
Write the approximate wavelengths for red light
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. 1000A}{}^\circ \\
& \text{B}\text{. 2000A}{}^\circ \\
& \text{C}\text{. 9000A}{}^\circ \\
& \text{D}\text{. 8000A}{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: The white light (Visible light) we see is a mixture of seven colours. The seven colours are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red. The visible light is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of waves of frequency ranging from a few Hertz to \[{{10}^{25}}\]Hertz.
Complete step by step answer:
The visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can see. More simply, this range of wavelengths is called visible light. The wavelength range of visible light is 380 nanometres to $760$ nanometres. The corresponding frequency range is \[400\text{ to }790\] Terahertz.
The wavelength of violet light ranges from \[380\text{ to }450\] nanometres. The wavelength of blue light ranges from $450$ nanometres to $495$ nanometres. The wavelength of green light is $495$ nanometres to $570$ nanometres. The wavelength of yellow is $570$ nanometres to $590$ nanometres. The wavelength of orange light is $590$ nanometres to $620$ nanometres. The wavelength of red light is $620$ nanometres to $750$ nanometres.
So the Red light lies in a wavelength range of $620$ nanometres to $750$ nanometres. Or the wavelength ranges from $6200A{}^\circ $ to $7500A{}^\circ $ . From the options the nearest value to this wavelength is option D.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: The electromagnetic radiation is broadly classified into the following types
Gamma radiation, X-ray radiation, Ultraviolet radiation, visible light, infrared radiation, Microwave radiation, Radio waves.
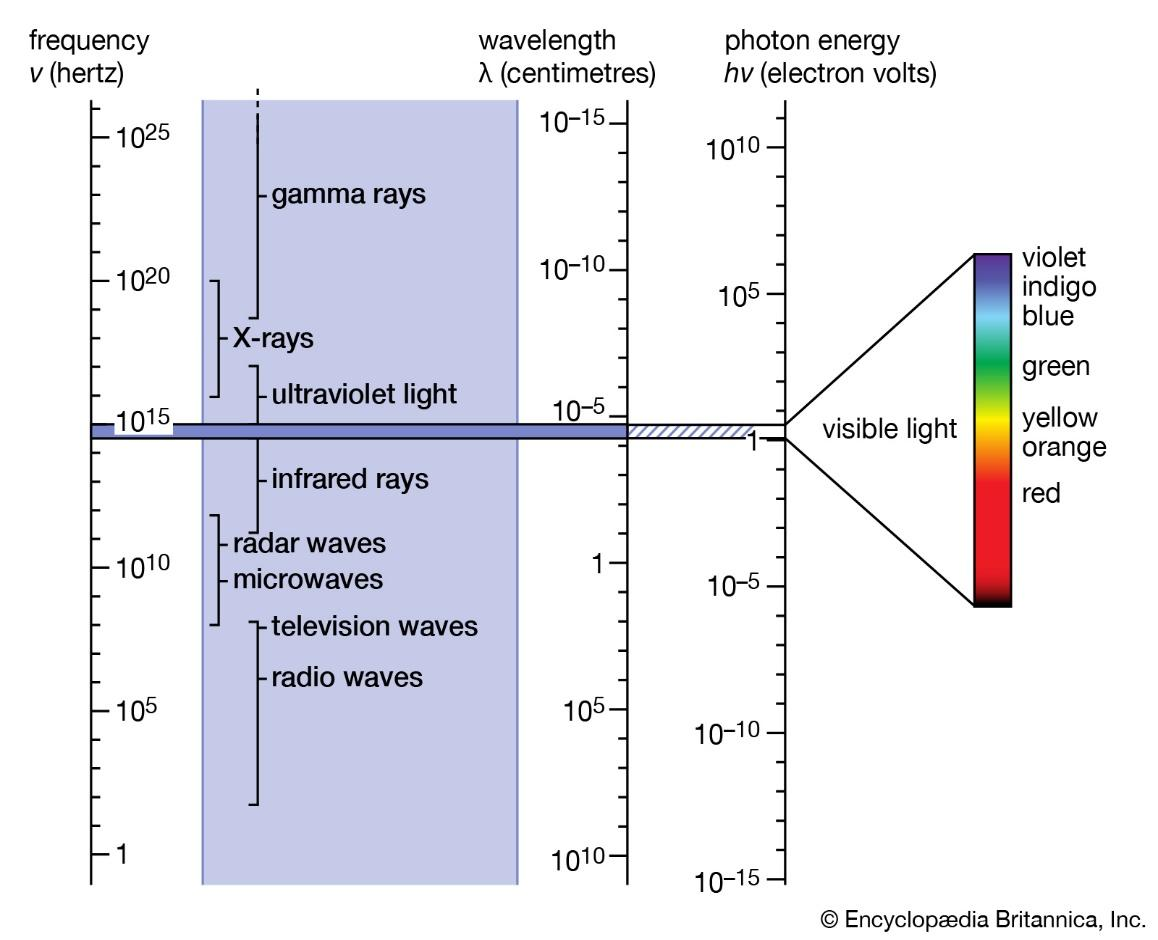
(i)Radio waves: Radio waves were produced by the accelerated motion of charges in wires. Radio waves are used in radio and television communication systems. Radio waves have high frequencies of $300$ gigahertz (GHz) and low frequency of $30$ hertz (Hz). The wavelength corresponding to frequency 300 GHz is 1 mm (which is shorter than the width of a rice grain); the wavelength corresponding to frequency 30 Hz is \[10,000\]km (which is longer than the radius of earth which is \[6400km\]).
