2}$ molecule, each chlorine atom shares one electron; therefore, the covalency of chlorine is one.
There are three types of covalent bonds:
\[ \bullet \] Single covalent bond
\[ \bullet \] Double covalent bond
\[ \bullet \] Triple covalent bond.
Chlorine forms a single covalent bond because each atom contributes one electron to form a shared pair. A single bond is represented by a single dash\[( - )\]
Chlorine atoms form a nonpolar covalent bond; a nonpolar covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electrons equally. The covalent bond between atoms of same elements is non-polar because both the atoms have equal electronegativities.
Note:
When two atoms of the same element form a covalent bond, the electron pairs are shared equally between the two atoms. But, when a covalent bond is formed between atoms of different electronegativities, the shared pair of electrons get displaced towards the atom which is more electronegative. As a result, one end of the molecule becomes slightly positively charged, and the other end becomes slightly negatively charged.
Complete answer:
The atomic number of chlorine is $17$ and it has $7$ valence electrons $(3{s^2}3{p^5})$. Chlorine needs one electron to attain a stable electronic configuration of argon, which has $8$ valence electrons $(3{s^2}3{p^6})$.
In the $C{l_2}$ molecule, each chlorine atom contributes one electron to form a common shared pair. By doing so, both of them complete their octets. In other words, they acquire the electronic configuration of argon.

Both $Cl$ have $7$ electrons. Now, both $Cl$ have complete octet by sharing one electron from each other.
The number of electrons an atom shares with the other atoms to form a chemical bond is called its covalency. For Example, in the $C{l_2}$ molecule, each chlorine atom shares one electron; therefore, the covalency of chlorine is one.
There are three types of covalent bonds:
\[ \bullet \] Single covalent bond
\[ \bullet \] Double covalent bond
\[ \bullet \] Triple covalent bond.
Chlorine forms a single covalent bond because each atom contributes one electron to form a shared pair. A single bond is represented by a single dash\[( - )\]
Chlorine atoms form a nonpolar covalent bond; a nonpolar covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electrons equally. The covalent bond between atoms of same elements is non-polar because both the atoms have equal electronegativities.
Note:
When two atoms of the same element form a covalent bond, the electron pairs are shared equally between the two atoms. But, when a covalent bond is formed between atoms of different electronegativities, the shared pair of electrons get displaced towards the atom which is more electronegative. As a result, one end of the molecule becomes slightly positively charged, and the other end becomes slightly negatively charged.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




