
Write the chemical reaction of chlorobenzene with respect to nitration.
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: Nitration of chlorobenzene is carried out in the presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid which generate the electrophile \[{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ + }}\] that attacks the chlorobenzene to give the desired nitrated product.
Complete step by step answer: Nitration of chlorobenzene is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Nitration takes place in the presence of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid. The reaction between these two acids generates an electrophile called nitronium ion, \[{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ + }}\] which is first step.
Chlorine being an electron donating group when attached to a benzene ring thereby activates the ortho and para position of the benzene where the nitronium attacks. Thus, we get two nitrated products, namely, ortho nitro chlorobenzene and para nitro chlorobenzene respectively.
Below is the detailed step by step mechanism:
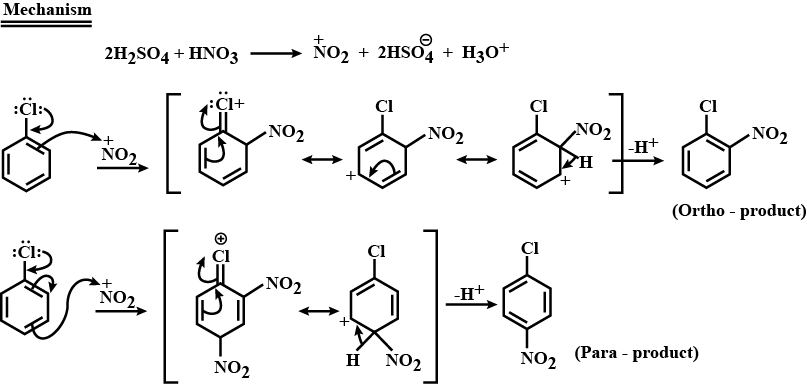
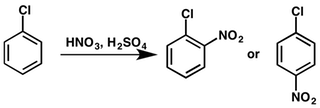
Hence, the overall chemical reaction of nitration of chlorobenzene can be represented as below:
Additional Information: Halide group is also a weak deactivating group that withdraws electrons from benzene rings. Therefore, when nitrobenzene is formed, the second nitration reaction goes much slower than the first due to a deficient number of electrons for the nucleophilic attack. In addition, to minimize secondary reaction, controlling the reaction temperature and relative reagent quantities are very important. Furthermore, the second nitration happens mostly at the meta position. This is due to the higher stability of substituents in the sigma complex at the meta position. Resonance structures determine the stability of the compound. More resonance structures usually mean a higher stability.
Note: Nitration of chlorobenzene will not give a meta substituted product since it is the chlorine group which directs the electrophile. Chlorine being an ortho para directing will not make the electrophile attack the meta substitution. Other than aromatic systems, chlorine is generally an electron donating group.
Complete step by step answer: Nitration of chlorobenzene is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Nitration takes place in the presence of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid. The reaction between these two acids generates an electrophile called nitronium ion, \[{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ + }}\] which is first step.
Chlorine being an electron donating group when attached to a benzene ring thereby activates the ortho and para position of the benzene where the nitronium attacks. Thus, we get two nitrated products, namely, ortho nitro chlorobenzene and para nitro chlorobenzene respectively.
Below is the detailed step by step mechanism:

Hence, the overall chemical reaction of nitration of chlorobenzene can be represented as below:

Additional Information: Halide group is also a weak deactivating group that withdraws electrons from benzene rings. Therefore, when nitrobenzene is formed, the second nitration reaction goes much slower than the first due to a deficient number of electrons for the nucleophilic attack. In addition, to minimize secondary reaction, controlling the reaction temperature and relative reagent quantities are very important. Furthermore, the second nitration happens mostly at the meta position. This is due to the higher stability of substituents in the sigma complex at the meta position. Resonance structures determine the stability of the compound. More resonance structures usually mean a higher stability.
Note: Nitration of chlorobenzene will not give a meta substituted product since it is the chlorine group which directs the electrophile. Chlorine being an ortho para directing will not make the electrophile attack the meta substitution. Other than aromatic systems, chlorine is generally an electron donating group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




