
Write short notes on chain-shortening and chain-lengthening reactions for sugars.
Answer
519k+ views
Hint: Carbohydrates: Large complex organic compounds composed of three basic components that are carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms are known as carbohydrates. Sugar is a type of carbohydrate with a molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\].
Complete answer:
Chain-shortening reactions of sugar:
Reducing the length of chain by carbon is termed as chain-shortening. The method for chain-shortening is known as Ruff Degradation which is explained as follows:
Step-1: The aldehyde group in the chain is oxidized to carboxylic group in the presence of bromine and water as follows:
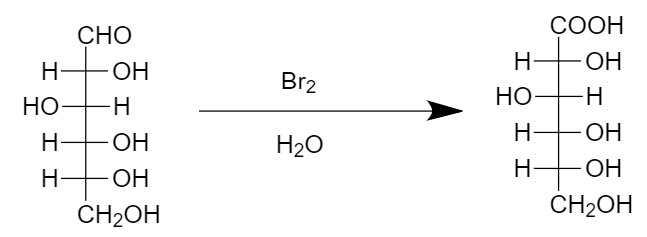
Step-2: Decarboxylation (of the compound formed in step-1) takes place in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, calcium carbonate and iron (III) acetate as follows:
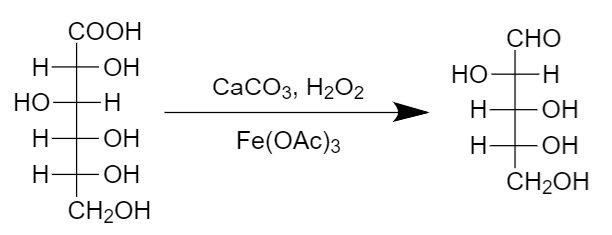
Hence the final compound has one carbon less than the reactant so chain-shortening of sugar molecule takes place.
Chain-lengthening reactions of sugar:
Increasing the length of chain of a compound by one carbon atom is termed as chain-lengthening. The Kiliani-Fischer synthesis is used to extend the carbon chain of a compound. Mechanism is for chain-lengthening reaction for sugar is as follows:
Step-1: Attack of cyanide ion on the aldehyde group of the compound takes place due to which formation of cyanohydrin group on the compound takes place as follows:
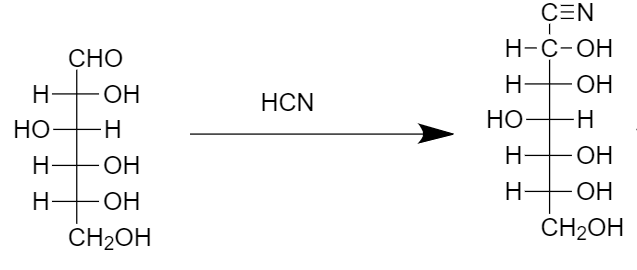
Step-2: Conversion of cyanohydrin group to the imine followed by hydrolysis in the acidic conditions takes place as follows:
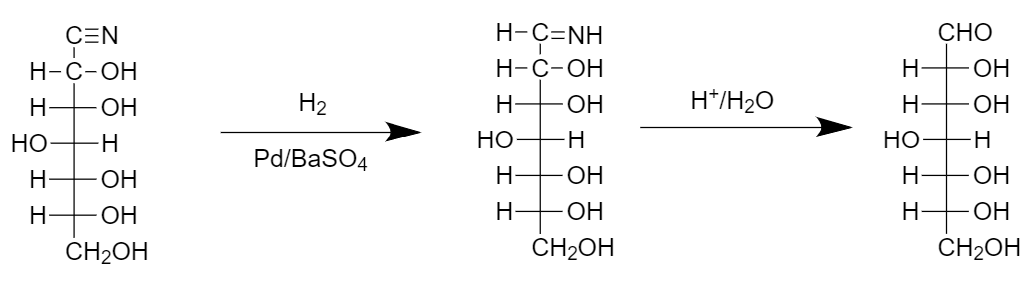
Hence the final compound has one carbon more than the reactant, so chain-lengthening of sugar molecules takes place.
Note:
In Kiliani-Fischer synthesis, two epimers are formed as the product whereas in Ruff-degradation, only the conformation of the reactant is retained.
Epimer: The two isomers of a compound having different configurations about a single asymmetric carbon atom.
Complete answer:
Chain-shortening reactions of sugar:
Reducing the length of chain by carbon is termed as chain-shortening. The method for chain-shortening is known as Ruff Degradation which is explained as follows:
Step-1: The aldehyde group in the chain is oxidized to carboxylic group in the presence of bromine and water as follows:

Step-2: Decarboxylation (of the compound formed in step-1) takes place in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, calcium carbonate and iron (III) acetate as follows:

Hence the final compound has one carbon less than the reactant so chain-shortening of sugar molecule takes place.
Chain-lengthening reactions of sugar:
Increasing the length of chain of a compound by one carbon atom is termed as chain-lengthening. The Kiliani-Fischer synthesis is used to extend the carbon chain of a compound. Mechanism is for chain-lengthening reaction for sugar is as follows:
Step-1: Attack of cyanide ion on the aldehyde group of the compound takes place due to which formation of cyanohydrin group on the compound takes place as follows:

Step-2: Conversion of cyanohydrin group to the imine followed by hydrolysis in the acidic conditions takes place as follows:

Hence the final compound has one carbon more than the reactant, so chain-lengthening of sugar molecules takes place.
Note:
In Kiliani-Fischer synthesis, two epimers are formed as the product whereas in Ruff-degradation, only the conformation of the reactant is retained.
Epimer: The two isomers of a compound having different configurations about a single asymmetric carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




