
Write short notes on the following,
(i) HVZ-reaction
(ii) Trans-esterification
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: The mechanism of HVZ reaction is different from other halogenation reactions as it takes place in the absence of halogen itself. Whereas, transesterification is basically conversion of one ester to another.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us learn about HVZ reactions and transesterification one by one.
HVZ reaction-
The Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction is used for the halogenation of any carboxylic acid at alpha carbon. Severe reactions conditions are required for the reaction to be carried out i.e. 373 k temperature and increased reaction time. This requires the catalyst as phosphorus or sometimes trihalides of the same. Whereas, some carboxylic acids do not require any catalyst for their halogenation.
This reaction takes place in the absence of halogen. The reaction starts with reacting $PB{{r}_{3}}$ with carboxylic acid to form acid bromide and HBr. This then catalyses the acid bromide enol formation. This acid bromide enol reacts with remaining $B{{r}_{2}}$ and gives alpha bromination.
General reaction-
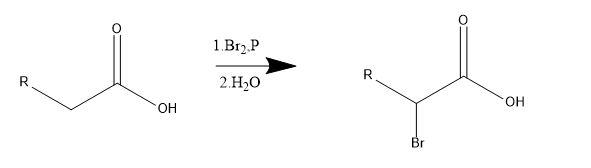
Transesterification-
There can be exchange of alkoxy groups when an ester is placed in excess of alcohol along with acid or base. The presence of alcohol in excess drives the reaction in forward direction.
The steps involved in transesterification is;
In basic conditions,
1. Alkoxide attack in the form of nucleophile.
2. Removal of leaving group.
In acidic conditions,
1. Activation of carbonyl towards nucleophilic attack by acid protonation.
2. Attack of nucleophile on carbonyl.
3. Transfer of proton.
4. Leaving group removal.
5. Deprotonation.
General reaction-
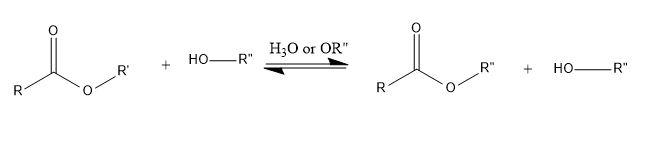
Note: HVZ reactions do not accomplish fluorination and iodination. Also, care should be taken as at high temperature formation of beta unsaturated carboxylic acid can take place. In transesterification, both the reactants and products are the same i.e. ester and alcohol; reaction is reversible. So, Le Chatelier’s principle should be used to drive reaction in a specific way.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us learn about HVZ reactions and transesterification one by one.
HVZ reaction-
The Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction is used for the halogenation of any carboxylic acid at alpha carbon. Severe reactions conditions are required for the reaction to be carried out i.e. 373 k temperature and increased reaction time. This requires the catalyst as phosphorus or sometimes trihalides of the same. Whereas, some carboxylic acids do not require any catalyst for their halogenation.
This reaction takes place in the absence of halogen. The reaction starts with reacting $PB{{r}_{3}}$ with carboxylic acid to form acid bromide and HBr. This then catalyses the acid bromide enol formation. This acid bromide enol reacts with remaining $B{{r}_{2}}$ and gives alpha bromination.
General reaction-

Transesterification-
There can be exchange of alkoxy groups when an ester is placed in excess of alcohol along with acid or base. The presence of alcohol in excess drives the reaction in forward direction.
The steps involved in transesterification is;
In basic conditions,
1. Alkoxide attack in the form of nucleophile.
2. Removal of leaving group.
In acidic conditions,
1. Activation of carbonyl towards nucleophilic attack by acid protonation.
2. Attack of nucleophile on carbonyl.
3. Transfer of proton.
4. Leaving group removal.
5. Deprotonation.
General reaction-

Note: HVZ reactions do not accomplish fluorination and iodination. Also, care should be taken as at high temperature formation of beta unsaturated carboxylic acid can take place. In transesterification, both the reactants and products are the same i.e. ester and alcohol; reaction is reversible. So, Le Chatelier’s principle should be used to drive reaction in a specific way.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