(ii)Microwaves: Microwaves (also known as short-wavelength radio waves), with frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range. Microwaves are produced by special vacuum tubes (called klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn diodes). Microwaves are suitable for the radar systems used in aircraft navigation because of their short wavelengths. Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation and the wavelength of microwaves ranges from about one meter to one millimetre.
(iii)Infrared waves: Infrared waves are produced by hot bodies and molecules. The wavelength range of infrared waves is \[700\] nanometres (nm) to 1 millimetre (mm).
(iv) Visible rays: It is the most familiar form of electromagnetic waves. It is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which can be detected by the human eye. The frequency of visible wave ranges from $4\times {{10}^{14}}Hz$ to $7\times {{10}^{14}}Hz$ and the corresponding wavelength is about\[700400nm\].
(v)Ultraviolet rays: It covers wavelengths ranging from about \[4\times {{10}^{-7}}m\left( 400nm \right)\] to\[6\times {{10}^{-10}}m\text{ }\left( 0.6\text{ }nm \right)\]. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is produced by special lamps and very hot bodies. The sun is an important source of ultraviolet light.
(vi) X-rays: The X-ray region lies beyond the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum. X-rays have several medical applications. It covers wavelengths from about ${{10}^{-8}}m$ down to ${{10}^{-13}}m$.
(vii) Gamma rays: Gamma rays lies in the upper frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum and wavelength ranges from \[{{10}^{-10}}m\] to less than ${{10}^{-14}}m$. This high frequency radiation is produced in nuclear reactions and also emitted by radioactive nuclei. Gamma rays are used in medicine to destroy Cancer cells.
Note: In the electromagnetic wave, lower wavelength or higher frequency waves have more energy. So gamma rays have the most energy and radio waves have lowest energy. Electromagnetic waves interact with matter via their electric and magnetic fields which set in oscillation charges present in all matter. The detailed interaction and so the mechanism of absorption, scattering, etc., depend on the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave, and the nature of the atoms and molecules in the medium.
Complete step by step answer:
The visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can see. More simply, this range of wavelengths is called visible light. The wavelength range of visible light is 380 nanometres to $760$ nanometres. The corresponding frequency range is \[400\text{ to }790\] Terahertz.
The wavelength of violet light ranges from \[380\text{ to }450\] nanometres. The wavelength of blue light ranges from $450$ nanometres to $495$ nanometres. The wavelength of green light is $495$ nanometres to $570$ nanometres. The wavelength of yellow is $570$ nanometres to $590$ nanometres. The wavelength of orange light is $590$ nanometres to $620$ nanometres. The wavelength of red light is $620$ nanometres to $750$ nanometres.
So the Red light lies in a wavelength range of $620$ nanometres to $750$ nanometres. Or the wavelength ranges from $6200A{}^\circ $ to $7500A{}^\circ $ . From the options the nearest value to this wavelength is option D.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: The electromagnetic radiation is broadly classified into the following types
Gamma radiation, X-ray radiation, Ultraviolet radiation, visible light, infrared radiation, Microwave radiation, Radio waves.

(i)Radio waves: Radio waves were produced by the accelerated motion of charges in wires. Radio waves are used in radio and television communication systems. Radio waves have high frequencies of $300$ gigahertz (GHz) and low frequency of $30$ hertz (Hz). The wavelength corresponding to frequency 300 GHz is 1 mm (which is shorter than the width of a rice grain); the wavelength corresponding to frequency 30 Hz is \[10,000\]km (which is longer than the radius of earth which is \[6400km\]).
(ii)Microwaves: Microwaves (also known as short-wavelength radio waves), with frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range. Microwaves are produced by special vacuum tubes (called klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn diodes). Microwaves are suitable for the radar systems used in aircraft navigation because of their short wavelengths. Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation and the wavelength of microwaves ranges from about one meter to one millimetre.
(iii)Infrared waves: Infrared waves are produced by hot bodies and molecules. The wavelength range of infrared waves is \[700\] nanometres (nm) to 1 millimetre (mm).
(iv) Visible rays: It is the most familiar form of electromagnetic waves. It is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which can be detected by the human eye. The frequency of visible wave ranges from $4\times {{10}^{14}}Hz$ to $7\times {{10}^{14}}Hz$ and the corresponding wavelength is about\[700400nm\].
(v)Ultraviolet rays: It covers wavelengths ranging from about \[4\times {{10}^{-7}}m\left( 400nm \right)\] to\[6\times {{10}^{-10}}m\text{ }\left( 0.6\text{ }nm \right)\]. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is produced by special lamps and very hot bodies. The sun is an important source of ultraviolet light.
(vi) X-rays: The X-ray region lies beyond the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum. X-rays have several medical applications. It covers wavelengths from about ${{10}^{-8}}m$ down to ${{10}^{-13}}m$.
(vii) Gamma rays: Gamma rays lies in the upper frequency range of the electromagnetic spectrum and wavelength ranges from \[{{10}^{-10}}m\] to less than ${{10}^{-14}}m$. This high frequency radiation is produced in nuclear reactions and also emitted by radioactive nuclei. Gamma rays are used in medicine to destroy Cancer cells.
Note: In the electromagnetic wave, lower wavelength or higher frequency waves have more energy. So gamma rays have the most energy and radio waves have lowest energy. Electromagnetic waves interact with matter via their electric and magnetic fields which set in oscillation charges present in all matter. The detailed interaction and so the mechanism of absorption, scattering, etc., depend on the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave, and the nature of the atoms and molecules in the medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




