
Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2- Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert.Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec.butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: We could solve this problem by keeping in mind the IUPAC rules for nomenclature for organic compounds. The rules which we need to remember for answering this question are the determination of the parent carbon chain by calculating the number of carbons in the longest carbon chain and the priority of functional groups.
Complete step by step solution:
- According to the IUPAC rules, in the nomenclature the first thing to select is the longest continuous chain and this chain is numbered. This numbering of the carbon chain should begin from the end that is close to the highest priority group which is called a functional group.
- Each of the above mentioned groups has a definite assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon atom it has been attached and the groups other than the principal functional groups are usually arranged alphabetically. Let’s write the structures of the given compounds according to these rules.
(i) 2- Chloro-3-methylpentane
It’s an aliphatic compound with the root word pentane which means there are five carbon chains. The second position is occupied by the chloro group and the third position in pentane chain is occupied by methyl group and the structure is given below
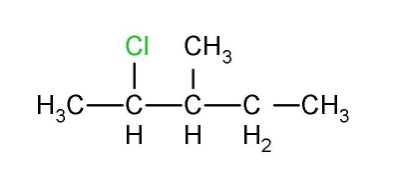
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
Here the chloro group and an ethyl group are attached in a cyclohexane ring at the positions 1 and 4 respectively and the structure is given below.
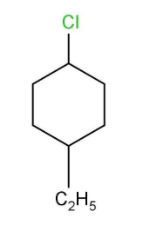
(iii) 4-tert.Butyl-3-iodoheptane
The longest chain will be a seven membered carbon chain and an iodine atom will be attached in the third position and the structure is given below.
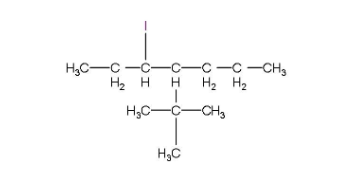
(iv) 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene
The longest chain will consist of four carbon atoms and two bromine atoms will be attached to this chain at the first and fourth positions in the carbon chain. The structure is given below.

(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec.butyl-2-methylbenzene.
The base root will be a benzene molecule and a bromine atom will be attached to first position, a butyl group to the fourth position and a methyl group in the second carbon atom in the ring and the structure is given below.
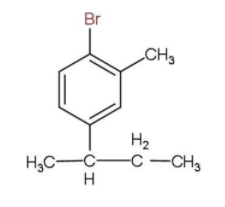
Note: It should be noted that every substituent should have a number and in the case of aromatic compounds such as benzene, the positions can also be referred to as Ortho, Meta and Para positions. Also, the use of commas and numbers to separate the substituents should also be noted.
Complete step by step solution:
- According to the IUPAC rules, in the nomenclature the first thing to select is the longest continuous chain and this chain is numbered. This numbering of the carbon chain should begin from the end that is close to the highest priority group which is called a functional group.
- Each of the above mentioned groups has a definite assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon atom it has been attached and the groups other than the principal functional groups are usually arranged alphabetically. Let’s write the structures of the given compounds according to these rules.
(i) 2- Chloro-3-methylpentane
It’s an aliphatic compound with the root word pentane which means there are five carbon chains. The second position is occupied by the chloro group and the third position in pentane chain is occupied by methyl group and the structure is given below

(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
Here the chloro group and an ethyl group are attached in a cyclohexane ring at the positions 1 and 4 respectively and the structure is given below.

(iii) 4-tert.Butyl-3-iodoheptane
The longest chain will be a seven membered carbon chain and an iodine atom will be attached in the third position and the structure is given below.

(iv) 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene
The longest chain will consist of four carbon atoms and two bromine atoms will be attached to this chain at the first and fourth positions in the carbon chain. The structure is given below.

(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec.butyl-2-methylbenzene.
The base root will be a benzene molecule and a bromine atom will be attached to first position, a butyl group to the fourth position and a methyl group in the second carbon atom in the ring and the structure is given below.

Note: It should be noted that every substituent should have a number and in the case of aromatic compounds such as benzene, the positions can also be referred to as Ortho, Meta and Para positions. Also, the use of commas and numbers to separate the substituents should also be noted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




