
Write structure of pyrophosphoric acid.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint:To write the structure of pyrophosphoric acid, the molecular formula of pyrophosphoric acid must be remembered which is ${{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of the pyrophosphoric acid are as following:
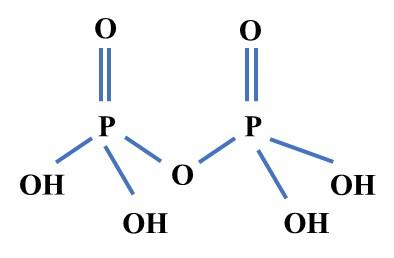
Pyrophosphoric acid can also be termed as diphosphoric acid which is an inorganic, medium strong acid. From the structure it is clearly seen that two phosphates interact with four hydroxyl (\[\text{-OH}\]) groups, which can donate protons ($\text{-H}$) in aqueous solution. According to Arrhenius, the agent provides protons ($\text{-H}$) in an aqueous solution of acid. As, pyrophosphoric acid has a capacity to donate four protons in aqueous media which is the reason behind its medium strong acidic nature. Pyrophosphoric acid is corrosive in nature. On the other hand during aqueous media it produces phosphoric acid, the reaction is given below:
${{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons \text{2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
The equilibrium reaction between phosphoric acid and pyrophoric acid is seen in the aqueous media.
Additional information: In biology, the pyrophosphates, anions or ester salts of pyrophosphoric acids, are important because during energy unit ATP (adenosine triphosphate) breakdown to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) or AMP (adenosine monophosphate) one or two molecules of anions of pyrophosphate (PPi) is released.
Note:
Pyrophosphoric acid is colourless, odourless, hygroscopic, and soluble in water, ether and alcohol. Pyrophosphoric acid is produced by the heat dehydration of phosphoric acid. It crystalizes in two anhydrous form among one is the metastable form melting at 54֯C and other one metastable form melting at 71֯C. In industry, pyrophosphoric acid is used as catalyst, metal treatment agent, organic per-oxide stabilizer agent and for the manufacturing of organic phosphate esters.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of the pyrophosphoric acid are as following:

Pyrophosphoric acid can also be termed as diphosphoric acid which is an inorganic, medium strong acid. From the structure it is clearly seen that two phosphates interact with four hydroxyl (\[\text{-OH}\]) groups, which can donate protons ($\text{-H}$) in aqueous solution. According to Arrhenius, the agent provides protons ($\text{-H}$) in an aqueous solution of acid. As, pyrophosphoric acid has a capacity to donate four protons in aqueous media which is the reason behind its medium strong acidic nature. Pyrophosphoric acid is corrosive in nature. On the other hand during aqueous media it produces phosphoric acid, the reaction is given below:
${{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons \text{2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$
The equilibrium reaction between phosphoric acid and pyrophoric acid is seen in the aqueous media.
Additional information: In biology, the pyrophosphates, anions or ester salts of pyrophosphoric acids, are important because during energy unit ATP (adenosine triphosphate) breakdown to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) or AMP (adenosine monophosphate) one or two molecules of anions of pyrophosphate (PPi) is released.
Note:
Pyrophosphoric acid is colourless, odourless, hygroscopic, and soluble in water, ether and alcohol. Pyrophosphoric acid is produced by the heat dehydration of phosphoric acid. It crystalizes in two anhydrous form among one is the metastable form melting at 54֯C and other one metastable form melting at 71֯C. In industry, pyrophosphoric acid is used as catalyst, metal treatment agent, organic per-oxide stabilizer agent and for the manufacturing of organic phosphate esters.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




