
Write short notes on lactose and maltose.
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint : Lactose and maltose are reducing disaccharides having only one of their two anomeric carbons involved in the glycosidic linkage and the other is free and can change to an open chain form with an aldehyde group. Lactose and maltose are also isomers as they have the same chemical formula $ {C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}} $ but they have different chemical structures.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
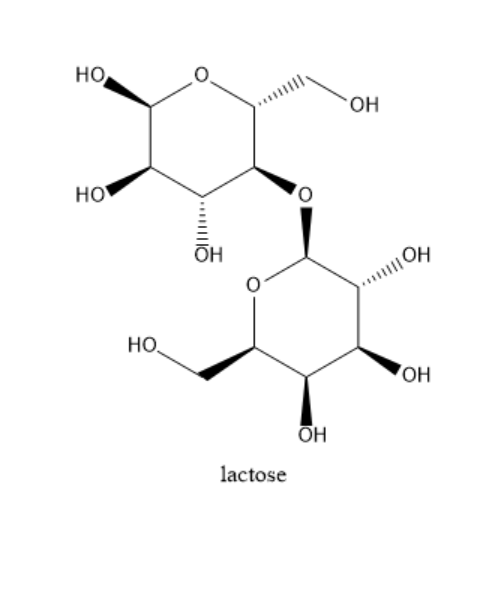
Lactose: Lactose has one galactose carbohydrate and one glucose carbohydrate. They are bound together with the help of a $ \beta - 1 - 4 $ glycosidic bond. It is a reducing sugar because it has a free hemiacetal hydroxide. It is the main ingredient in the milk of all the mammals. It is not sweet to taste. In the structure of lactose, there is one difference between galactose and glucose. The fourth carbon of galactose has a different orientation in galactose than in sucrose. The structure of lactose is given below:
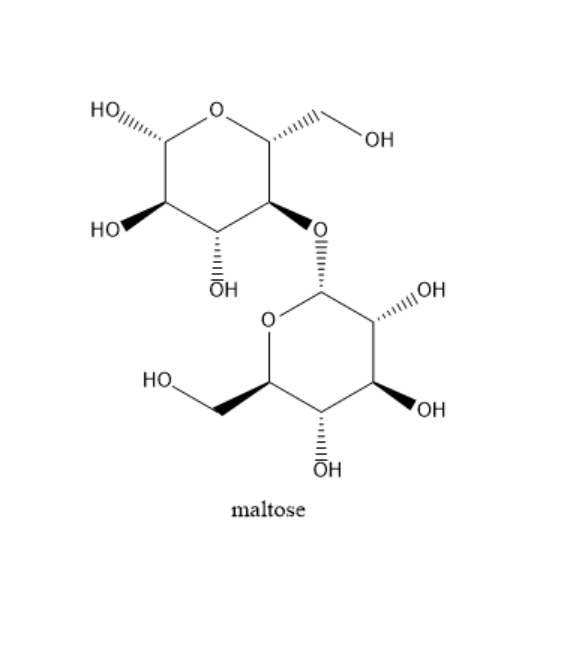
Maltose: Two glucose monosaccharide molecules are bound together in maltose. There is a $ \alpha - 1 - 4 $ link between the first carbon atom glucose and the fourth carbon of another glucose molecule. One mole of maltose gives two moles of D-glucose on acid catalyzed hydrolysis. It has a free hemiacetal hydroxide. So it can undergo mutarotation also. It can exist as $ \alpha - {\text{Maltose}} $ and $ \beta - {\text{Maltose}} $ . Due to this reason, it gives positive tests with tollens and benedict's reagent. The structure of maltose is as follows:
Note :
Disaccharides are also called double sugars or boises. The sugar formed when two monosaccharides are linked together by a glycosidic linkage is called a disaccharide. They are simple sugars that are soluble in water. Sucrose, lactose and maltose are common disaccharides.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Lactose: Lactose has one galactose carbohydrate and one glucose carbohydrate. They are bound together with the help of a $ \beta - 1 - 4 $ glycosidic bond. It is a reducing sugar because it has a free hemiacetal hydroxide. It is the main ingredient in the milk of all the mammals. It is not sweet to taste. In the structure of lactose, there is one difference between galactose and glucose. The fourth carbon of galactose has a different orientation in galactose than in sucrose. The structure of lactose is given below:

Maltose: Two glucose monosaccharide molecules are bound together in maltose. There is a $ \alpha - 1 - 4 $ link between the first carbon atom glucose and the fourth carbon of another glucose molecule. One mole of maltose gives two moles of D-glucose on acid catalyzed hydrolysis. It has a free hemiacetal hydroxide. So it can undergo mutarotation also. It can exist as $ \alpha - {\text{Maltose}} $ and $ \beta - {\text{Maltose}} $ . Due to this reason, it gives positive tests with tollens and benedict's reagent. The structure of maltose is as follows:

Note :
Disaccharides are also called double sugars or boises. The sugar formed when two monosaccharides are linked together by a glycosidic linkage is called a disaccharide. They are simple sugars that are soluble in water. Sucrose, lactose and maltose are common disaccharides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




