
With the help of a diagram explain the process of gametogenesis.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: After spore meiosis the gametophytes emerge from haploid spores. Often called alternation of generations is the presence of a multicellular, haploid process of the life cycle among meiosis and gametogenesis.
Complete Answer:
First we should know about gametogenesis to answer this question. Gametogenesis is the mechanism of gametes formation in animals which reproduce sexually.
Male gamete forming phase i.e., spermatozoa is known as spermatogenesis. The mechanism of female gamete formation, i.e., the ovum is named oogenesis.
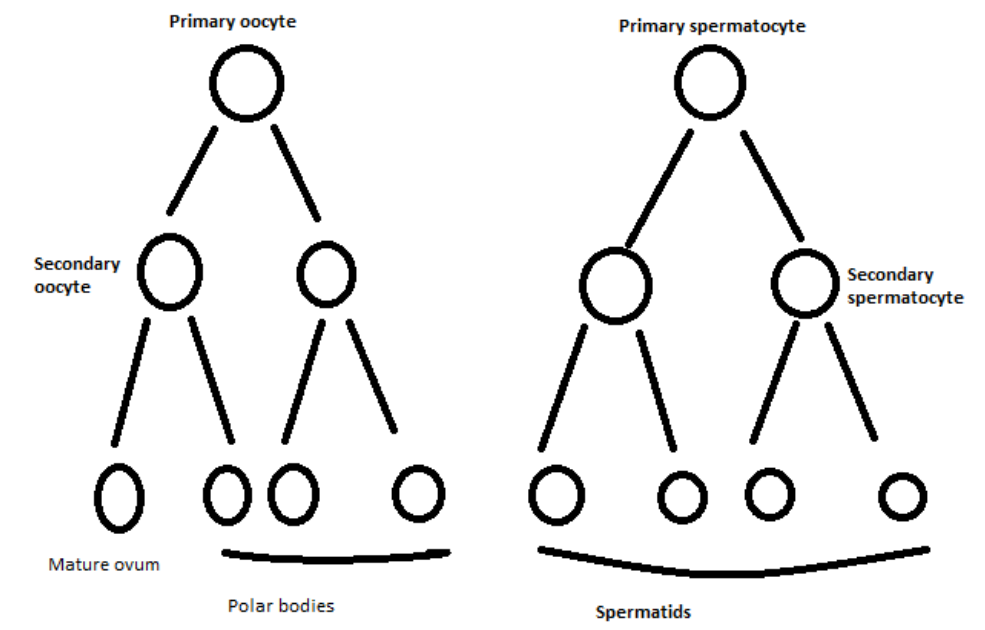
Spermatogenesis: The spermatogenesis process is performed in male gonads. The primordial cells show mitosis to form multiple spermatogonia from which a primary spermatocyte is formed.
It undergoes meiosis 1 in order to form secondary haploid spermatozoa. The secondary spermatocyte is exposed to meiosis II which is equational to haploid sperm development.
Oogenesis: The ovary's germ cells showed mitosis and formed multiple oogonies.
One of the oogonium creates a primary oocyte that I undertake to form a secondary oocyte and a polar body. To create the haploid ovum, the secondary oocyte and polar must undergo meiosis II with three polar bodies.
Note: Meiosis is a basic aspect of gametogenesis but meiosis' protective mechanism is still a matter of controversy. The joining of homologous chromosomes and recombination of homologous chromosomes is a crucial occurrence during meiosis.
Complete Answer:
First we should know about gametogenesis to answer this question. Gametogenesis is the mechanism of gametes formation in animals which reproduce sexually.
Male gamete forming phase i.e., spermatozoa is known as spermatogenesis. The mechanism of female gamete formation, i.e., the ovum is named oogenesis.
Spermatogenesis: The spermatogenesis process is performed in male gonads. The primordial cells show mitosis to form multiple spermatogonia from which a primary spermatocyte is formed.
It undergoes meiosis 1 in order to form secondary haploid spermatozoa. The secondary spermatocyte is exposed to meiosis II which is equational to haploid sperm development.
Oogenesis: The ovary's germ cells showed mitosis and formed multiple oogonies.
One of the oogonium creates a primary oocyte that I undertake to form a secondary oocyte and a polar body. To create the haploid ovum, the secondary oocyte and polar must undergo meiosis II with three polar bodies.

Note: Meiosis is a basic aspect of gametogenesis but meiosis' protective mechanism is still a matter of controversy. The joining of homologous chromosomes and recombination of homologous chromosomes is a crucial occurrence during meiosis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




