
Write resonance structure of $NO_{3}^{-}$ and $N{{O}_{2}}$
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: All non-metals form metal oxides with oxygen, which reacts with water that will form acids or with bases forms salts. Most nonmetals form oxyacid’s from their acidic oxides. A set of two or Lewis structures collectively describes the electronic bonding of a single polyatomic species including fractional charges are resonance structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Based on resonance structures of single polyatomic species are capable of describing delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula with an integer number of covalent bonds.
The nitrate ($NO_{3}^{-}$ ) ion:
Count the valence electrons $=$ no of nitrogen atoms $\times 5$electrons $+$ no of oxygen atoms $\times 6$ electrons $+$ one electron.
\[=1\times 5+3\times 6+1=24electrons\]
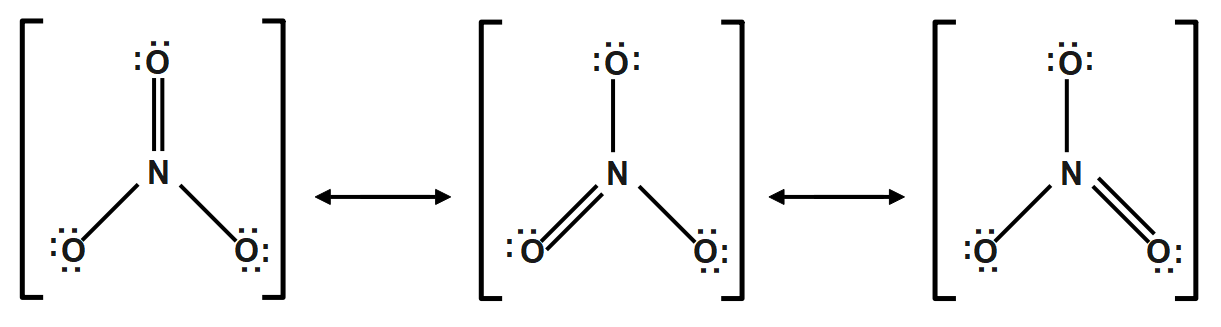
The below diagram shows the bond connectivity and octet electrons to the atoms bonded to the central atom which is the trigonal planar and the possible resonance structures are:
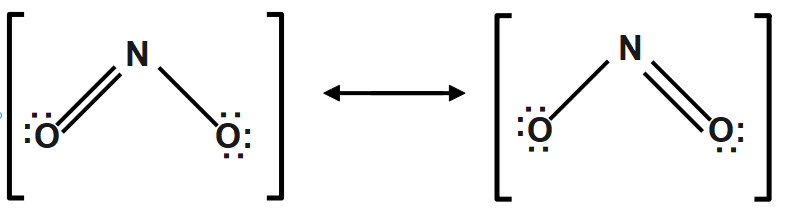
Nitrogen dioxide ($N{{O}_{2}}$ ): Nitrogen dioxide contains an odd number of $17$ valence electrons and it behaves as a typical odd molecule. It exhibits a resonance structure on dimerization, Nitrogen dioxide converted to stable dinitrogen tetraoxide molecule with an even number of molecules.
Note: Sometimes Lewis structure is not enough for explaining bonding in some molecules or ions and a single Lewis formula is not sufficient to describe the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several structures. For example, ozone is an allotrope of oxygen with a V-shaped structure with an $O-O-O$ bond angle of $117.5{}^\circ $
Complete step by step answer:
Based on resonance structures of single polyatomic species are capable of describing delocalized electrons that cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula with an integer number of covalent bonds.
The nitrate ($NO_{3}^{-}$ ) ion:
Count the valence electrons $=$ no of nitrogen atoms $\times 5$electrons $+$ no of oxygen atoms $\times 6$ electrons $+$ one electron.
\[=1\times 5+3\times 6+1=24electrons\]
The below diagram shows the bond connectivity and octet electrons to the atoms bonded to the central atom which is the trigonal planar and the possible resonance structures are:

Nitrogen dioxide ($N{{O}_{2}}$ ): Nitrogen dioxide contains an odd number of $17$ valence electrons and it behaves as a typical odd molecule. It exhibits a resonance structure on dimerization, Nitrogen dioxide converted to stable dinitrogen tetraoxide molecule with an even number of molecules.

Note: Sometimes Lewis structure is not enough for explaining bonding in some molecules or ions and a single Lewis formula is not sufficient to describe the delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several structures. For example, ozone is an allotrope of oxygen with a V-shaped structure with an $O-O-O$ bond angle of $117.5{}^\circ $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




