
: Write balanced chemical equations for the action of:
A.Phosphorus trichloride on propan-2-ol
B.Hydrogen bromide on styrene in the presence of a peroxide
C.Methyl bromide on silver propanoate
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of nucleophilic substitution reactions and anti-markovnikov rule of addition in case of peroxides.
Complete step by step answer:
A.When propan -2-ol is treated with \[PC{l_3}\] , 2-chloropropane is obtained.
The balanced reaction of this process can be represented by the equation: \[3C{H_3} - CH\left( {OH} \right) - C{H_3} + PC{l_{3}} \to 3C{H_3} - CH\left( {Cl} \right) - C{H_3} + {H_3}P{O_3}\]
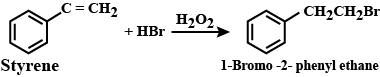
B.When styrene is treated with \[HBr\] in the presence of peroxide there is addition of bromine according to anti markovnikov rule. The final major product of this reaction is 1-Bromo-2-phenyl ethane is obtained.
The balanced reaction of this process can be represented by the equation:
C.When methyl bromide is treated with silver propanoate, methyl propanoate and silver bromide precipitate are obtained. The balanced reaction of this process can be represented by the equation :\[{\text{Silver}}\,{\text{propanoate}} + {\text{Methyl Bromide}} \to {\text{Methylpropanoate }}{\text{ + AgBr}}\left( \downarrow \right)\]
Note:
Anti-Markovnikov rule explains the regiochemistry where the substituent is bonded to a less substituted carbon, rather than the more substituted carbon. This process is quite unusual, as carbocations which are commonly formed during alkene, or alkyne reactions tend to favour the more substituted carbon. Anti Markovnikov addition reaction is found to follow a free radical mechanism. The peroxide compound involved helps in the generation of free radicals. A general mechanism of anti-Markovnikov addition reaction is discussed below:
Generation of free radical through homolytic cleavage of peroxide compound.
Attack of generated free radical on hydrogen halide to form halide radical through homolysis
Attack of generated halide radical on alkene molecule to form alkyl radical through homolysis.
Attack of a generated alkyl radical on hydrogen halide to form alkyl halide through homolytic cleavage of hydrogen halide bond.
Complete step by step answer:
A.When propan -2-ol is treated with \[PC{l_3}\] , 2-chloropropane is obtained.
The balanced reaction of this process can be represented by the equation: \[3C{H_3} - CH\left( {OH} \right) - C{H_3} + PC{l_{3}} \to 3C{H_3} - CH\left( {Cl} \right) - C{H_3} + {H_3}P{O_3}\]
B.When styrene is treated with \[HBr\] in the presence of peroxide there is addition of bromine according to anti markovnikov rule. The final major product of this reaction is 1-Bromo-2-phenyl ethane is obtained.
The balanced reaction of this process can be represented by the equation:

C.When methyl bromide is treated with silver propanoate, methyl propanoate and silver bromide precipitate are obtained. The balanced reaction of this process can be represented by the equation :\[{\text{Silver}}\,{\text{propanoate}} + {\text{Methyl Bromide}} \to {\text{Methylpropanoate }}{\text{ + AgBr}}\left( \downarrow \right)\]
Note:
Anti-Markovnikov rule explains the regiochemistry where the substituent is bonded to a less substituted carbon, rather than the more substituted carbon. This process is quite unusual, as carbocations which are commonly formed during alkene, or alkyne reactions tend to favour the more substituted carbon. Anti Markovnikov addition reaction is found to follow a free radical mechanism. The peroxide compound involved helps in the generation of free radicals. A general mechanism of anti-Markovnikov addition reaction is discussed below:
Generation of free radical through homolytic cleavage of peroxide compound.
Attack of generated free radical on hydrogen halide to form halide radical through homolysis
Attack of generated halide radical on alkene molecule to form alkyl radical through homolysis.
Attack of a generated alkyl radical on hydrogen halide to form alkyl halide through homolytic cleavage of hydrogen halide bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




