
Why is RNA unstable?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: RNA stands for ribonucleic acid is a single strand involved in several functions such as replication, transcription, translation and expression of genes. It is made up of nucleotides, a sugar-phosphate backbone and nucleobases. These bases are guanine, cytosine, adenine and uracil.
Complete answer:
To answer this question you must know about RNA.
Ribonucleic acid is a linear molecule composed of four types of smaller molecules called ribonucleotide bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. RNA is often compared to a copy from a reference book, or a template, because it carries the same information as its DNA template but,not used for long term storage.
Each ribonucleic base consists of a ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. adjacent ribose nucleotide bases are chemically attached to one another in a chain via chemical bonds called phosphodiester bonds.
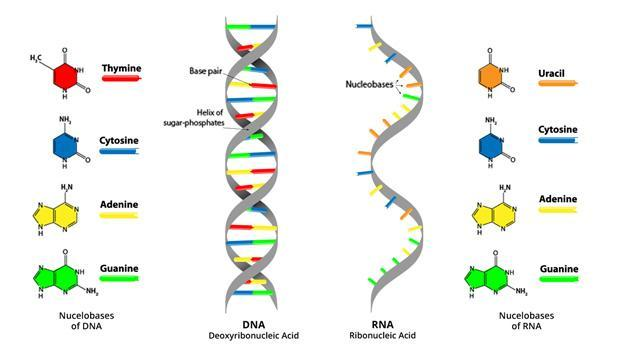
RNA usually single –stranded, and it contain ribose sugar which is characterized by the presence of the 2 –hydroxyl group on the pentose ring rather than deoxyribose sugars which does not have 2’OH group this makes RNA more unstable because it is more susceptible to hydrolysis. RNA hydrolysis occurs when the deprotonated 2’OH of the ribose sugars occurs.
RNA contains ribose sugar with presence of the 2'hydroxyle group, this feature makes RNA chemically unstable compared to DNA.
Note:
RNA is synthesized from DNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase during the process of transcription. The new RNA sequences are complementary to their DNA template, rather than being identical copies of the template. RNA is then translated into protein by a structure called ribosomes. Some RNA molecules are involved in switching genes on and off, and other RNA molecules make up the critical protein synthesis machinery in ribosomes.
Complete answer:
To answer this question you must know about RNA.
Ribonucleic acid is a linear molecule composed of four types of smaller molecules called ribonucleotide bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. RNA is often compared to a copy from a reference book, or a template, because it carries the same information as its DNA template but,not used for long term storage.
Each ribonucleic base consists of a ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. adjacent ribose nucleotide bases are chemically attached to one another in a chain via chemical bonds called phosphodiester bonds.

RNA usually single –stranded, and it contain ribose sugar which is characterized by the presence of the 2 –hydroxyl group on the pentose ring rather than deoxyribose sugars which does not have 2’OH group this makes RNA more unstable because it is more susceptible to hydrolysis. RNA hydrolysis occurs when the deprotonated 2’OH of the ribose sugars occurs.
RNA contains ribose sugar with presence of the 2'hydroxyle group, this feature makes RNA chemically unstable compared to DNA.
Note:
RNA is synthesized from DNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase during the process of transcription. The new RNA sequences are complementary to their DNA template, rather than being identical copies of the template. RNA is then translated into protein by a structure called ribosomes. Some RNA molecules are involved in switching genes on and off, and other RNA molecules make up the critical protein synthesis machinery in ribosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




