
With the help of a block diagram, explain the operation of the FM superheterodyne receiver.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: A superheterodyne receiver is a radio frequency receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal into an Intermediate frequency (IF), this allows the signal to be processed more conveniently than processing the original carrier frequency.
Complete Step by step answer:
Following is the block diagram for an FM superheterodyne receiver-
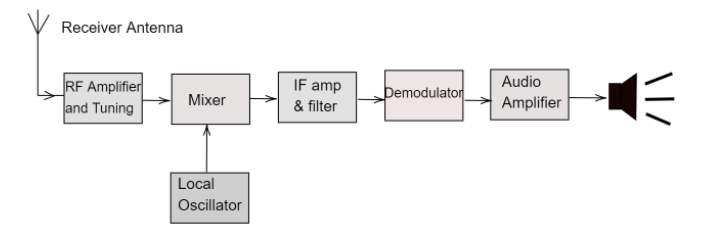
The receiver first receives the signals from the antenna and is fed to the RF Amplifier. In the RF amplifier, they are also tuned in order to remove any unwanted signals from other frequencies.
The tuned signals from the RF amplifier mixes with the incoming local frequency signals which are generated from a local oscillator. This mixing process is done in the mixer and this mixing creates an intermediate frequency (IF).
The intermediate frequency formed by the mixing is more convenient to process as compared to the original carrier frequency.
The intermediate frequency is then amplified and filtered, this amplitude is maintained by using a limiter. During filtering, the signals of a particular channel can be selected. As compared to RF filtering, the IF filter can be tuned better than the RF filter because it can be designed for a fixed frequency.
This signal is then applied to a demodulator which is an FM detector, this detector demodulates the output. It is also possible to switch between different demodulators to achieve the desired output form.
This demodulated signal is then audio amplified using a loudspeaker where it converts to sound waves of the audible frequency.
Note: The speciality of a superheterodyne FM receiver is that it mixes the original incoming frequency from a source with a locally generated frequency, this allows the receiver to filter and select only the desired RF signals.
Complete Step by step answer:
Following is the block diagram for an FM superheterodyne receiver-

The receiver first receives the signals from the antenna and is fed to the RF Amplifier. In the RF amplifier, they are also tuned in order to remove any unwanted signals from other frequencies.
The tuned signals from the RF amplifier mixes with the incoming local frequency signals which are generated from a local oscillator. This mixing process is done in the mixer and this mixing creates an intermediate frequency (IF).
The intermediate frequency formed by the mixing is more convenient to process as compared to the original carrier frequency.
The intermediate frequency is then amplified and filtered, this amplitude is maintained by using a limiter. During filtering, the signals of a particular channel can be selected. As compared to RF filtering, the IF filter can be tuned better than the RF filter because it can be designed for a fixed frequency.
This signal is then applied to a demodulator which is an FM detector, this detector demodulates the output. It is also possible to switch between different demodulators to achieve the desired output form.
This demodulated signal is then audio amplified using a loudspeaker where it converts to sound waves of the audible frequency.
Note: The speciality of a superheterodyne FM receiver is that it mixes the original incoming frequency from a source with a locally generated frequency, this allows the receiver to filter and select only the desired RF signals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




