
Working of a betatron is not based upon which of the following theories?
A. Changing magnetic fields induced electric fields.
B. charged particles at rest can be accelerated only by electric field.
C. Magnetic fields can apply a force on moving charges which is perpendicular to both magnetic field and motion of the particle.
D. $\beta $ particles are emitted in the radioactive decay process.

Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint:A betatron is a cyclic particle accelerator. It is used to accelerate electrons from rest. That electric field is induced by varying magnetic fields. It accelerates the electrons to a high speed in a circular orbit. High energy electrons are nothing but $\beta $ particles. Hence, the name betatron. The main principle of the betatron is that the varying magnetic field in the primary coil accelerates the electrons because of which they rotate in the same direction of that of the current induced in the secondary coil.
Complete step by step answer:
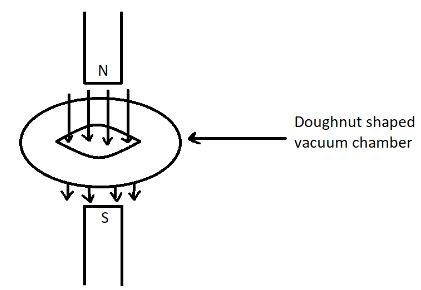
Let’s first know the working of the betatron and try to answer the question. The magnets produce a varying magnetic flux in the same direction as the doughnut shaped vacuum chamber, this produces an electric field along the circular axis of the vacuum chamber. Any particle inside the chamber will be accelerated because of the force of the electric field.
When the particle experiences a force, originally it has to shoot out and become lost. But if we make sure that the centripetal force = magnetic force, then the particle will be rotating in the doughnut shaped vacuum chamber. For every rotation around the chamber, the electron loses a potential difference, which is equal to the induced EMF.
$\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{a} = qvB$
Now, if we go through all the options, we get:
Option A: Changing magnetic field induced electric field.
The electric field is produced by the varying magnetic field produced by the electromagnets.
Hence, this is correct.
Option B: charged particles at rest can be accelerated only by electric field.
Yes, charged particles at rest when acted upon by an electric field, produce a force which is equal to the product of the electric field and their charge.
$F = Eq$
A magnetic field does not have any effect on a particle at rest. Hence, this is also correct.
Option C: Magnetic fields can apply a force on moving charges which is perpendicular to both magnetic field and motion of the particle.
The magnetic force on moving charges is perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field. That direction is given by the right hand rule where the direction of force is pointed by the thumb, magnetic field is pointed by the middle finger and the direction of velocity is given by the direction pointed out by the thumb.
Option D: $\beta $ particles are emitted in the radioactive decay process.
The $\beta $ particles emitted here are not because of the radioactive decay process but because of the electromagnetic process and electric field produced by it.Hence, this is wrong and is not a principle of betatron.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:Knowing the principle and having a clear idea of the working of the betatron will help us solve the question. Students have a misconception and assume that $\beta $ particles are always associated with radioactive decay. We need to remember that this question has nothing to do with radioactive decay but the $\beta $ particles are because of the electromagnets and electric field.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first know the working of the betatron and try to answer the question. The magnets produce a varying magnetic flux in the same direction as the doughnut shaped vacuum chamber, this produces an electric field along the circular axis of the vacuum chamber. Any particle inside the chamber will be accelerated because of the force of the electric field.
When the particle experiences a force, originally it has to shoot out and become lost. But if we make sure that the centripetal force = magnetic force, then the particle will be rotating in the doughnut shaped vacuum chamber. For every rotation around the chamber, the electron loses a potential difference, which is equal to the induced EMF.
$\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{a} = qvB$
Now, if we go through all the options, we get:
Option A: Changing magnetic field induced electric field.
The electric field is produced by the varying magnetic field produced by the electromagnets.
Hence, this is correct.
Option B: charged particles at rest can be accelerated only by electric field.
Yes, charged particles at rest when acted upon by an electric field, produce a force which is equal to the product of the electric field and their charge.
$F = Eq$
A magnetic field does not have any effect on a particle at rest. Hence, this is also correct.
Option C: Magnetic fields can apply a force on moving charges which is perpendicular to both magnetic field and motion of the particle.
The magnetic force on moving charges is perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field. That direction is given by the right hand rule where the direction of force is pointed by the thumb, magnetic field is pointed by the middle finger and the direction of velocity is given by the direction pointed out by the thumb.
Option D: $\beta $ particles are emitted in the radioactive decay process.
The $\beta $ particles emitted here are not because of the radioactive decay process but because of the electromagnetic process and electric field produced by it.Hence, this is wrong and is not a principle of betatron.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:Knowing the principle and having a clear idea of the working of the betatron will help us solve the question. Students have a misconception and assume that $\beta $ particles are always associated with radioactive decay. We need to remember that this question has nothing to do with radioactive decay but the $\beta $ particles are because of the electromagnets and electric field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




