
Write down the structural formula of ethane and ethene.
Answer
513k+ views
Hint: The organic compounds which are composed of only hydrogen and carbon atoms are known as hydrocarbons. In the compounds, the hydrogen atoms are bonded to carbon atoms via covalent bonds and carbon atoms in the compounds show catenation i.e., have a tendency to form long chains and ring like structures.
Complete answer: Hydrocarbons are classified into two types which are discussed below.
Saturated hydrocarbons:
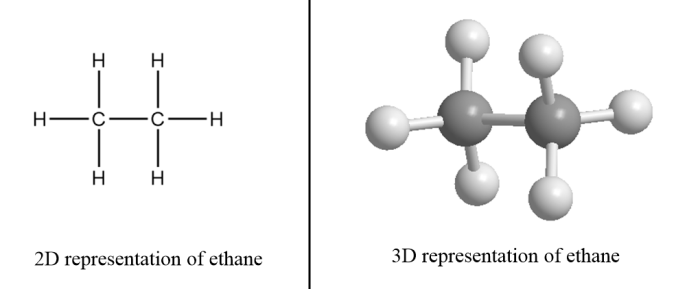
These hydrocarbons are also known as alkanes. In these hydrocarbons, a carbon atom is bonded to another carbon atom via a single bond and each carbon atom present in the structure of alkane is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. It has a tetrahedral geometry and the general formula for alkanes is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where n denotes the number of carbon atoms present in alkane.
For example: Ethane- There are two carbon atoms in ethane i.e., the value of n for ethane molecules is $2$. So, the formula for ethane $ = {C_2}{H_{2 \times 2 + 2}}$.
$\therefore $Structural formula of ethane $ = {C_2}{H_6}$
Unsaturated hydrocarbons:
These are further divided into two types i.e., alkenes and alkynes.
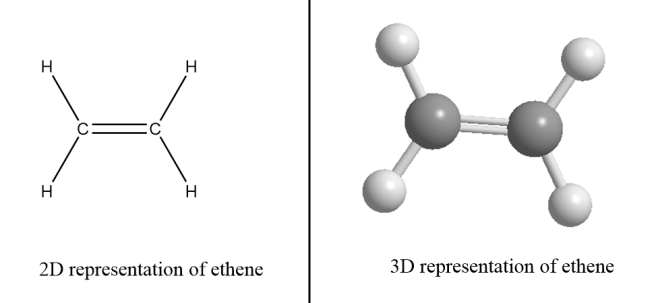
Alkenes- These are the hydrocarbons in which at least one carbon atom is bonded via double bond in the structure and that carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ hybridized. It has a planar geometry and general formula for alkenes is \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}\] where the value of n$ = 2,3,4 \cdot \cdot \cdot $ i.e., the compound must consist of at least two carbon atoms to form an alkene.
For example: Ethene- There are two carbon atoms in ethene i.e., value of n for ethene molecule is $2$. So, the formula for ethene $ = {C_2}{H_{2 \times 2}}$.
$\therefore $Structural formula of ethene $ = {C_2}{H_4}$
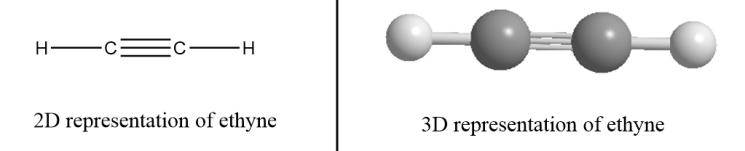
Alkynes- These are the hydrocarbons in which at least one carbon atom is bonded via triple bond in the structure and that carbon atom is $sp$ hybridized. It has a linear geometry and general formula for alkynes is \[{C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}\] where the value of n$ = 2,3,4 \cdot \cdot \cdot $ i.e., the compound must consist of at least two carbon atoms to form an alkyne.
For example: Ethyne- There are two carbon atoms in ethyne i.e., the value of n for ethyne molecules is $2$. So, the formula for ethyne $ = {C_2}{H_{2 \times 2 - 2}}$.
$\therefore $Structural formula of ethene $ = {C_2}{H_2}$
Hence, the structural formula of ethane and ethene is ${C_2}{H_6}$ and ${C_2}{H_4}$ respectively.
Note:
It is important to note that a series of compounds which consist of similar chemical properties and functional groups but differ by $C{H_2}$ group in the structure is known as a homologous series. The general formula given to alkanes, alkenes and alkynes is based on the concept of homologous series.
Complete answer: Hydrocarbons are classified into two types which are discussed below.
Saturated hydrocarbons:
These hydrocarbons are also known as alkanes. In these hydrocarbons, a carbon atom is bonded to another carbon atom via a single bond and each carbon atom present in the structure of alkane is $s{p^3}$ hybridized. It has a tetrahedral geometry and the general formula for alkanes is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where n denotes the number of carbon atoms present in alkane.
For example: Ethane- There are two carbon atoms in ethane i.e., the value of n for ethane molecules is $2$. So, the formula for ethane $ = {C_2}{H_{2 \times 2 + 2}}$.
$\therefore $Structural formula of ethane $ = {C_2}{H_6}$

Unsaturated hydrocarbons:
These are further divided into two types i.e., alkenes and alkynes.
Alkenes- These are the hydrocarbons in which at least one carbon atom is bonded via double bond in the structure and that carbon atom is $s{p^2}$ hybridized. It has a planar geometry and general formula for alkenes is \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}\] where the value of n$ = 2,3,4 \cdot \cdot \cdot $ i.e., the compound must consist of at least two carbon atoms to form an alkene.
For example: Ethene- There are two carbon atoms in ethene i.e., value of n for ethene molecule is $2$. So, the formula for ethene $ = {C_2}{H_{2 \times 2}}$.
$\therefore $Structural formula of ethene $ = {C_2}{H_4}$

Alkynes- These are the hydrocarbons in which at least one carbon atom is bonded via triple bond in the structure and that carbon atom is $sp$ hybridized. It has a linear geometry and general formula for alkynes is \[{C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}\] where the value of n$ = 2,3,4 \cdot \cdot \cdot $ i.e., the compound must consist of at least two carbon atoms to form an alkyne.
For example: Ethyne- There are two carbon atoms in ethyne i.e., the value of n for ethyne molecules is $2$. So, the formula for ethyne $ = {C_2}{H_{2 \times 2 - 2}}$.
$\therefore $Structural formula of ethene $ = {C_2}{H_2}$

Hence, the structural formula of ethane and ethene is ${C_2}{H_6}$ and ${C_2}{H_4}$ respectively.
Note:
It is important to note that a series of compounds which consist of similar chemical properties and functional groups but differ by $C{H_2}$ group in the structure is known as a homologous series. The general formula given to alkanes, alkenes and alkynes is based on the concept of homologous series.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




