
With respect to the conformers of ethane, which of the following statements is true?
A.Bond angle changes but bond length remain same
B.Both bond angle and bond length changes
C.Both bond angle and bond length remain same
D.None of the above
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:Since, we know that there are seven sigma bonds in the ethane molecule, rotation about the six carbon-hydrogen bonds does not result in any change in the shape of the molecule as the hydrogen atoms are essentially spherical. The rotation about the carbon-carbon bond, however, results in many different possible molecular conformations.
Complete answer:
Conformational isomerism involves rotation about sigma bonds, and does not involve any differences in the connectivity or geometry of bonding. Two or more structures that are categorized as conformational isomers, or conformers, are really just two of the exact same molecules that differ only in terms of the angle about one or more sigma bonds.
The six carbon-hydrogen bonds and the two carbons at \[{120^0}\]angles, which is what the actual tetrahedral geometry looks like when viewed from this perspective and flattened into two dimensions.
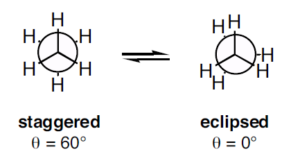
In the ‘staggered’ conformation, in which all of the C-H bonds on the front carbon are positioned at dihedral angles of ${60^0}$relative to the C-H bonds on the back carbon. In this conformation, the distance between the bonds is maximized. And If we now rotate the front \[C{H_3}\] group ${60^0}$clockwise, the molecule is in the highest energy ‘eclipsed' conformation, where the hydrogens on the front carbon are as close as possible to the hydrogens on the back carbon.
Hence, conformers of ethane have different dihedral angles and there is no change in bond angles and the bond lengths in the conformations of ethane. The only change taking place is the change in the dihedral angle.
Thus, both the bond angle and bond length are the same
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
If the groups are large enough to have a significant effect on the energy of rotation, they may tend to prefer certain spatial arrangements rather than others. These different spatial arrangements of the groups give rise to conformers.
Complete answer:
Conformational isomerism involves rotation about sigma bonds, and does not involve any differences in the connectivity or geometry of bonding. Two or more structures that are categorized as conformational isomers, or conformers, are really just two of the exact same molecules that differ only in terms of the angle about one or more sigma bonds.
The six carbon-hydrogen bonds and the two carbons at \[{120^0}\]angles, which is what the actual tetrahedral geometry looks like when viewed from this perspective and flattened into two dimensions.

In the ‘staggered’ conformation, in which all of the C-H bonds on the front carbon are positioned at dihedral angles of ${60^0}$relative to the C-H bonds on the back carbon. In this conformation, the distance between the bonds is maximized. And If we now rotate the front \[C{H_3}\] group ${60^0}$clockwise, the molecule is in the highest energy ‘eclipsed' conformation, where the hydrogens on the front carbon are as close as possible to the hydrogens on the back carbon.
Hence, conformers of ethane have different dihedral angles and there is no change in bond angles and the bond lengths in the conformations of ethane. The only change taking place is the change in the dihedral angle.
Thus, both the bond angle and bond length are the same
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
If the groups are large enough to have a significant effect on the energy of rotation, they may tend to prefer certain spatial arrangements rather than others. These different spatial arrangements of the groups give rise to conformers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




