
Write the formula and draw the electron dot structure of Carbon tetrachloride.
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: Electron Dot structures also known as the Lewis electron Dot structures, are diagrams that depict the bonding between different atoms and also show their valence electrons and lone pairs, if any exists. It mostly has two types of dots $ \times \& \circ $ that represent electrons from two different atoms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical formula of Carbon Tetrachloride is $ CC{l_4} $ . In this the central atom is carbon, which is attached to four chlorine atoms. Carbon belongs to the group 14 of the periodic table and has four valence electrons in the outermost shell. Chlorine belongs to the Halides Family of the Group 17 of the periodic table, and has seven valence electrons in the outermost shell. Chlorine gains one of the four electrons of carbon and attains the eight electron stability. Carbon shares it’s four electrons with four chlorine atoms as it is difficult to lose/gain 4 electrons energy wise. Hence Group 14 elements attain stability by sharing electrons.
The Lewis dot structure deals with only the valence electrons of an element, and shows the bonding precisely. The outermost electron count can be easily figured out.
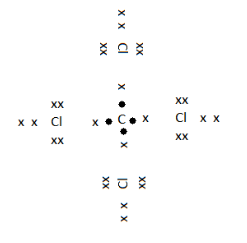
In the given image the electrons represented by $ \bullet $ are the valence electrons of Carbon and that represented by $ \times $ are the valence electrons of Chlorine. As we can see that by sharing its four valence electrons with 4 chlorines, carbon has gained an overall electron count of 8 electrons, making it stable. And that of Chlorine, it has gained one electron, making its count 8.
Note:
The main disadvantage of this structure is that it doesn’t explain the geometry of the molecule. It violates the octet rule in which the central atom has more than eight electrons. It doesn’t give information about the energy of the covalent bond formed.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical formula of Carbon Tetrachloride is $ CC{l_4} $ . In this the central atom is carbon, which is attached to four chlorine atoms. Carbon belongs to the group 14 of the periodic table and has four valence electrons in the outermost shell. Chlorine belongs to the Halides Family of the Group 17 of the periodic table, and has seven valence electrons in the outermost shell. Chlorine gains one of the four electrons of carbon and attains the eight electron stability. Carbon shares it’s four electrons with four chlorine atoms as it is difficult to lose/gain 4 electrons energy wise. Hence Group 14 elements attain stability by sharing electrons.
The Lewis dot structure deals with only the valence electrons of an element, and shows the bonding precisely. The outermost electron count can be easily figured out.

In the given image the electrons represented by $ \bullet $ are the valence electrons of Carbon and that represented by $ \times $ are the valence electrons of Chlorine. As we can see that by sharing its four valence electrons with 4 chlorines, carbon has gained an overall electron count of 8 electrons, making it stable. And that of Chlorine, it has gained one electron, making its count 8.
Note:
The main disadvantage of this structure is that it doesn’t explain the geometry of the molecule. It violates the octet rule in which the central atom has more than eight electrons. It doesn’t give information about the energy of the covalent bond formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




