
With a mixture of conc. \[HN{O_3}\] and conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] anisole gives ______________.
A.Ortho nitro anisole
B.Para nitro anisole
C.Ortho and para nitro anisole
D.Meta nitro anisole
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:The attachment of an electrophile ortho or para to anisole leads to a more stable complex because of resonance involving the electron donating substituent. On the other hand, meta-attack does not permit any resonance stabilization or interaction and order of the distribution of final products in the reaction is Para > ortho >> meta.
Complete answer:
All of the ortho, para-directing substituents are either alkyl groups or groups that have unshared electron pairs on atoms directly attached to the benzene ring. Although other types of ortho, para-directing groups are known, the principles on which ortho, para-directing effects are based can be understood by considering electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene derivatives containing these types of substituents.
Anisole which is also known as methoxybenzene is an electron-rich arene that will react with nitric acid
(\[HN{O_3}\]) in the presence of sulphuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) in an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
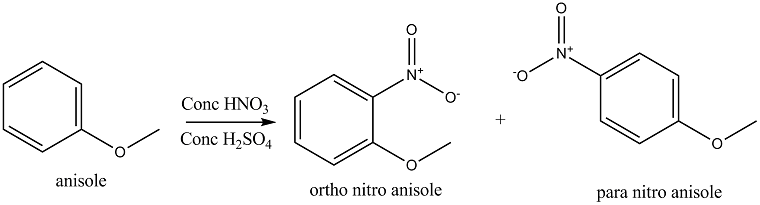
When anisole is nitrated with a mixture of conc. \[HN{O_3}\] and conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] (nitrating mixture), anisole gives ortho nitro anisole (minor product) and para nitro anisole (major product). Methoxy group (\[ - OC{H_3}\] group) is activating an ortho para directing group. The reaction is shown below:
Note:
When we see the reaction of a general electrophile \[{E^ + }\] with anisole (methoxybenzene). We notice that the atom that is directly attached to the benzene ring i.e., the oxygen of the methoxy group has unshared electron pairs. Reaction of \[{E^ + }\] at the para position of anisole gives a carbocation intermediate. Nitration is used to add nitrogen to a benzene ring, which can be used further in substitution reactions and as sulfonation is a reversible reaction, it can also be used in further substitution reactions in the form of a directing blocking group because it can be easily removed.
Complete answer:
All of the ortho, para-directing substituents are either alkyl groups or groups that have unshared electron pairs on atoms directly attached to the benzene ring. Although other types of ortho, para-directing groups are known, the principles on which ortho, para-directing effects are based can be understood by considering electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene derivatives containing these types of substituents.
Anisole which is also known as methoxybenzene is an electron-rich arene that will react with nitric acid
(\[HN{O_3}\]) in the presence of sulphuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) in an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
When anisole is nitrated with a mixture of conc. \[HN{O_3}\] and conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] (nitrating mixture), anisole gives ortho nitro anisole (minor product) and para nitro anisole (major product). Methoxy group (\[ - OC{H_3}\] group) is activating an ortho para directing group. The reaction is shown below:

Note:
When we see the reaction of a general electrophile \[{E^ + }\] with anisole (methoxybenzene). We notice that the atom that is directly attached to the benzene ring i.e., the oxygen of the methoxy group has unshared electron pairs. Reaction of \[{E^ + }\] at the para position of anisole gives a carbocation intermediate. Nitration is used to add nitrogen to a benzene ring, which can be used further in substitution reactions and as sulfonation is a reversible reaction, it can also be used in further substitution reactions in the form of a directing blocking group because it can be easily removed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




