
Write the differences between static electricity and electric current.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Electricity can refer either to the energy or the flow of energy stored in the form of charged packets in a body. The cause of static electricity is the building up of the charges on the surface of an object, called as insulator while current electricity is the flow of charge through an object, called as conductor. There can be various basis differences between the static electricity and the current electricity which need to be studied.
Complete step by step answer:
Static electricity can be defined as the electricity which is created on the surface of an object due to the displacement of negative charges.
Electric current is a phenomenon created by the flow of electrons. It is a common phenomenon which we can see in the working of almost all electrical appliances.
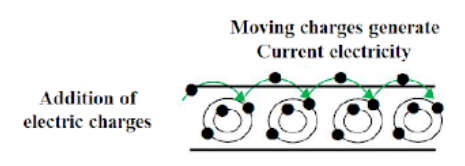
We will write down the differences between the two on a number of factors in the form of a table.
Note:
The most significant difference between the static electricity and the current electricity is that in that static electricity the charges are at rest and they are accumulated on the surface of the insulator, whereas, in current electricity the electrons are in state of motion inside the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
Static electricity can be defined as the electricity which is created on the surface of an object due to the displacement of negative charges.
Electric current is a phenomenon created by the flow of electrons. It is a common phenomenon which we can see in the working of almost all electrical appliances.

We will write down the differences between the two on a number of factors in the form of a table.
| S. no. | Basis of difference | Static electricity | Electric current |
| 1 | Material | It can be developed on any type of material, either it be conductor or an insulator. | The current is produced only in conductors as it is due to movement of electrons. |
| 2 | Time period | Time period is short, as it exists for a very short period of time. | A comparative long time period. |
| 3 | Measuring device | It can be measured with a Gold leaf electroscope. | It can be measured with an Analog or a Digital meter. |
| 4 | Magnetic Field | Static electricity doesn’t induce any magnetic field. | A magnetic field is induced every time an electric current is produced. |
| 5 | Example | Lightning in the sky etc. | It can be seen in electrical equipment like TV, bulb etc. |
Note:
The most significant difference between the static electricity and the current electricity is that in that static electricity the charges are at rest and they are accumulated on the surface of the insulator, whereas, in current electricity the electrons are in state of motion inside the conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




